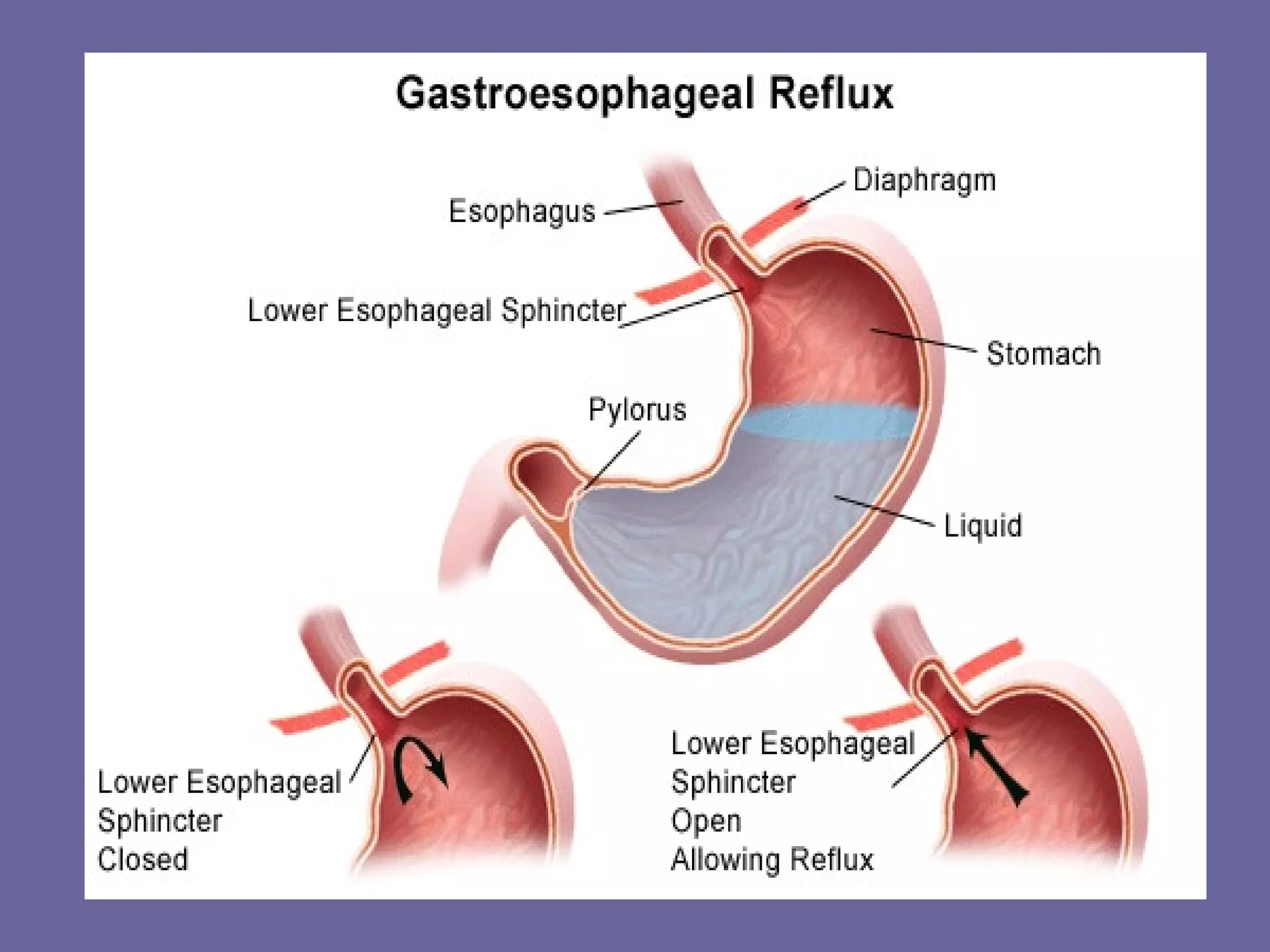
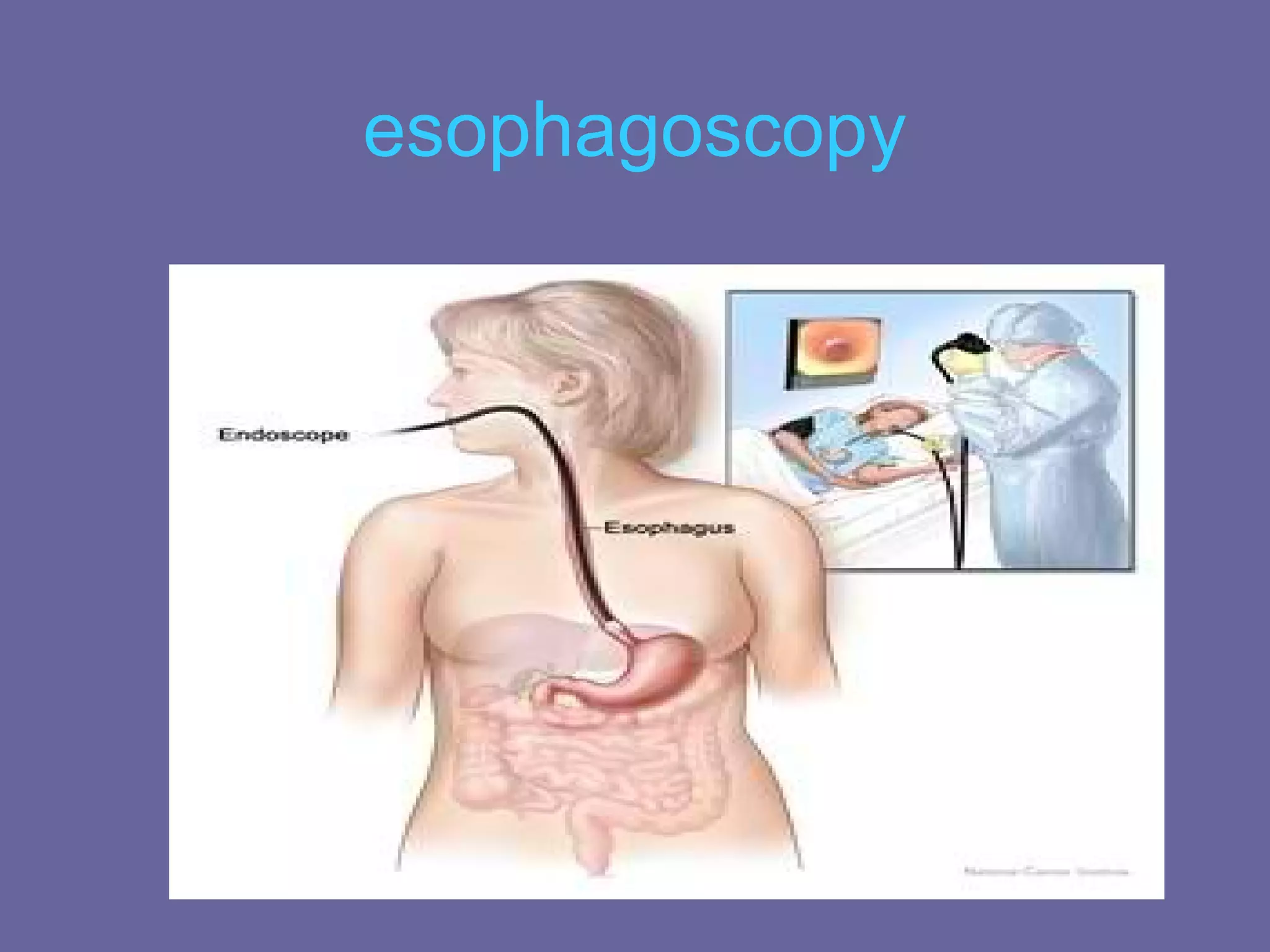
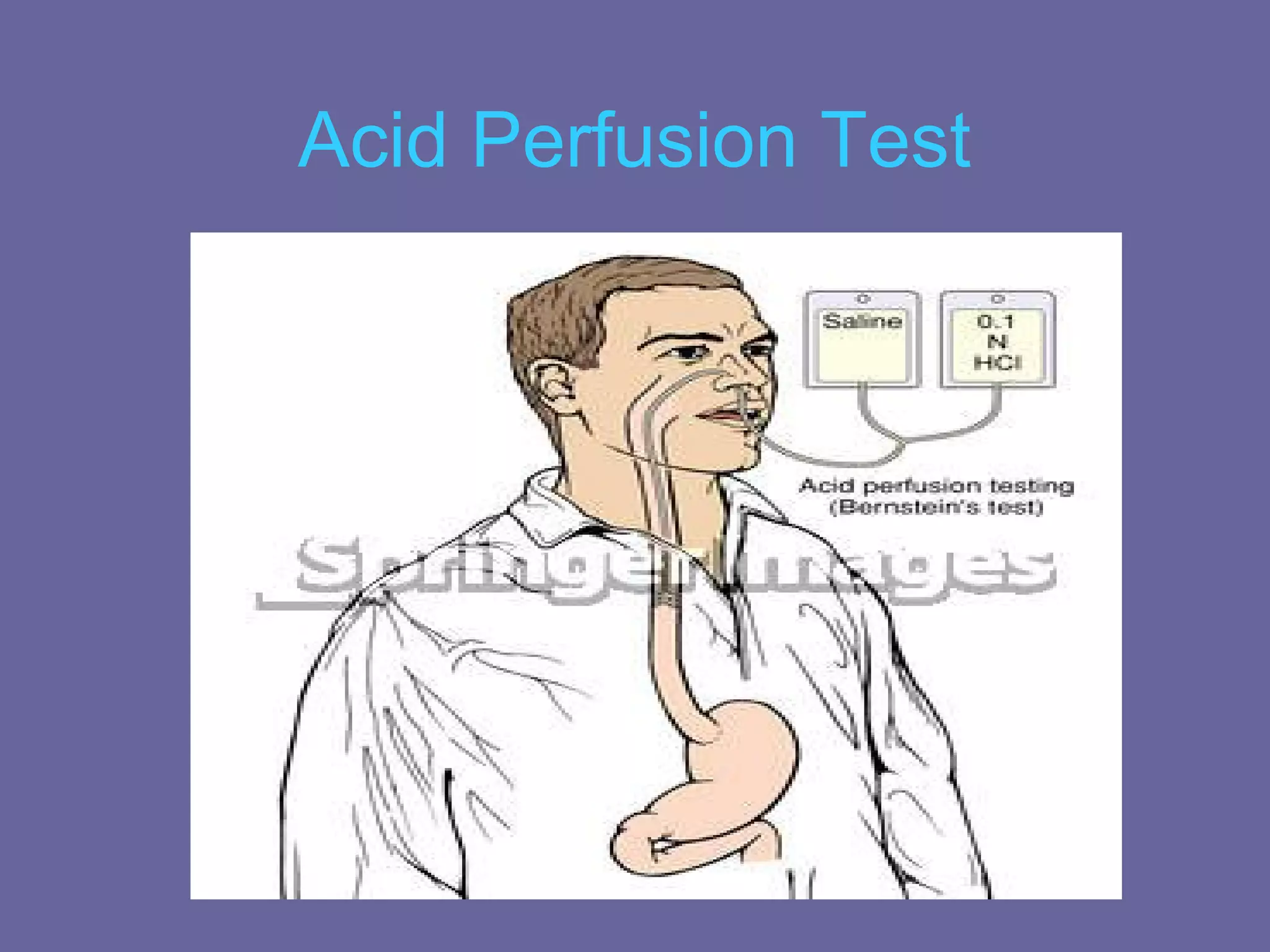
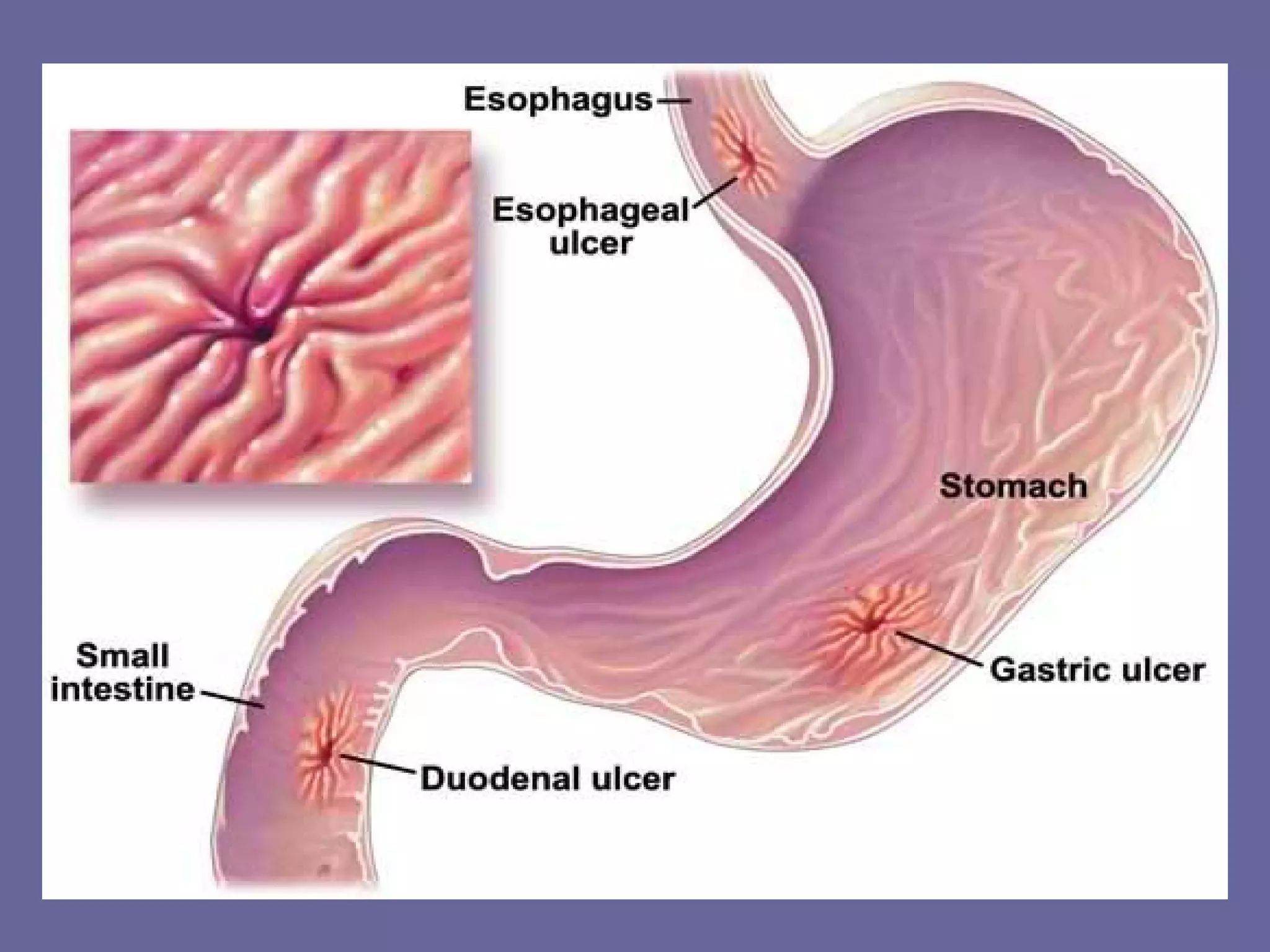
This document discusses several upper gastrointestinal disorders including GERD, peptic ulcer disease, gastric cancer, and their associated risk factors, clinical manifestations, diagnoses, and treatments. GERD is caused by esophageal reflux and common symptoms include heartburn and acid regurgitation. Risk factors include obesity, smoking, and high-fat foods. Diagnoses may involve barium swallow, endoscopy, or acid perfusion tests. Treatment involves dietary changes, medications like antacids or proton pump inhibitors, and lifestyle modifications. Peptic ulcers are breaks in the stomach or duodenal mucosa and are associated with protein meals, alcohol, smoking, NSAIDs, and H. pylori infection. Gastric cancer