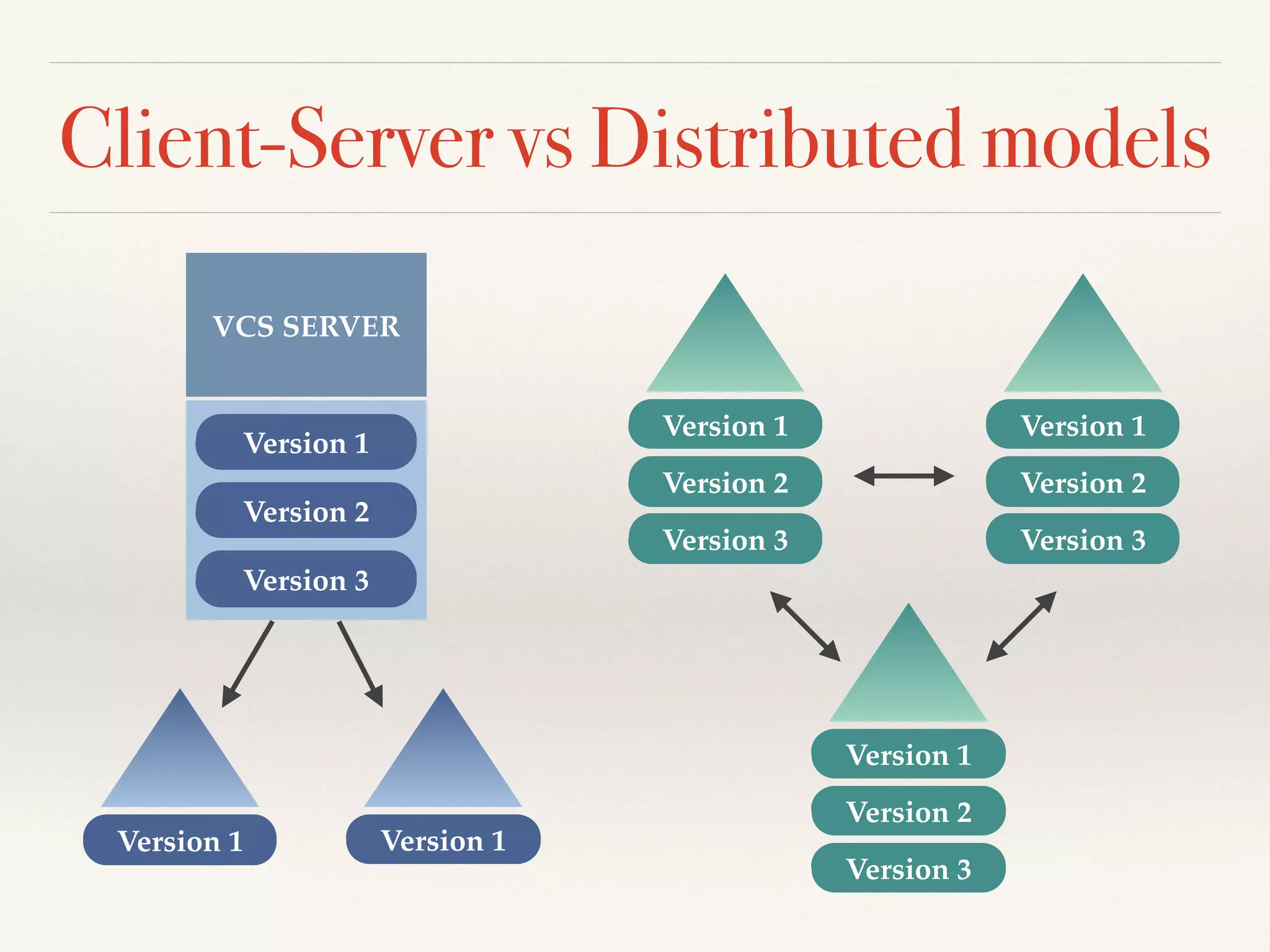
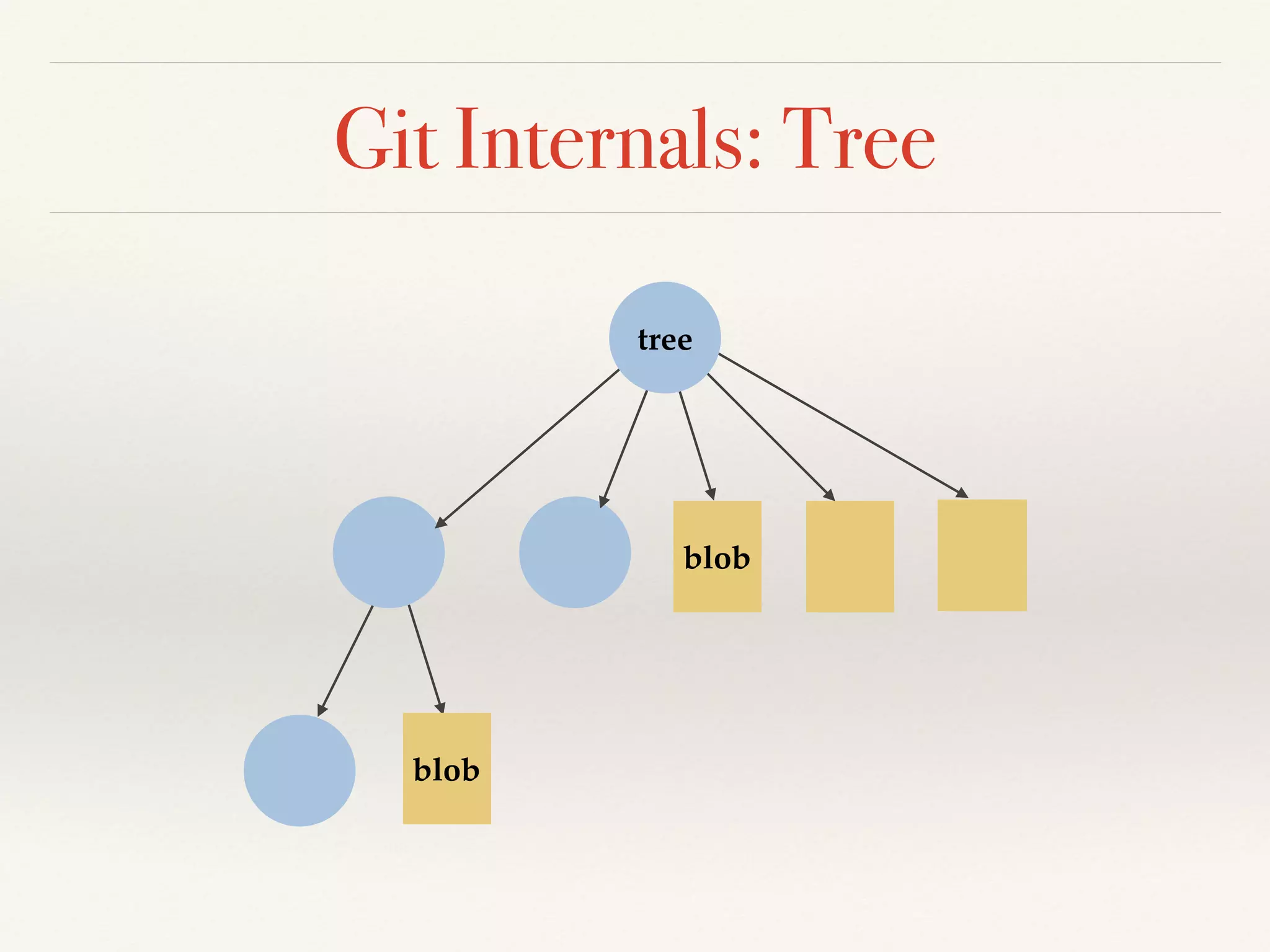
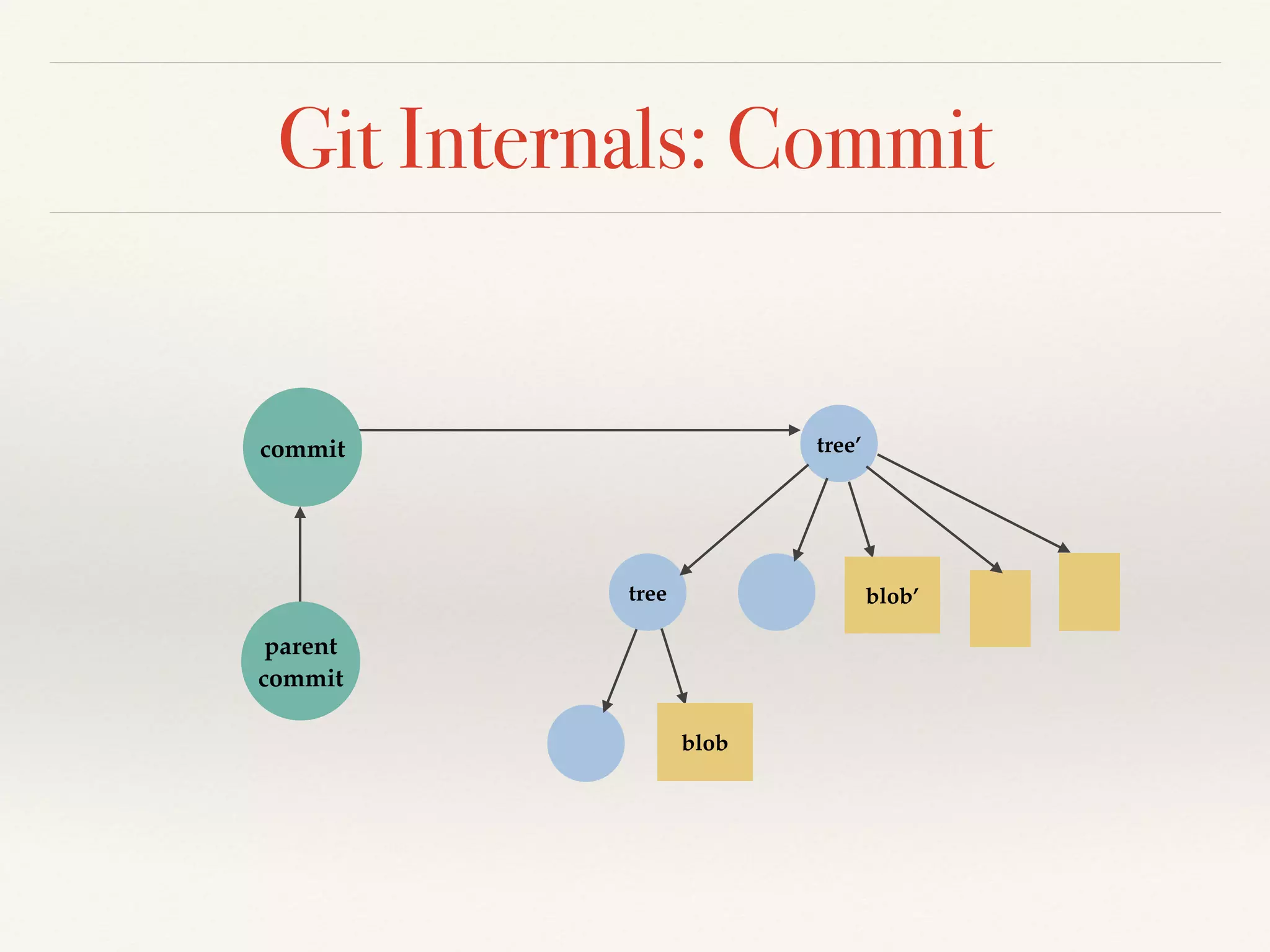
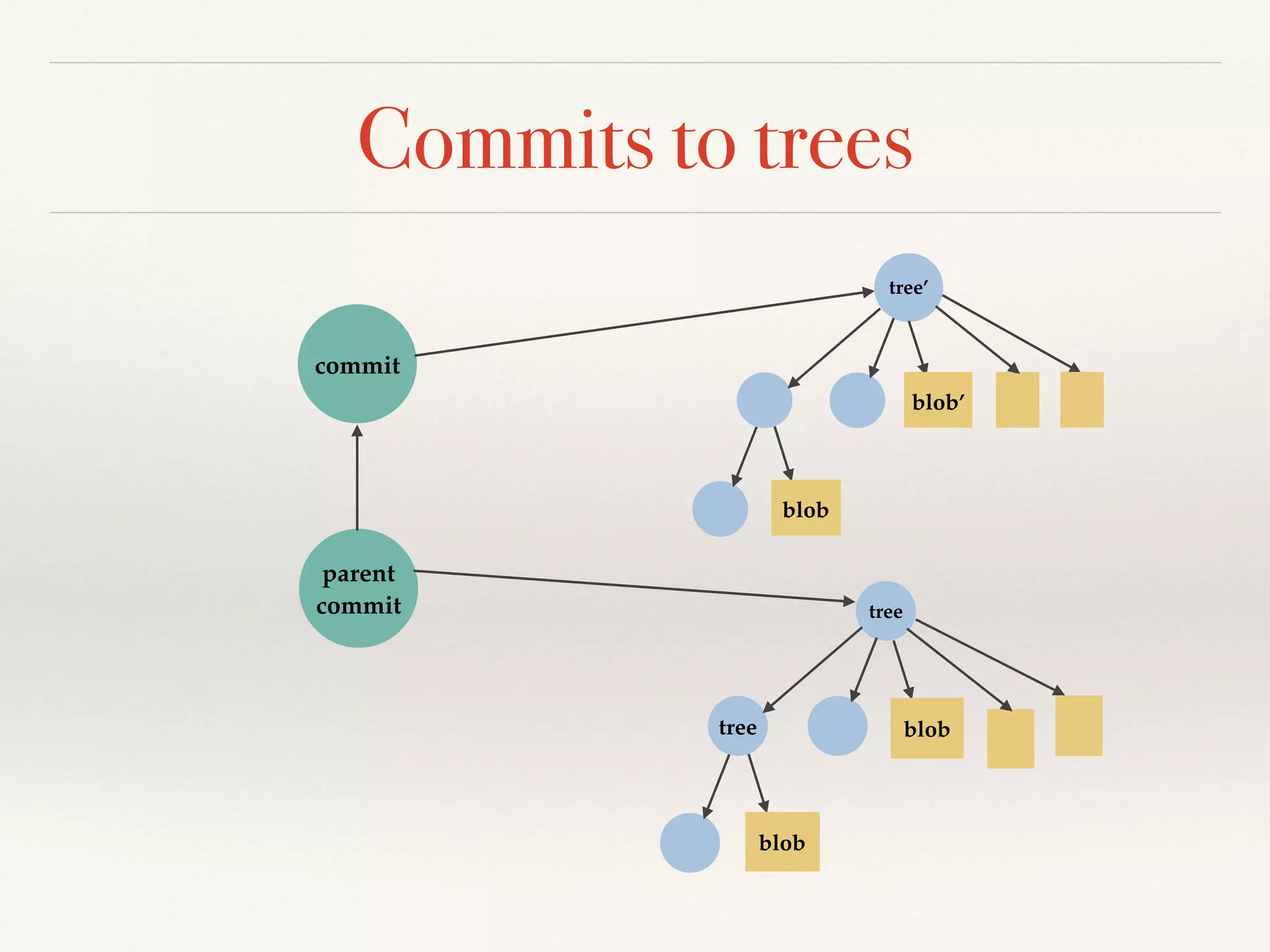
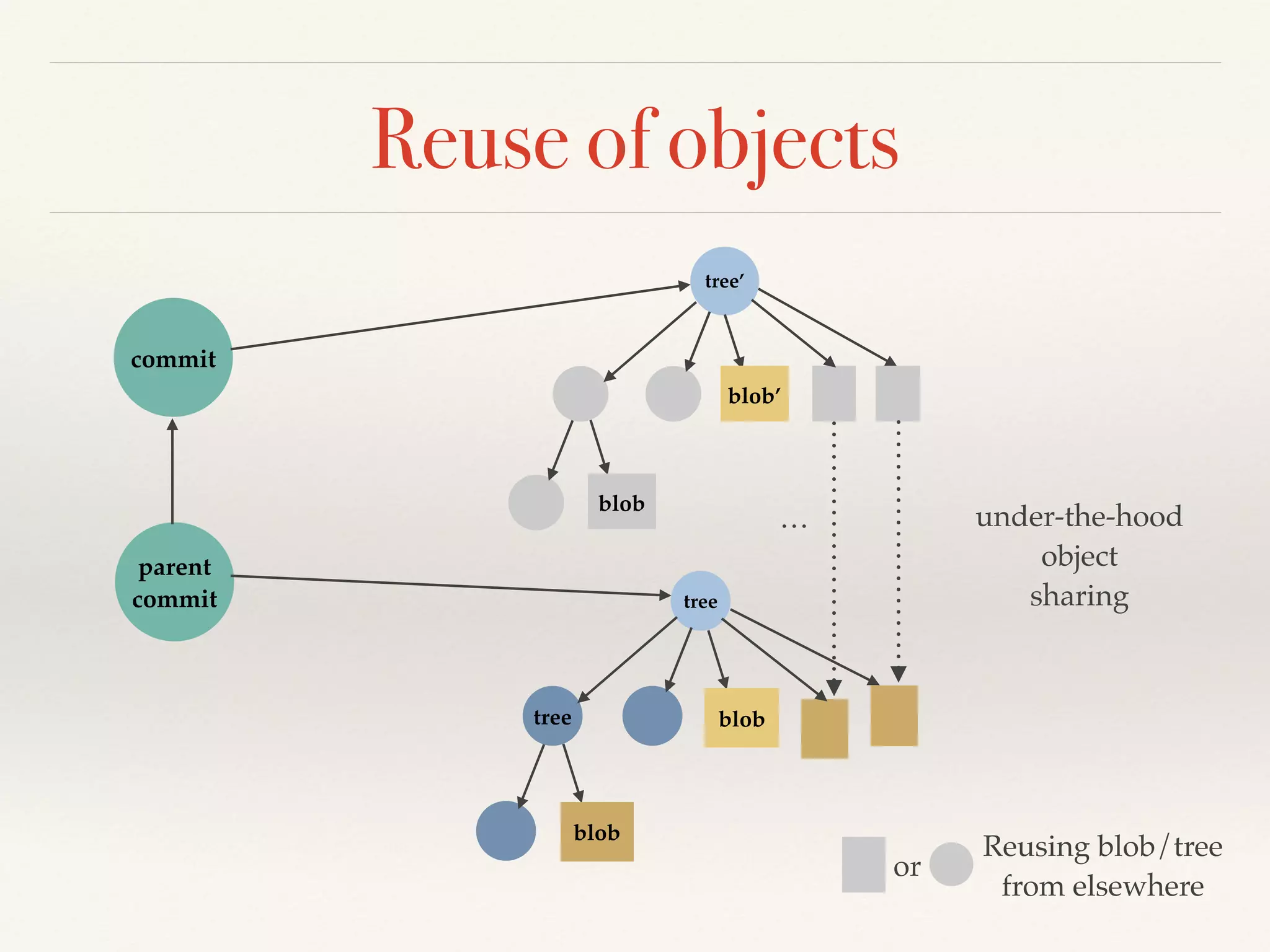
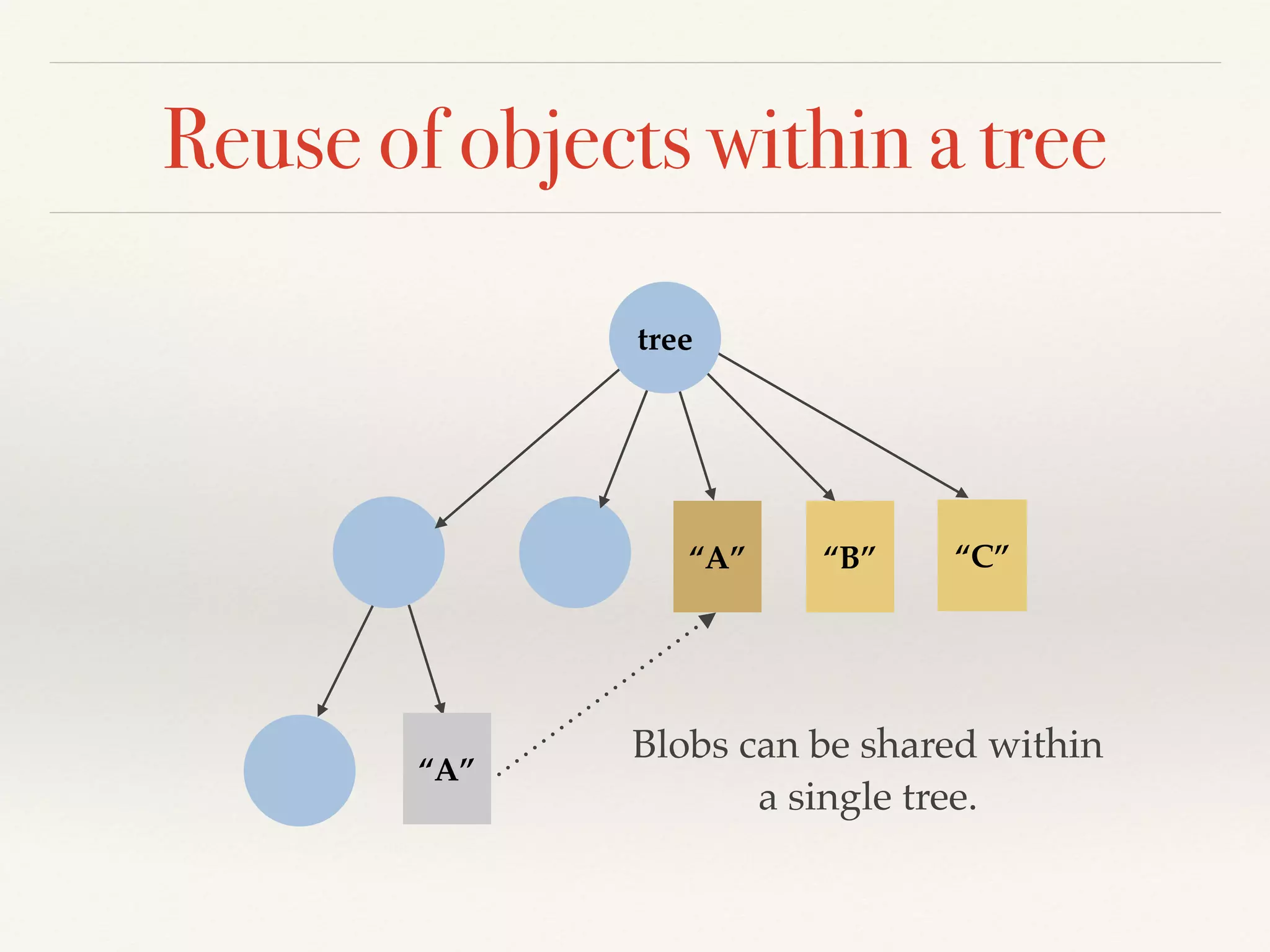
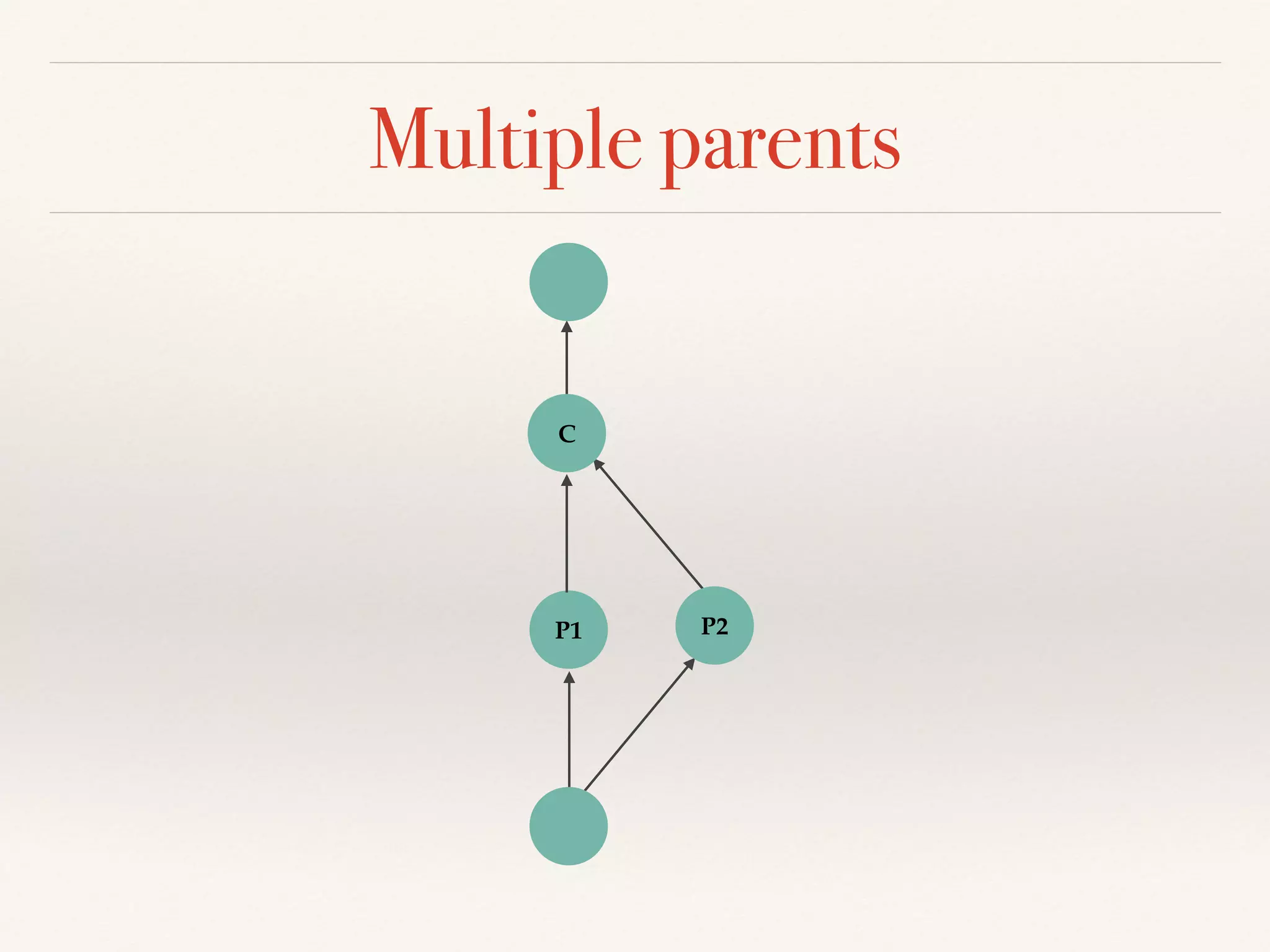
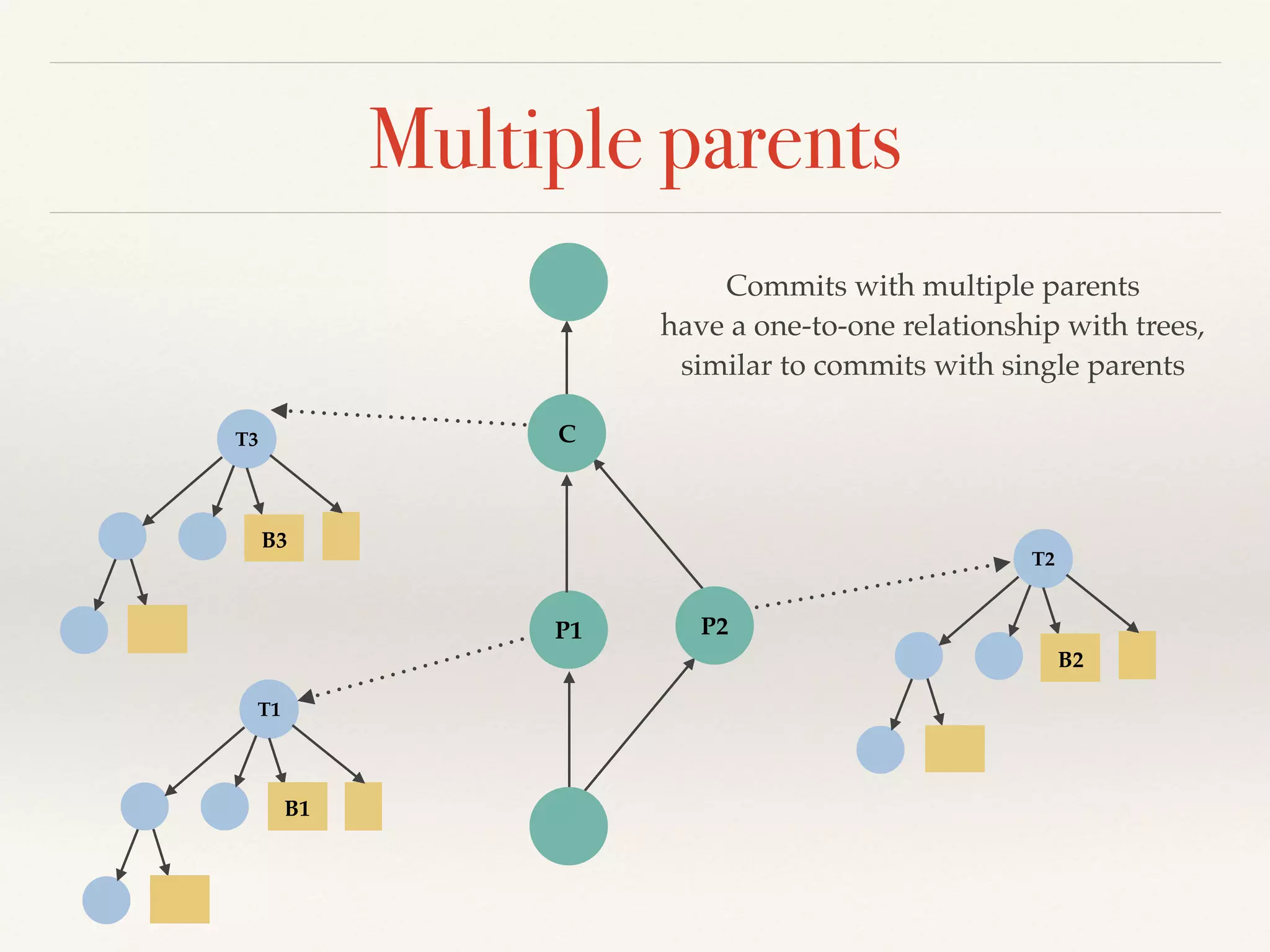
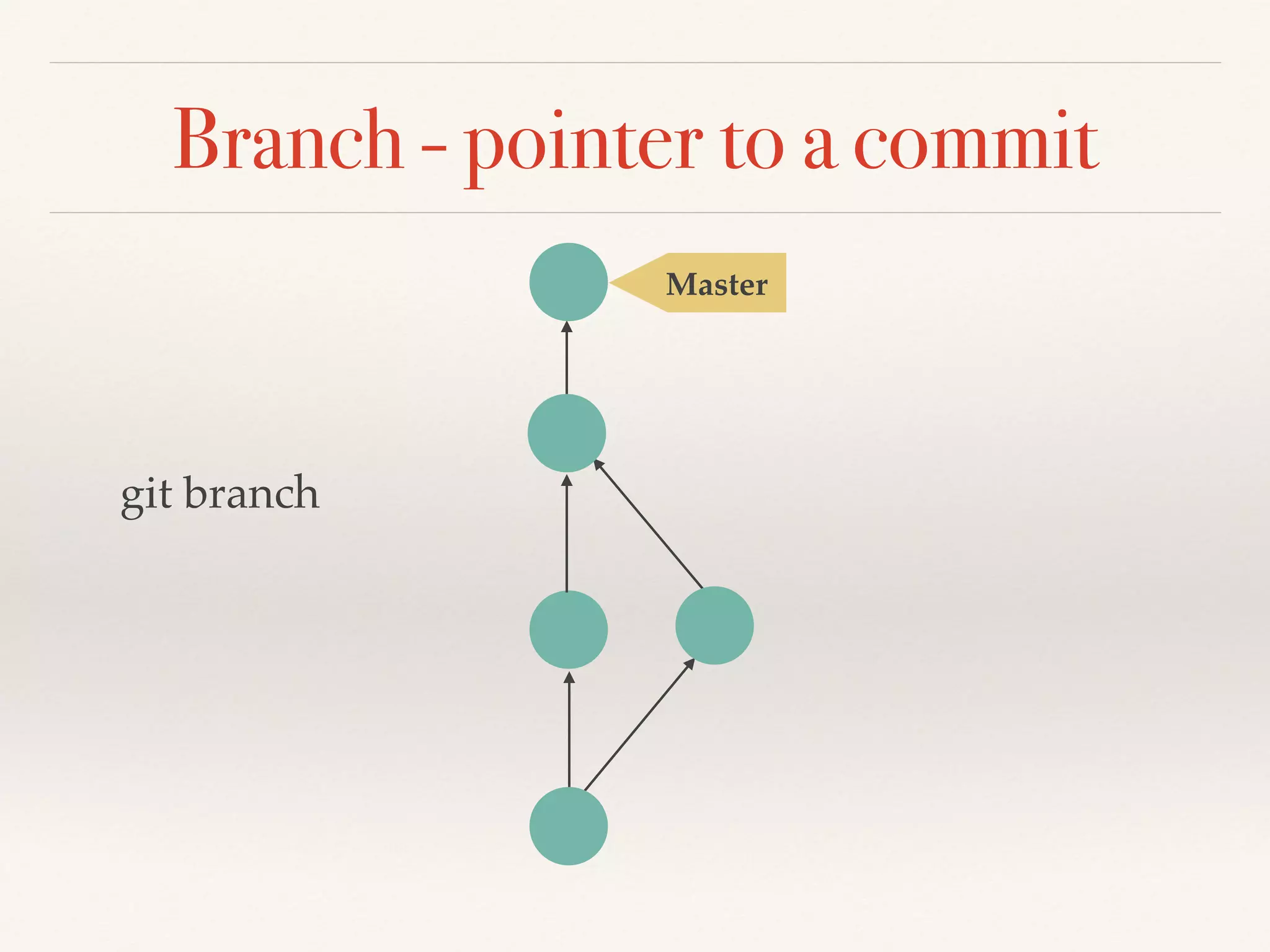
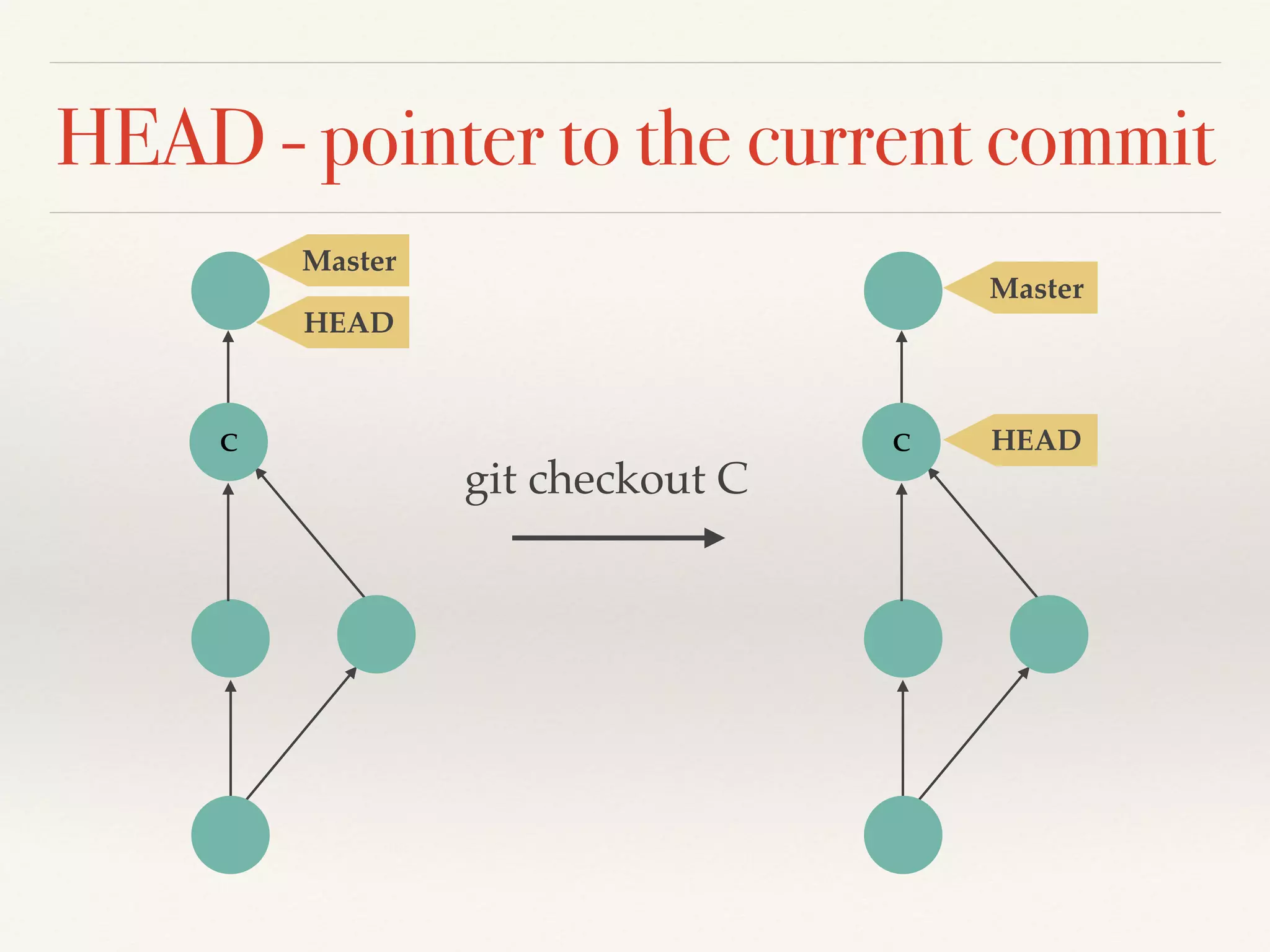
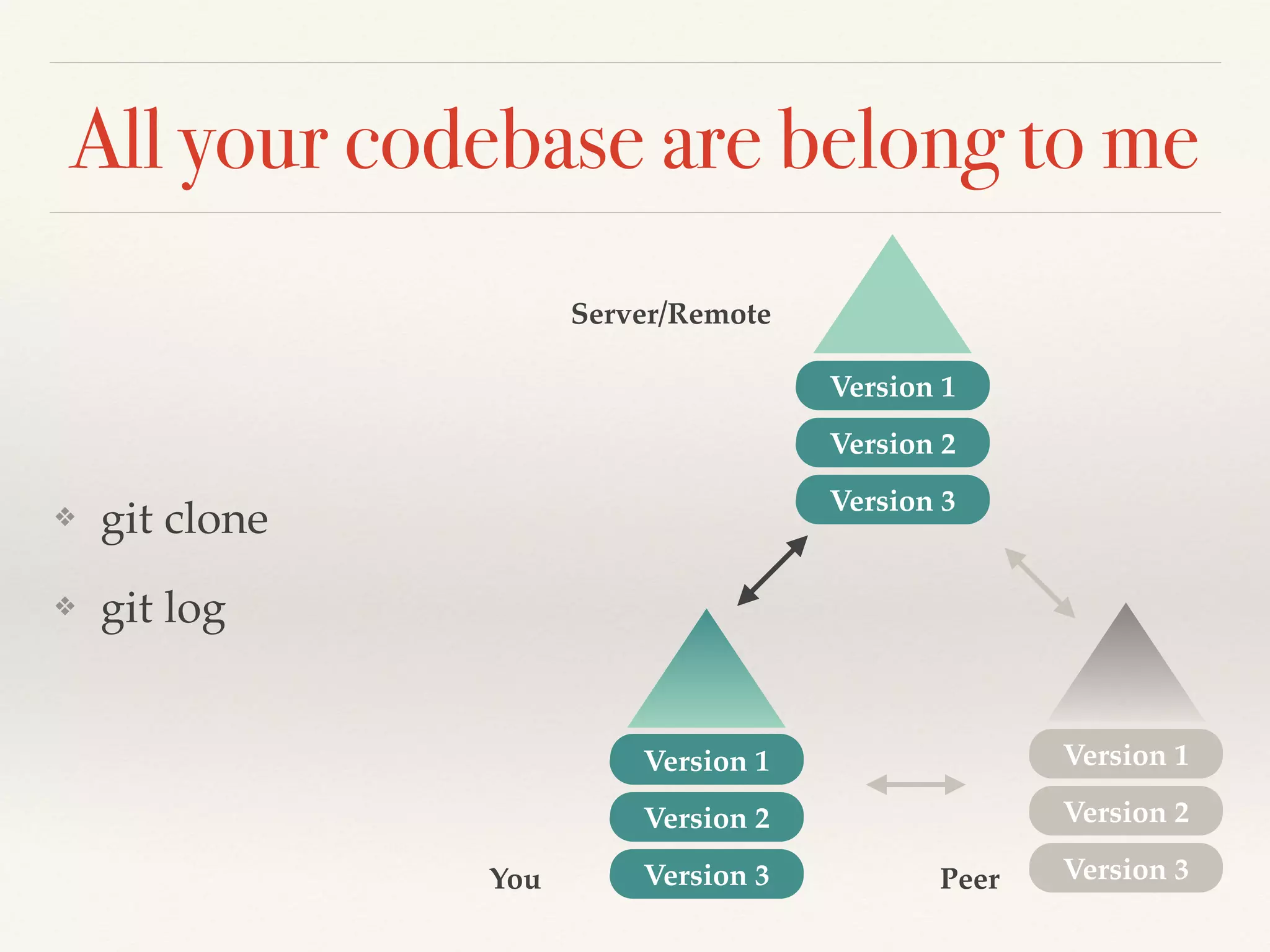
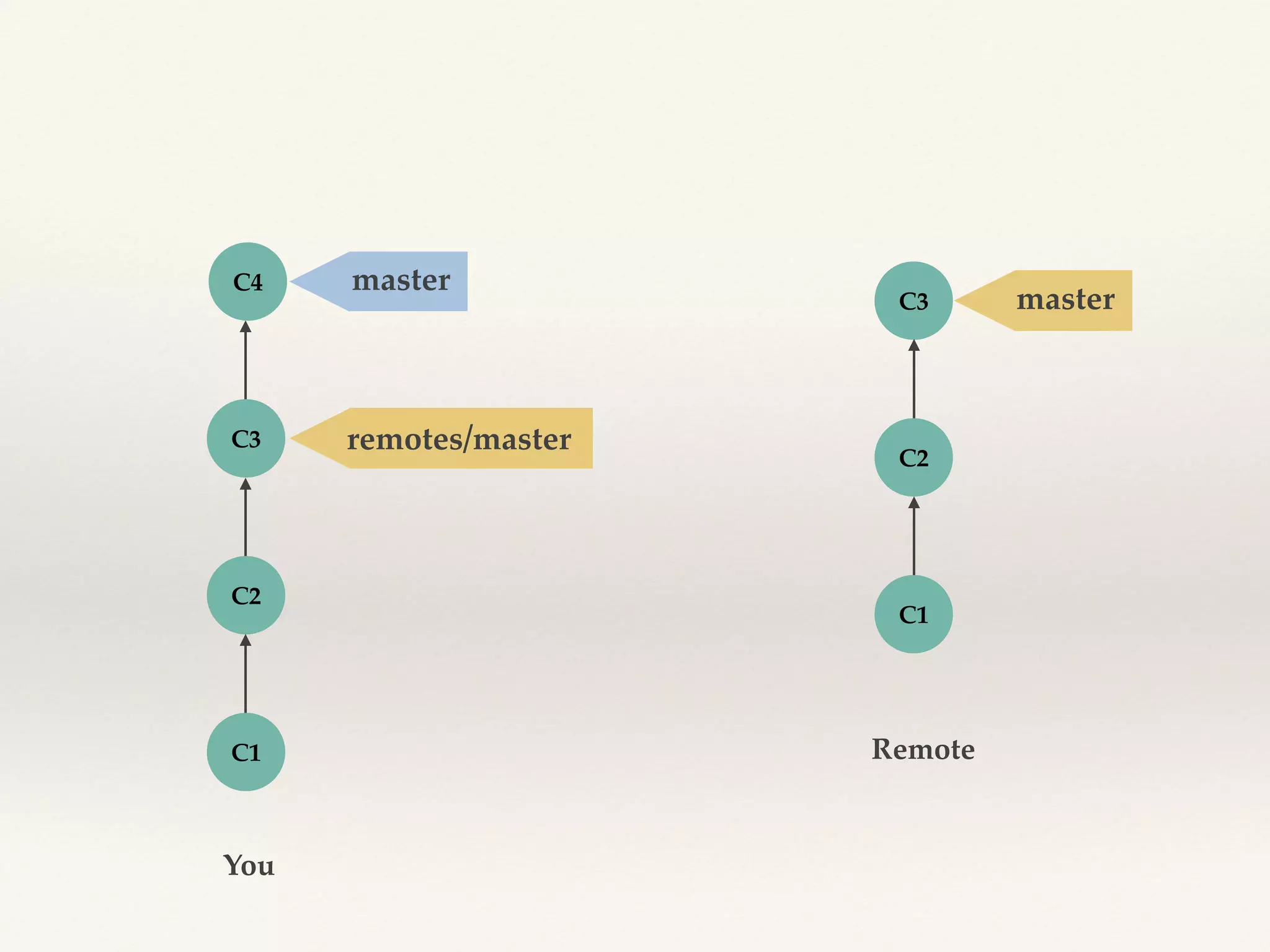
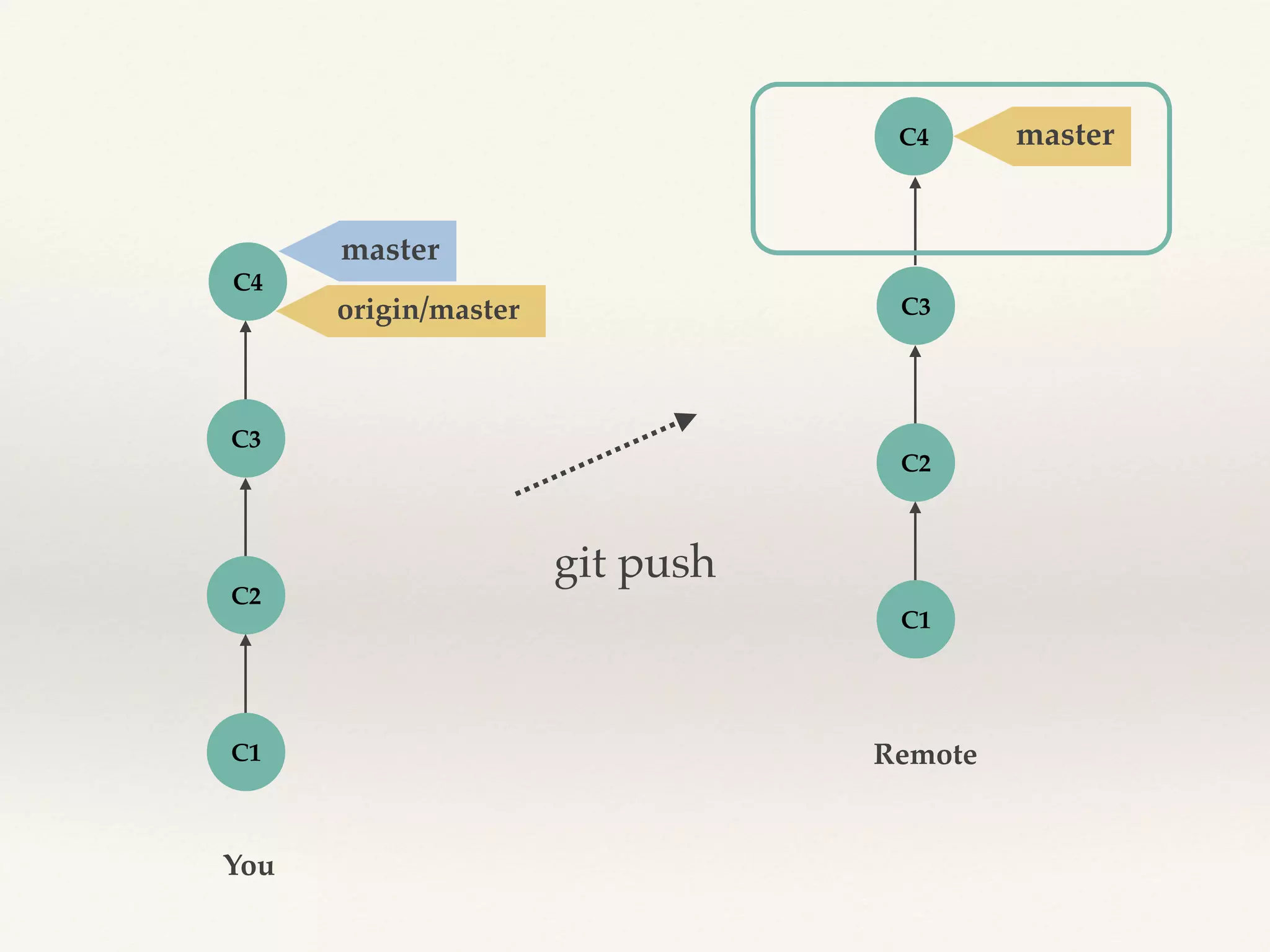
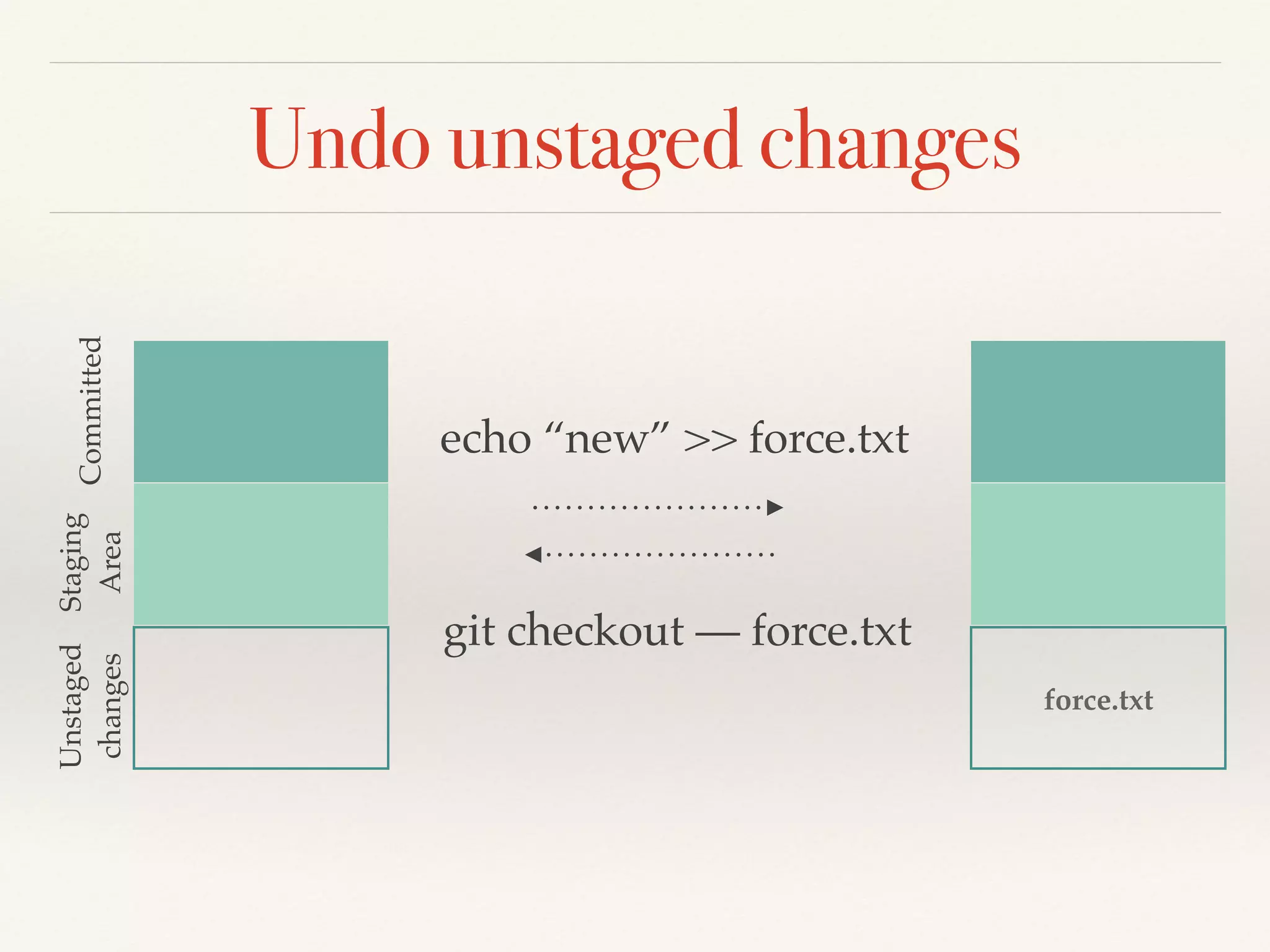
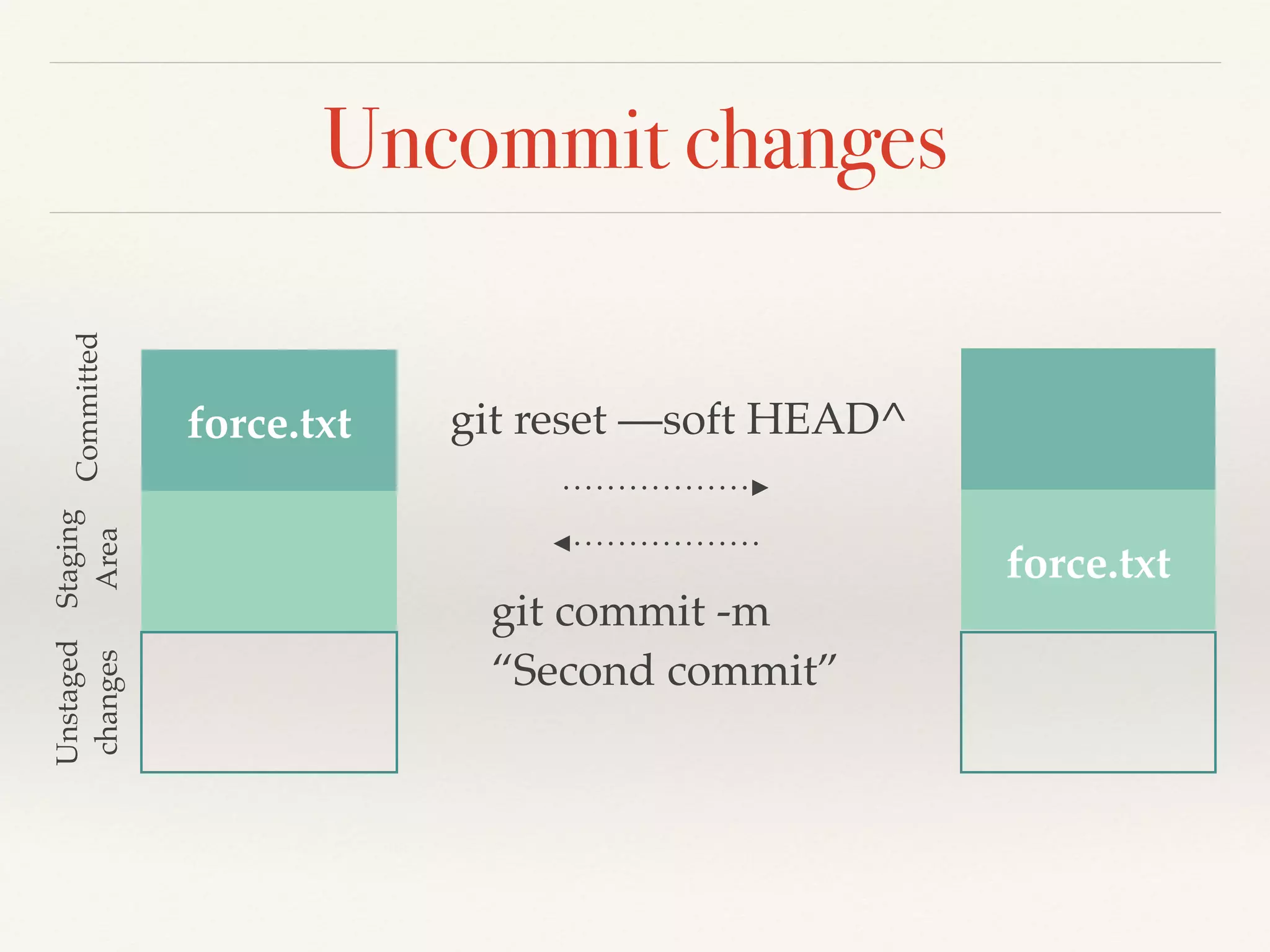
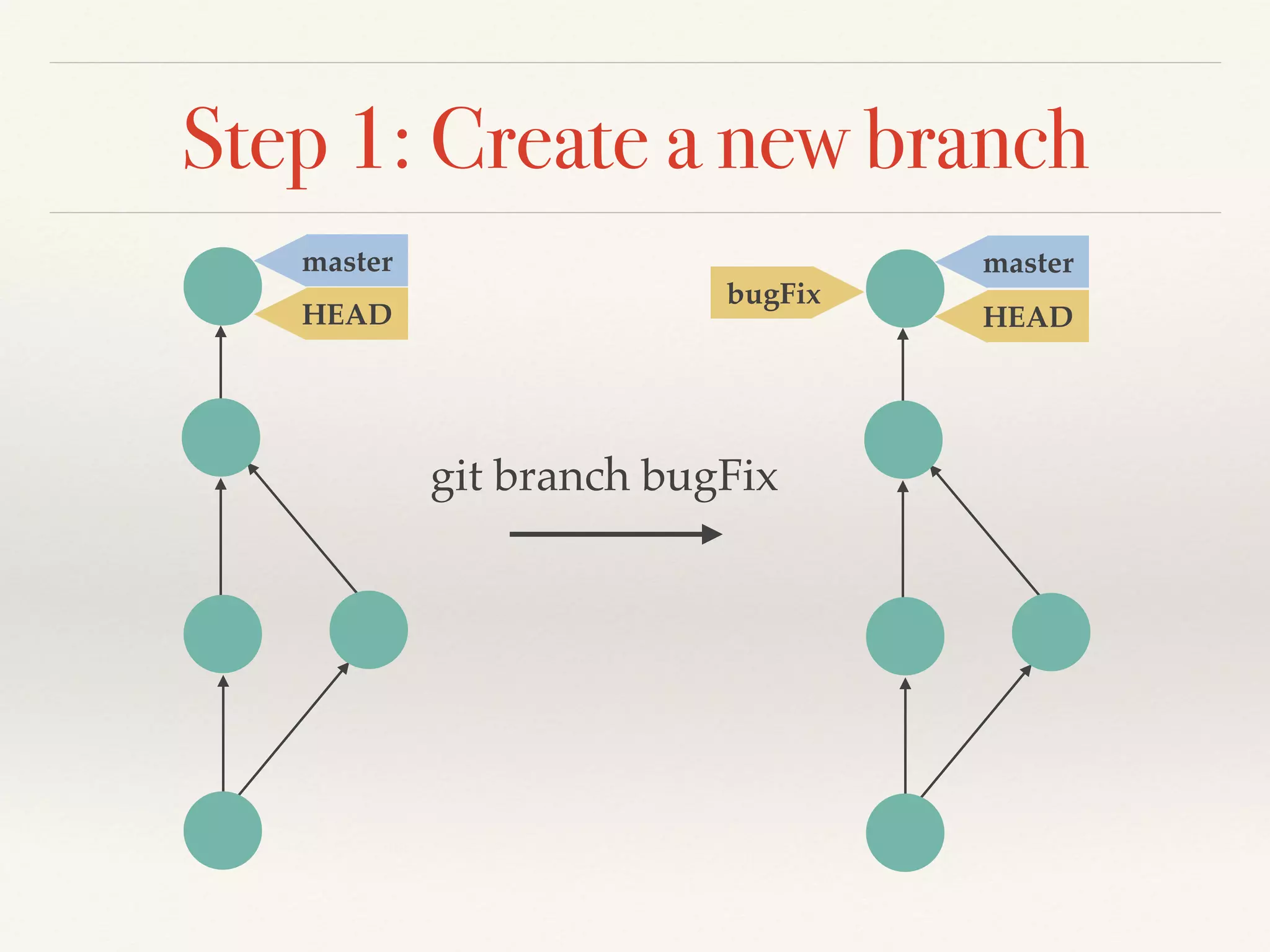
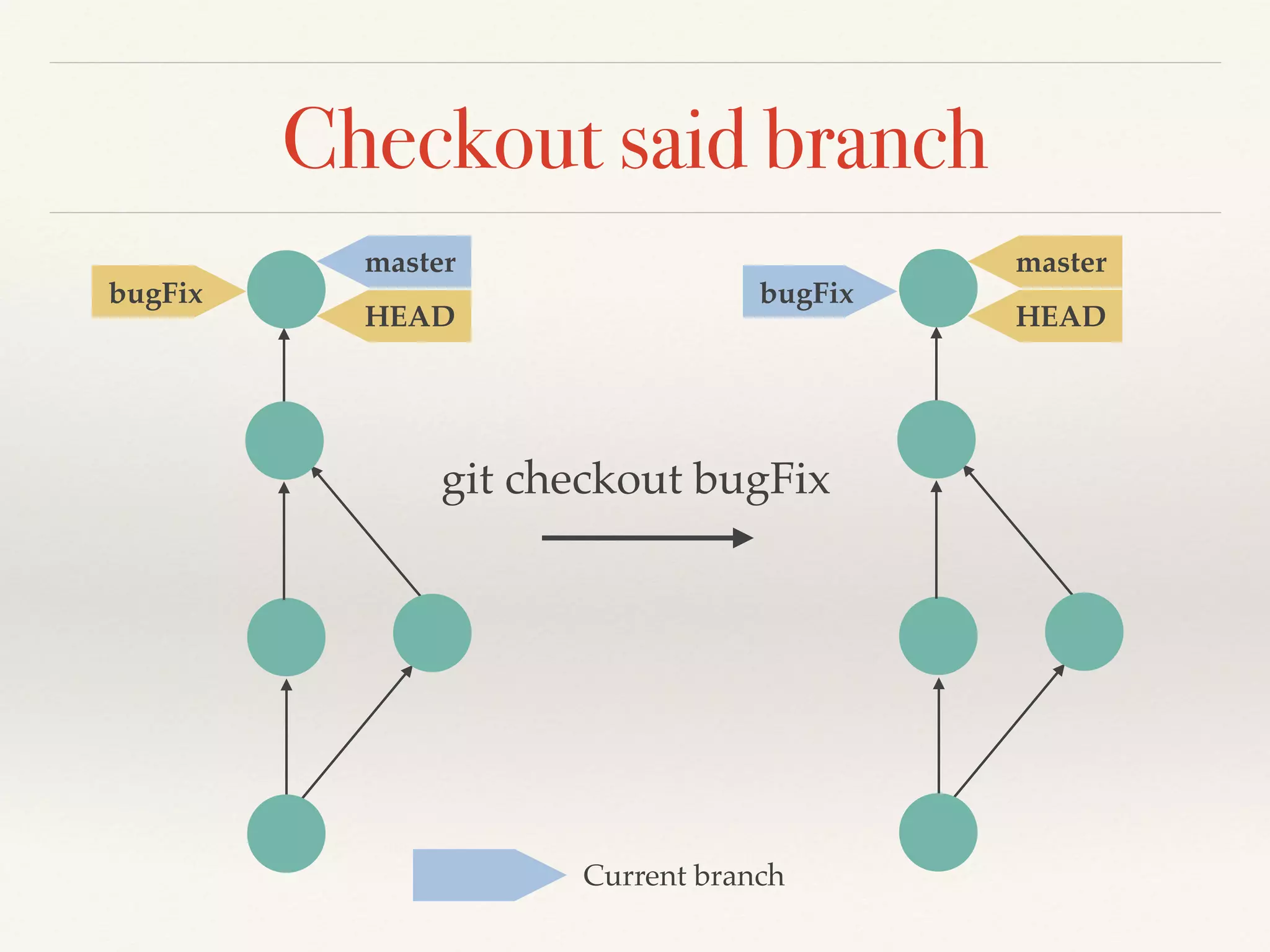
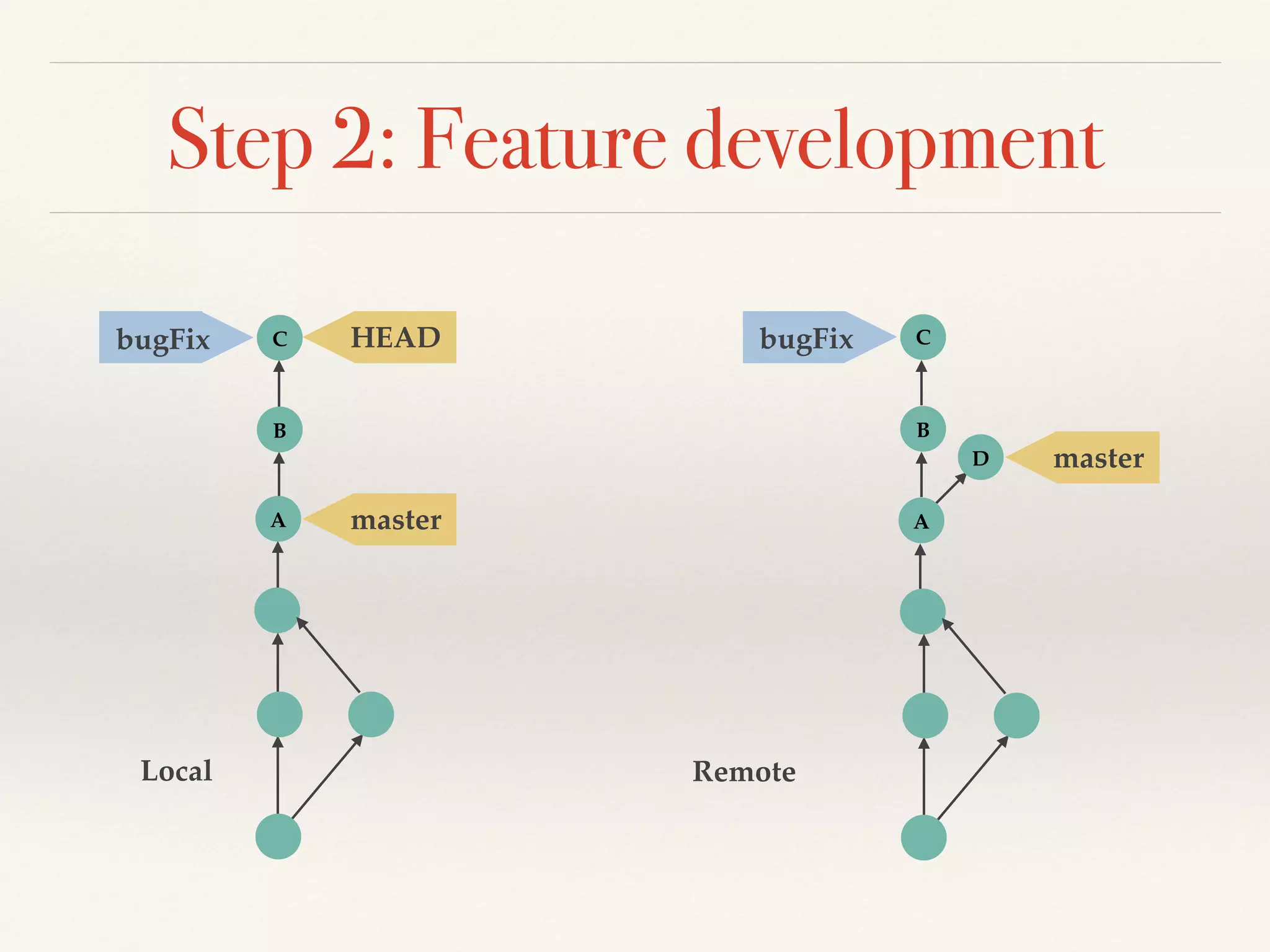
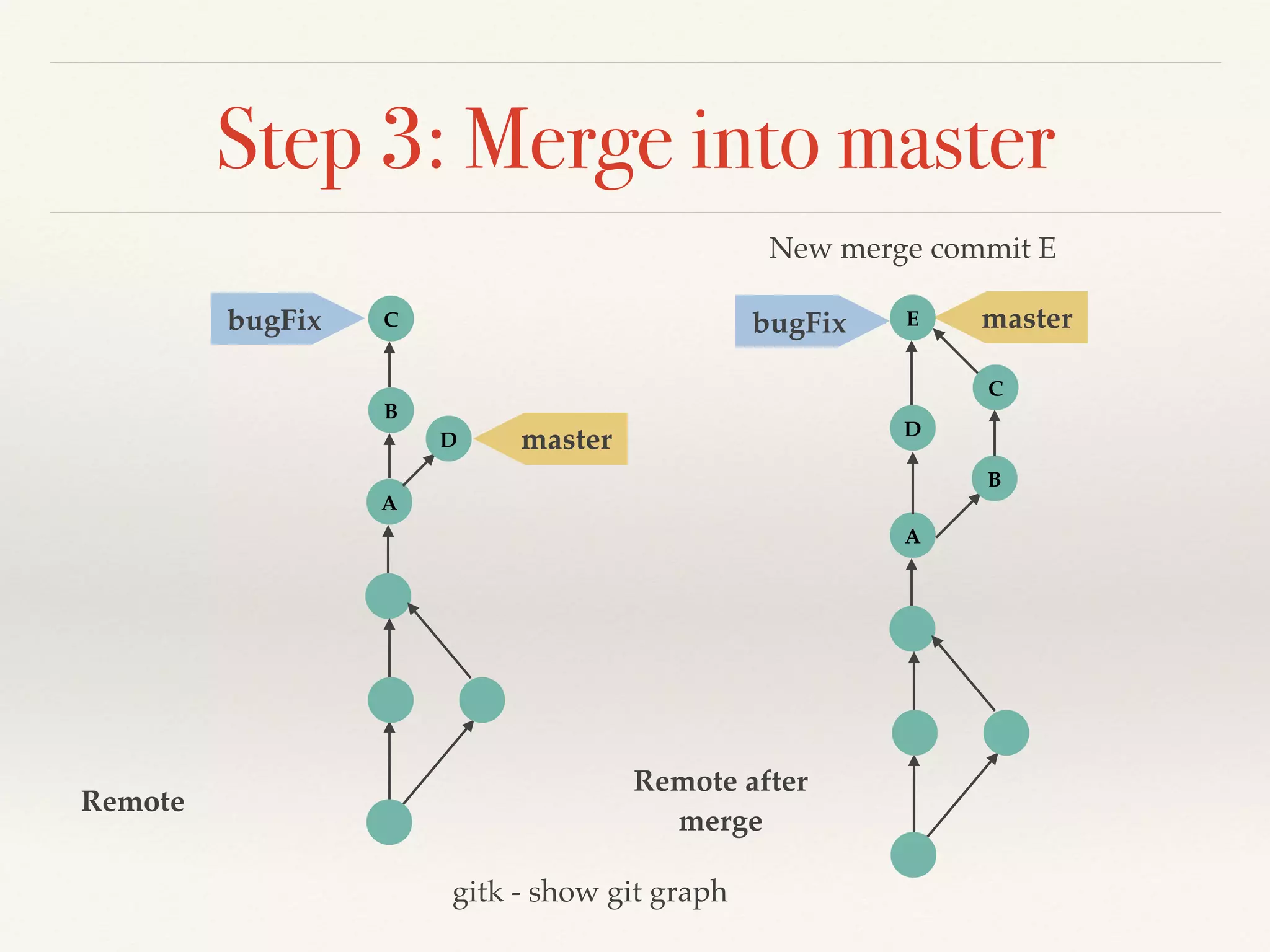
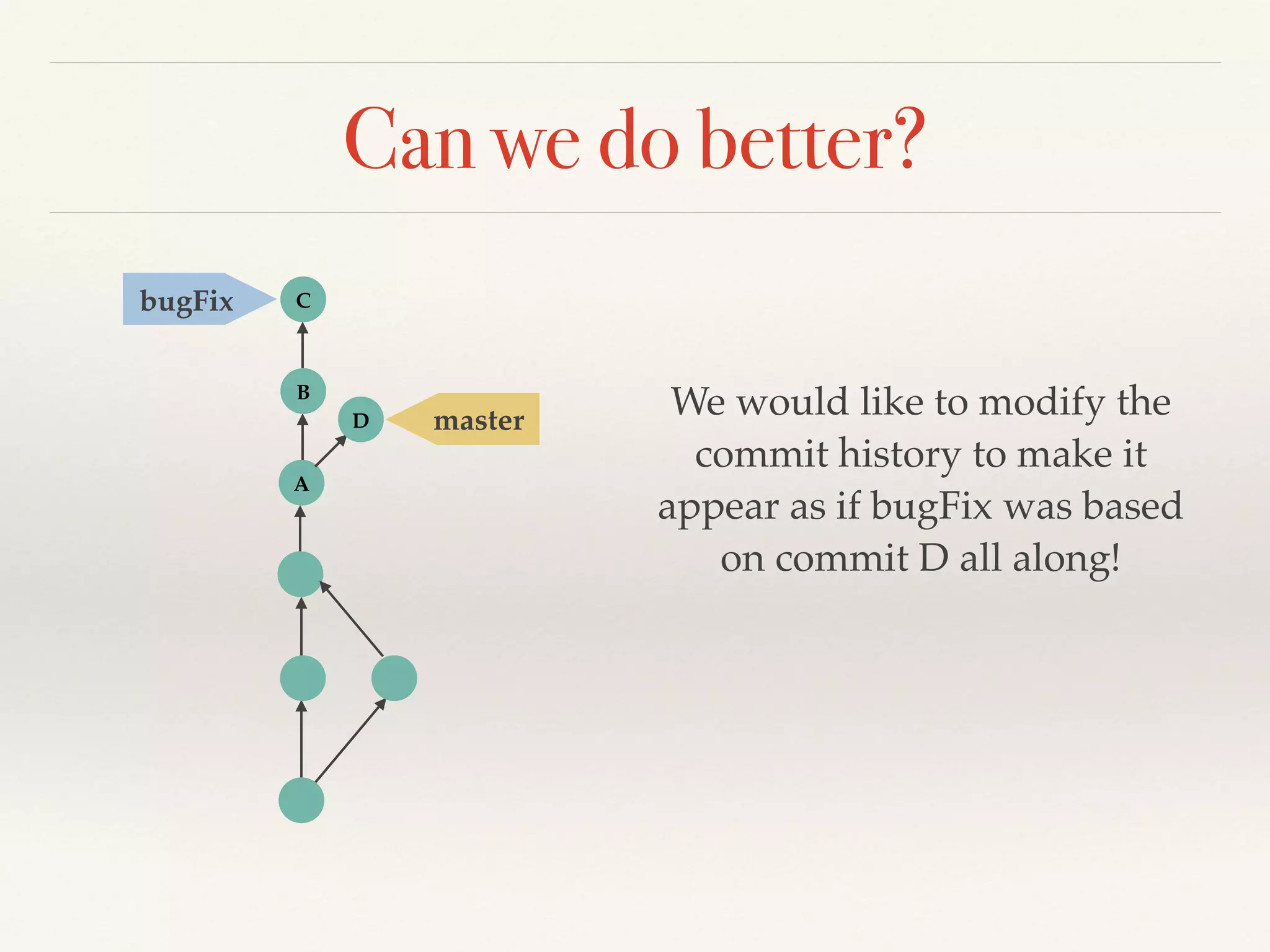
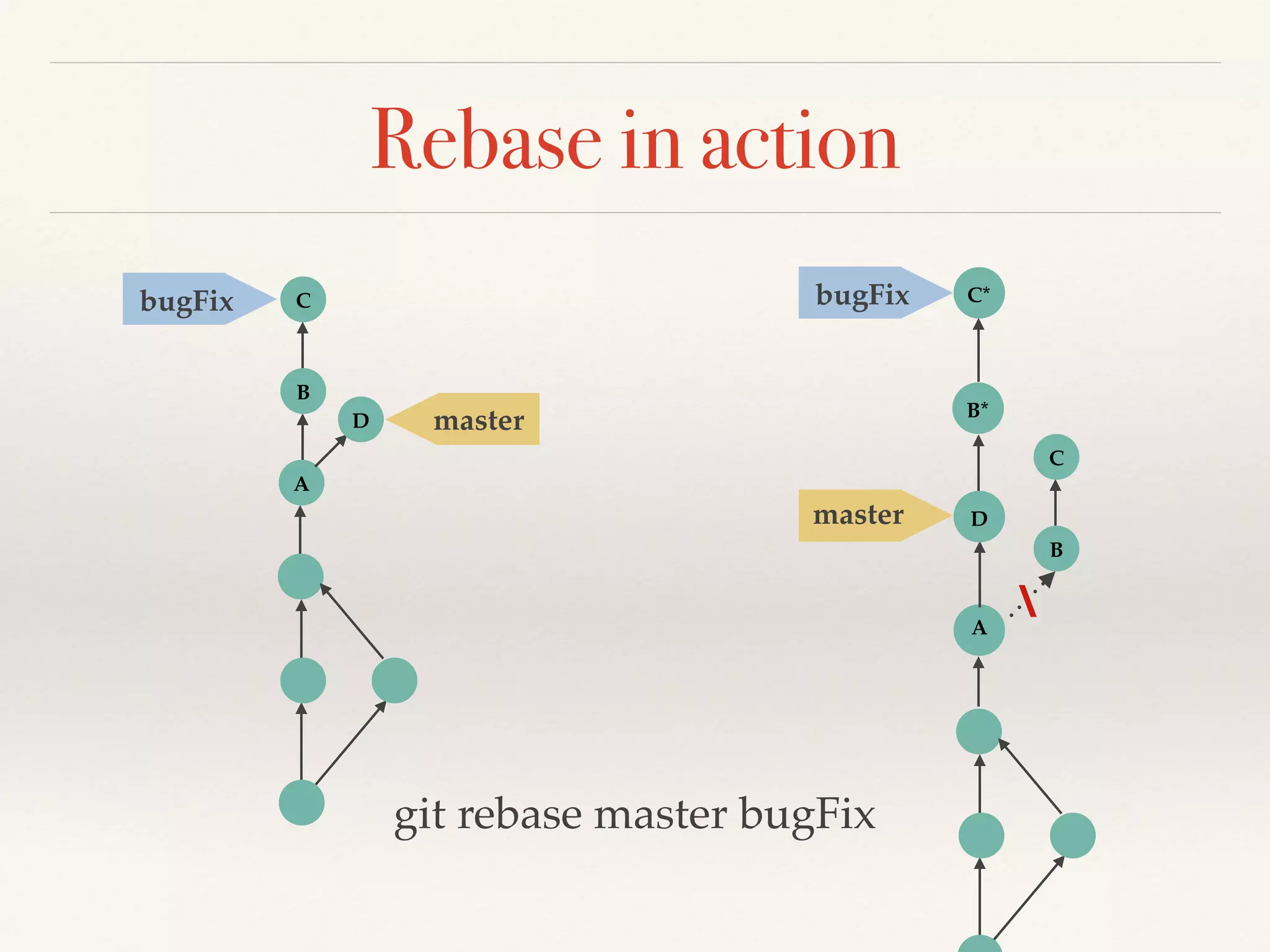
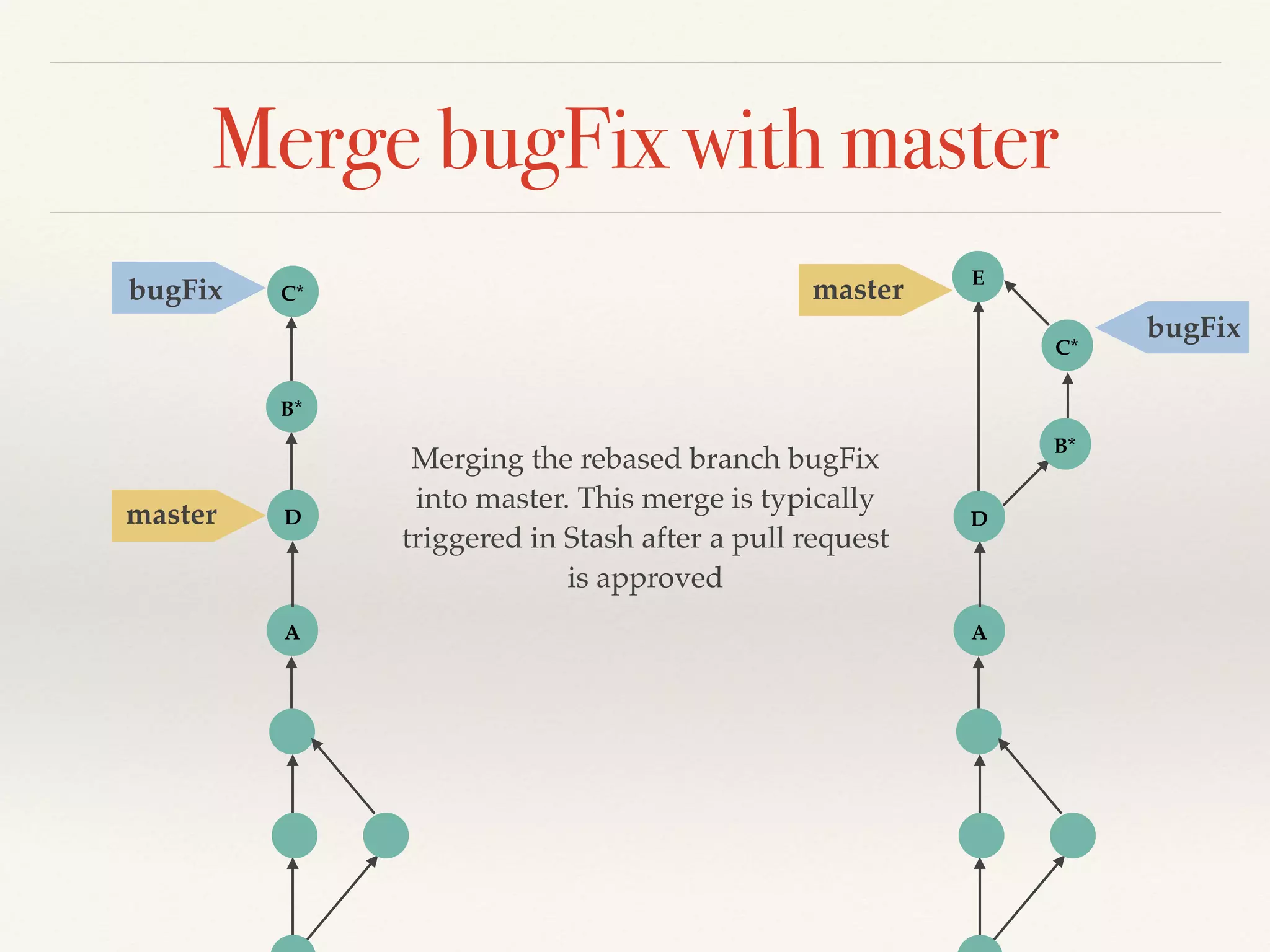
Git is a distributed version control system that provides faster performance compared to client-server systems like Perforce. It works by storing content and metadata in objects that are identified by cryptographic hashes, including blobs for file contents and trees and commits for snapshots. Developers can work locally and commit changes to their local repository, and integrate changes with remote repositories using branches and merging.