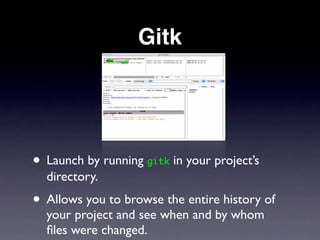
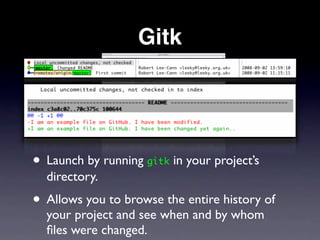
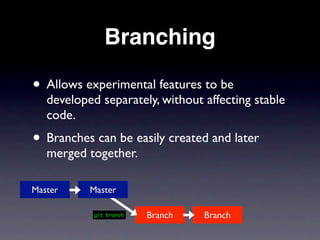
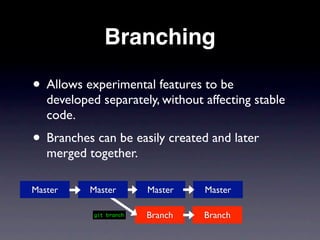
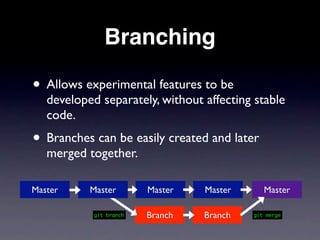
This document provides an overview of version control with Git. It explains what version control and Git are, how to install and configure Git, how to perform basic tasks like initializing a repository and making commits, and how to collaborate using features like branching and pushing/pulling from remote repositories. Key points covered include allowing the tracking of changes, maintaining file history, and enabling multiple people to work on the same project simultaneously without conflicts.