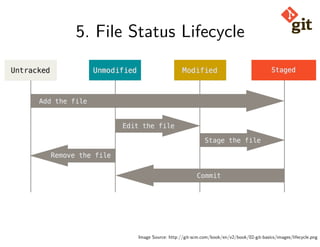
The document provides a comprehensive tutorial on using Git, covering installation, configuration of the first repository, file lifecycle, and common commands such as staging, undo, logging, remote management, branching, and tagging. It emphasizes the benefits of Git for collaboration and organization. Resources and examples are drawn from git-scm.com.