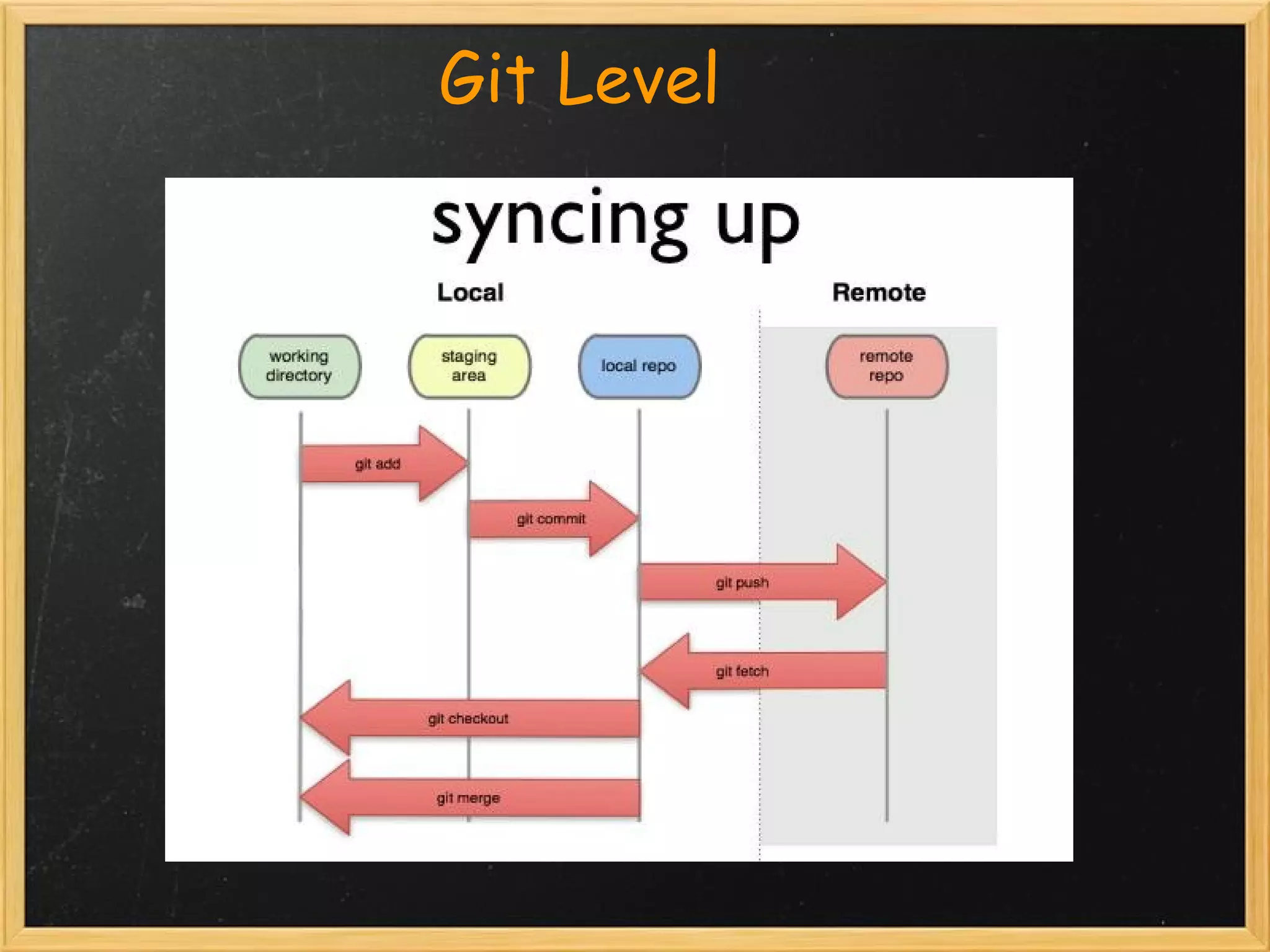
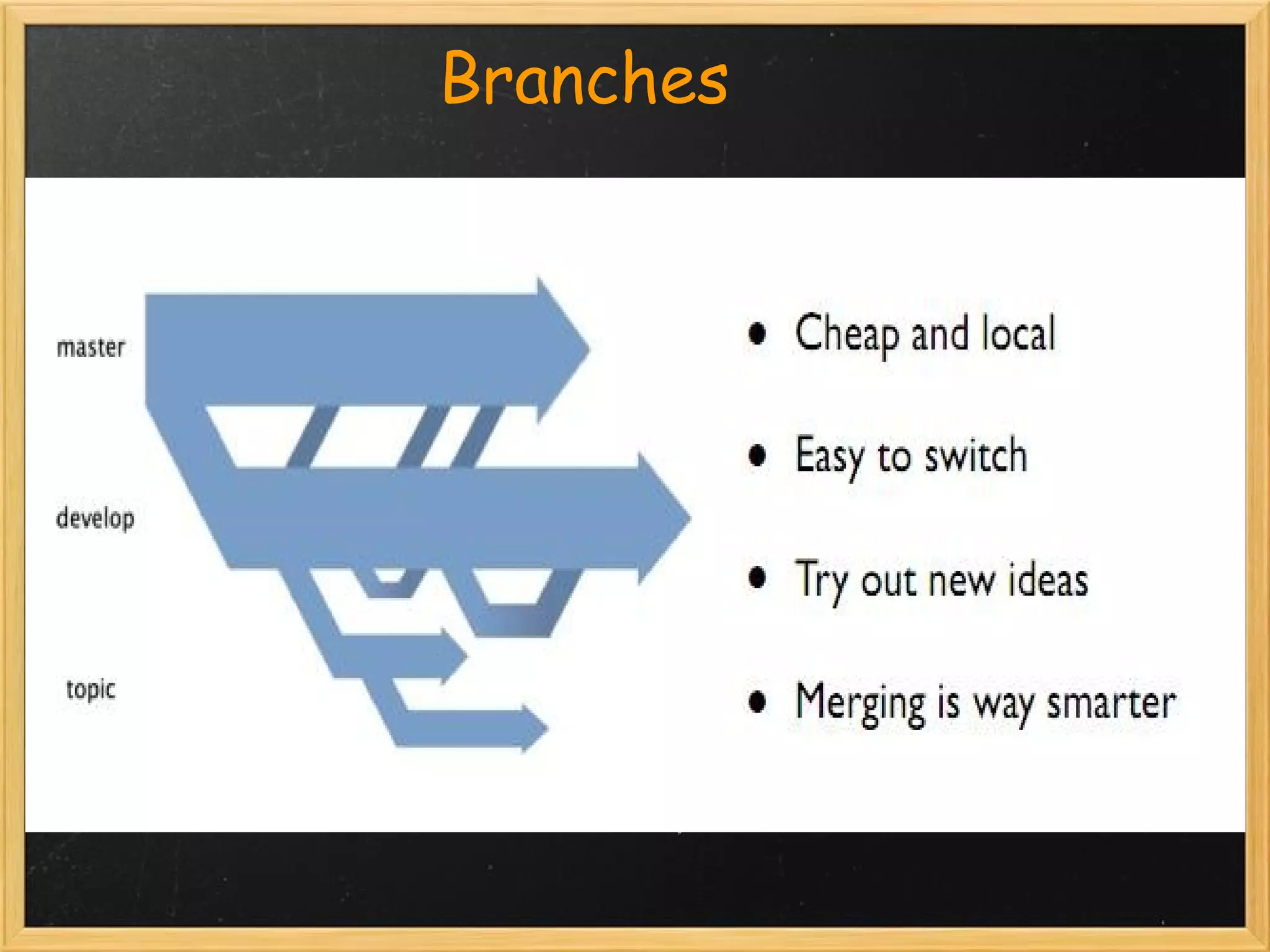
The document provides an overview of Git, a distributed version control system created by Linus Torvalds, highlighting its key features and advantages over traditional systems like CVS and SVN. It covers basic Git commands for repository management, including setup, committing changes, branching, merging, and handling common situations. Additionally, it offers resources for further learning about Git commands and best practices.














![Resources
• http://gitref.org [For basics commands]
• http://progit.org/book/
• http://www.slideshare.net/search/slideshow?
searchfrom=header&q=git](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gitbasic-120129013752-phpapp01/75/Git-basic-18-2048.jpg)