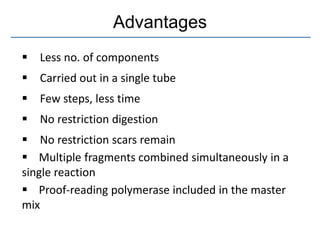
Gibson assembly is a DNA assembly method that allows joining of multiple DNA fragments in a single isothermal reaction to produce a single double stranded molecule. It involves three enzymes - T5 exonuclease, DNA phusion polymerase, and Taq DNA ligase. The enzymes are mixed with DNA fragments that have 20-40 bp overlapping regions. T5 exonuclease exposes complementary sequences, polymerase fills gaps, and ligase seals nicks to produce the full assembly. Gibson assembly has advantages like being carried out in one tube in one step with no restriction enzymes, but requires long overlapping oligonucleotides and errors can occur at junctions.