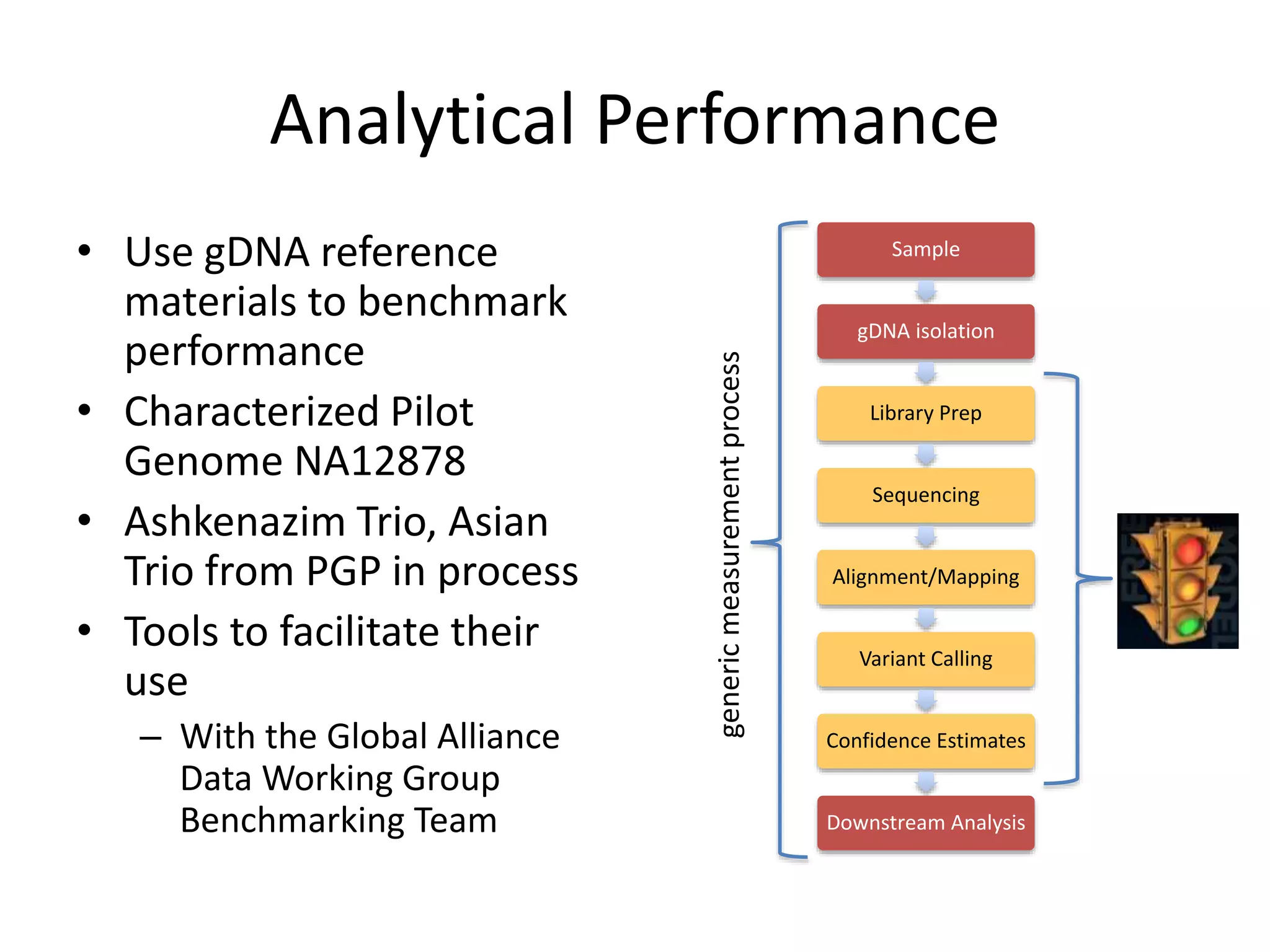
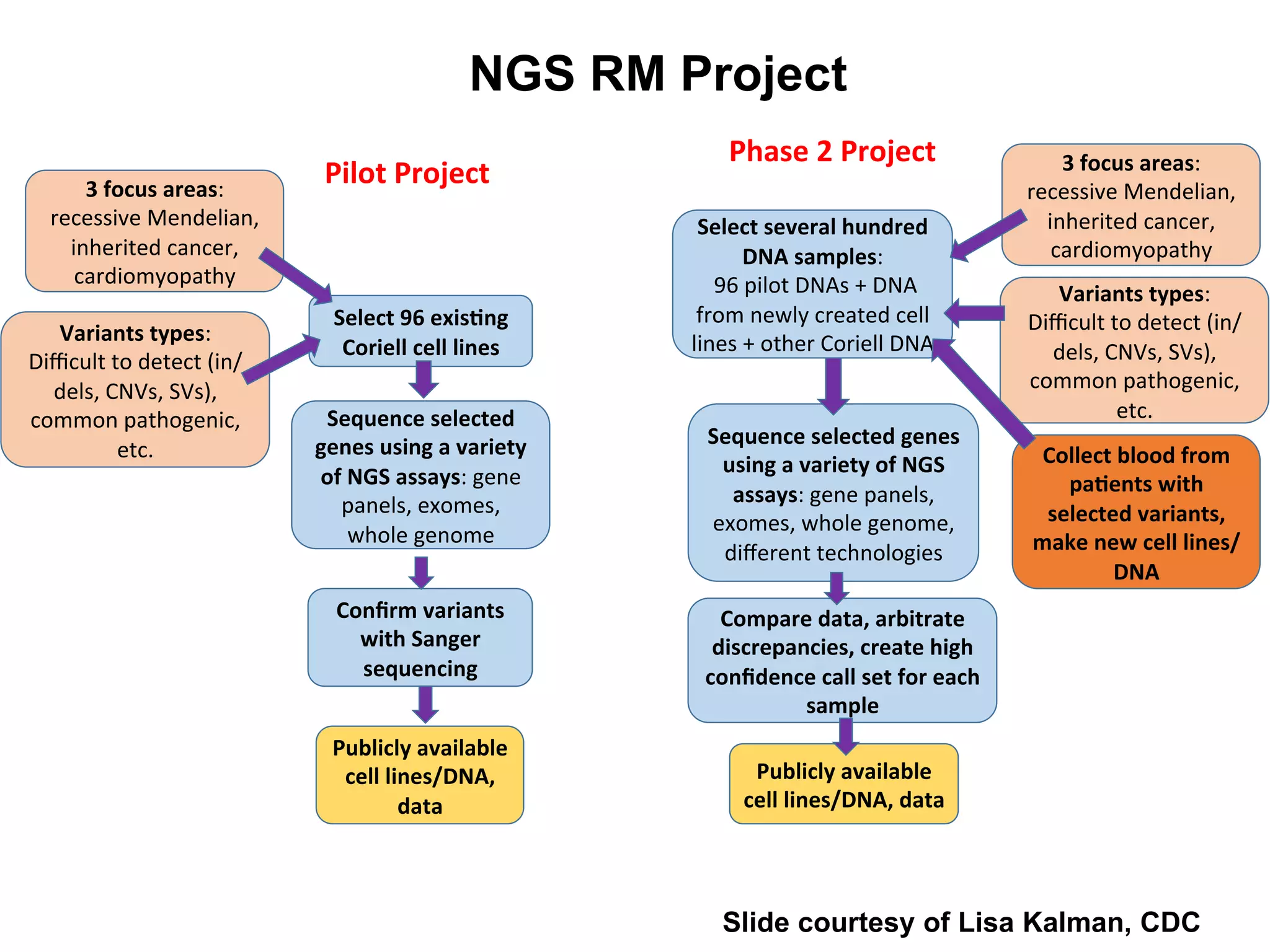
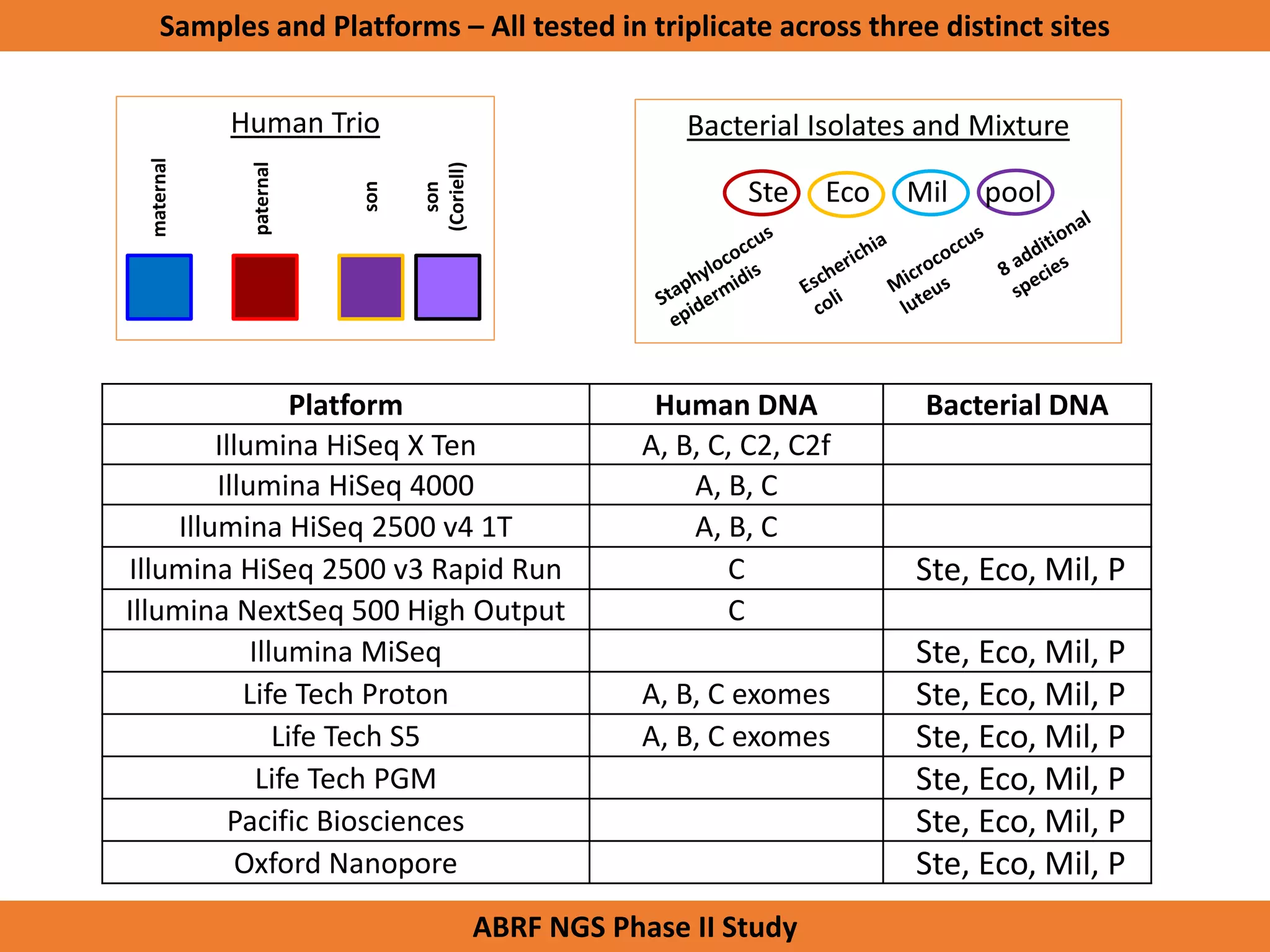
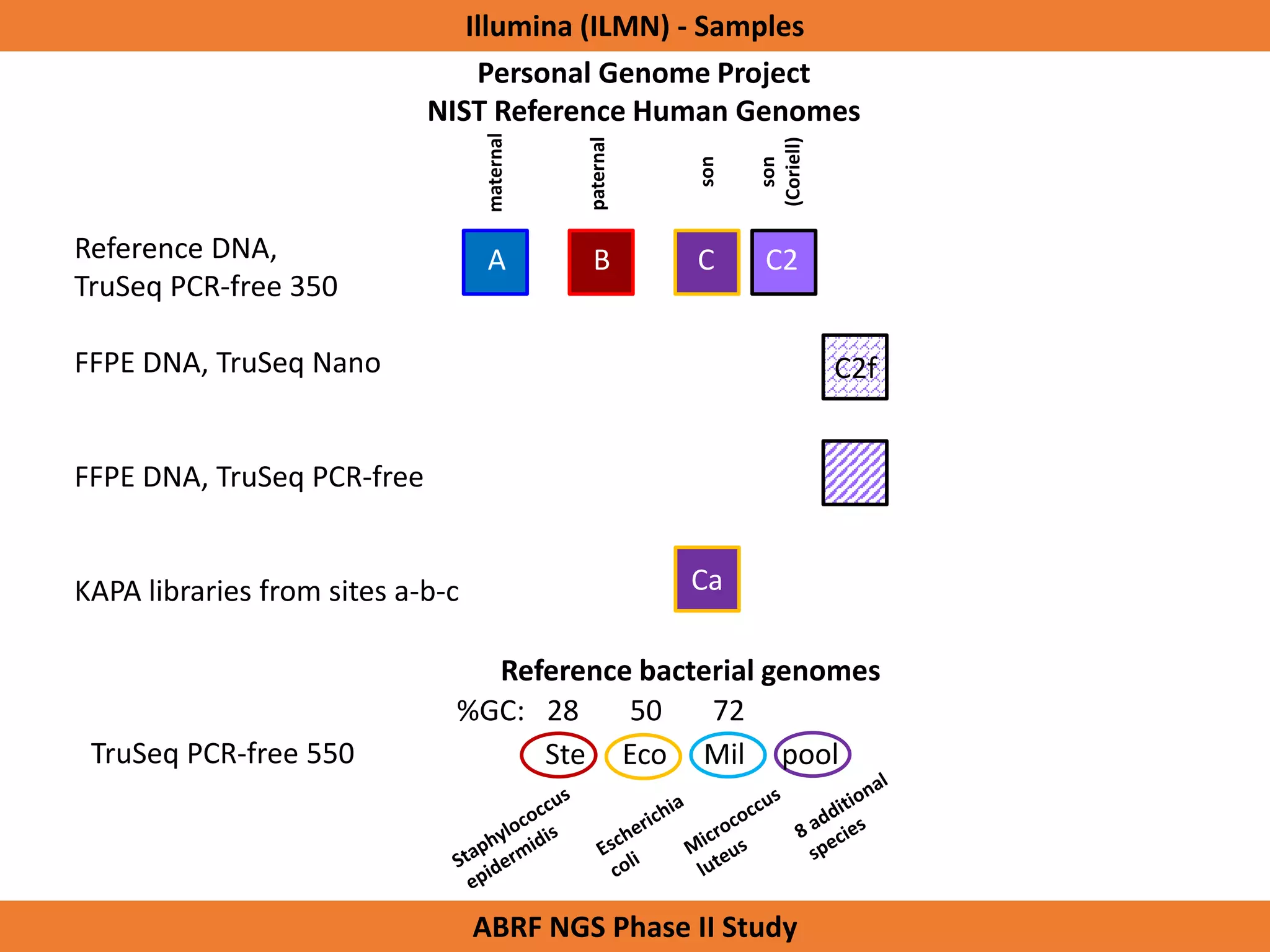
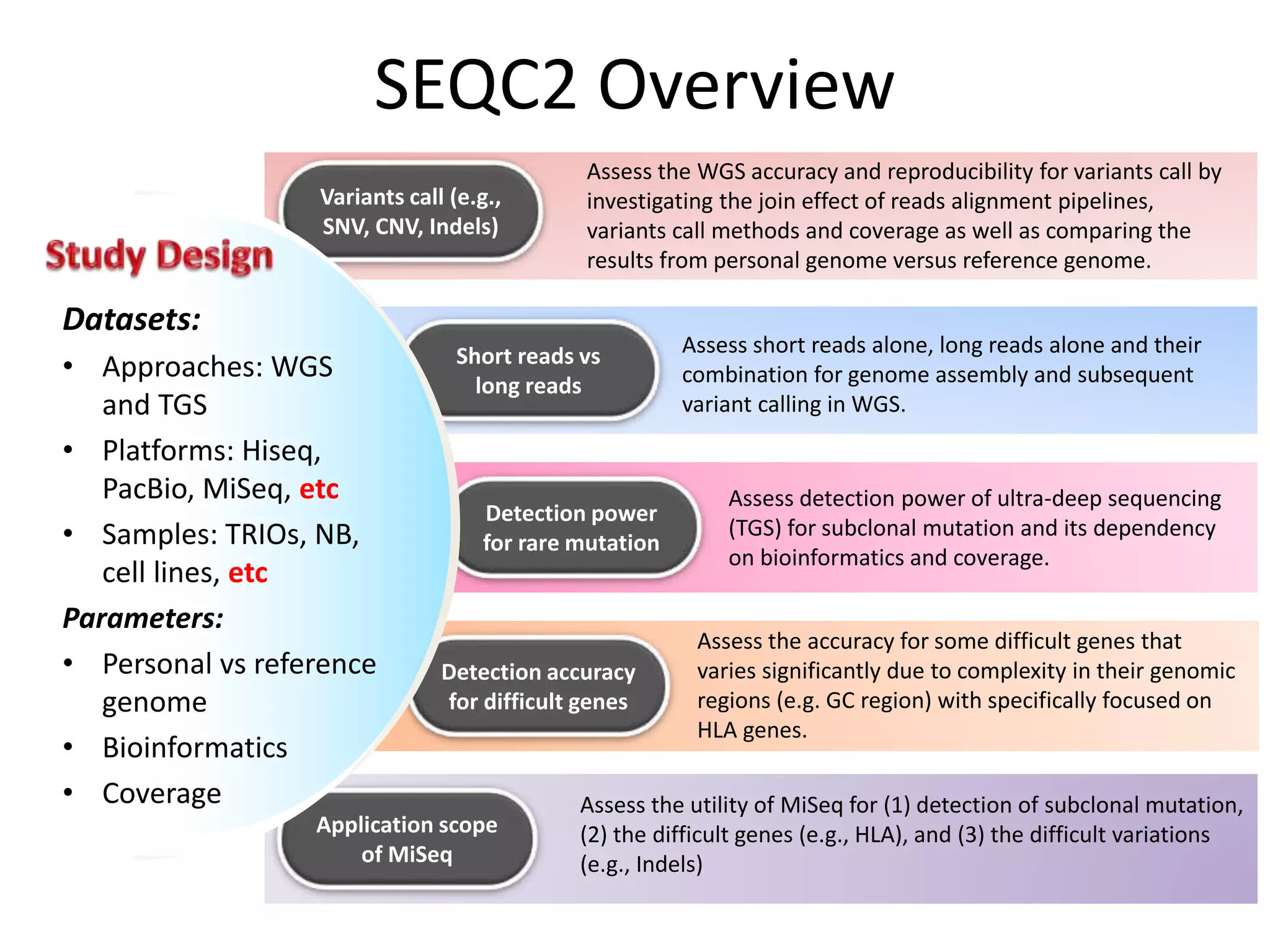
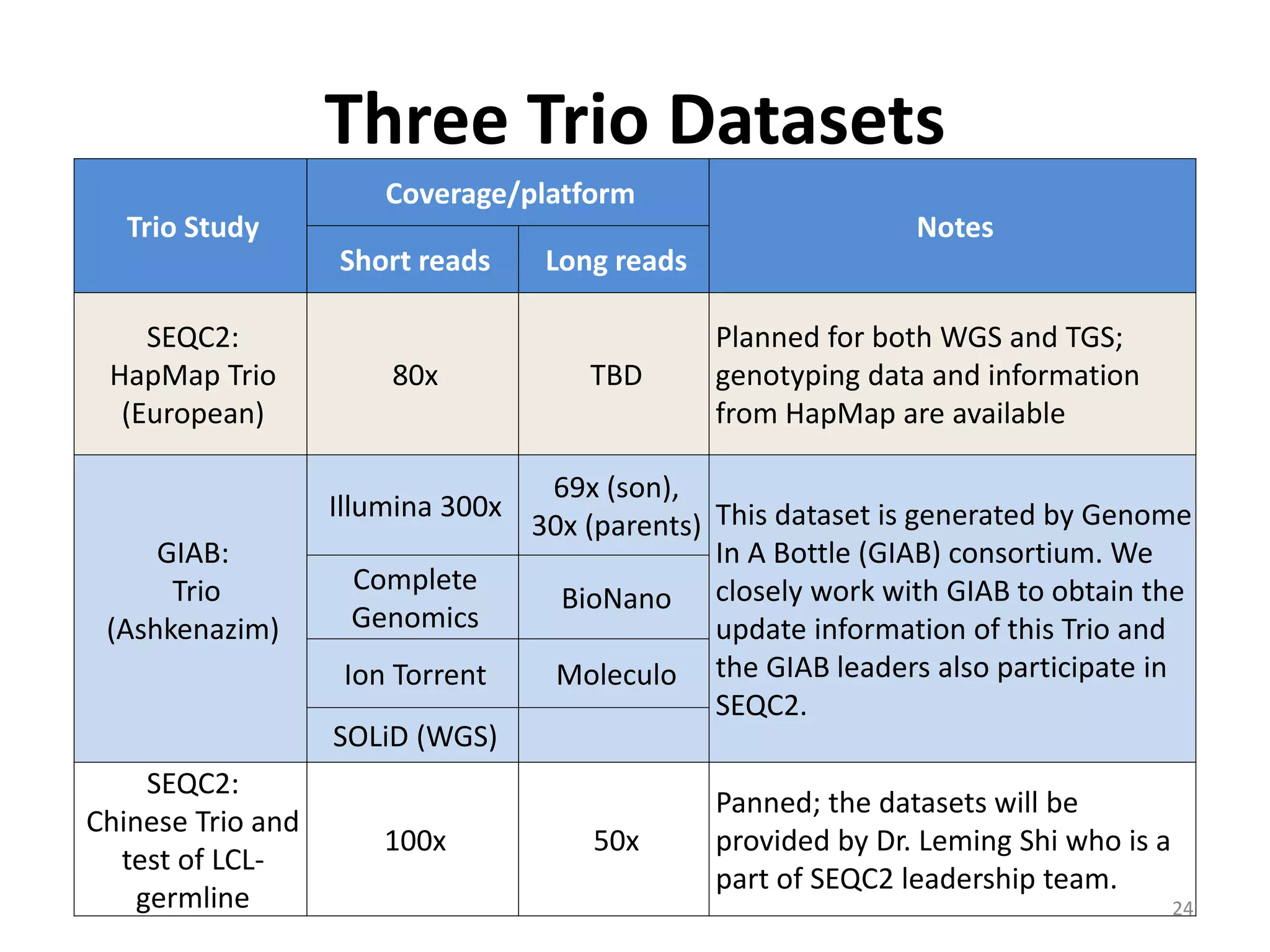
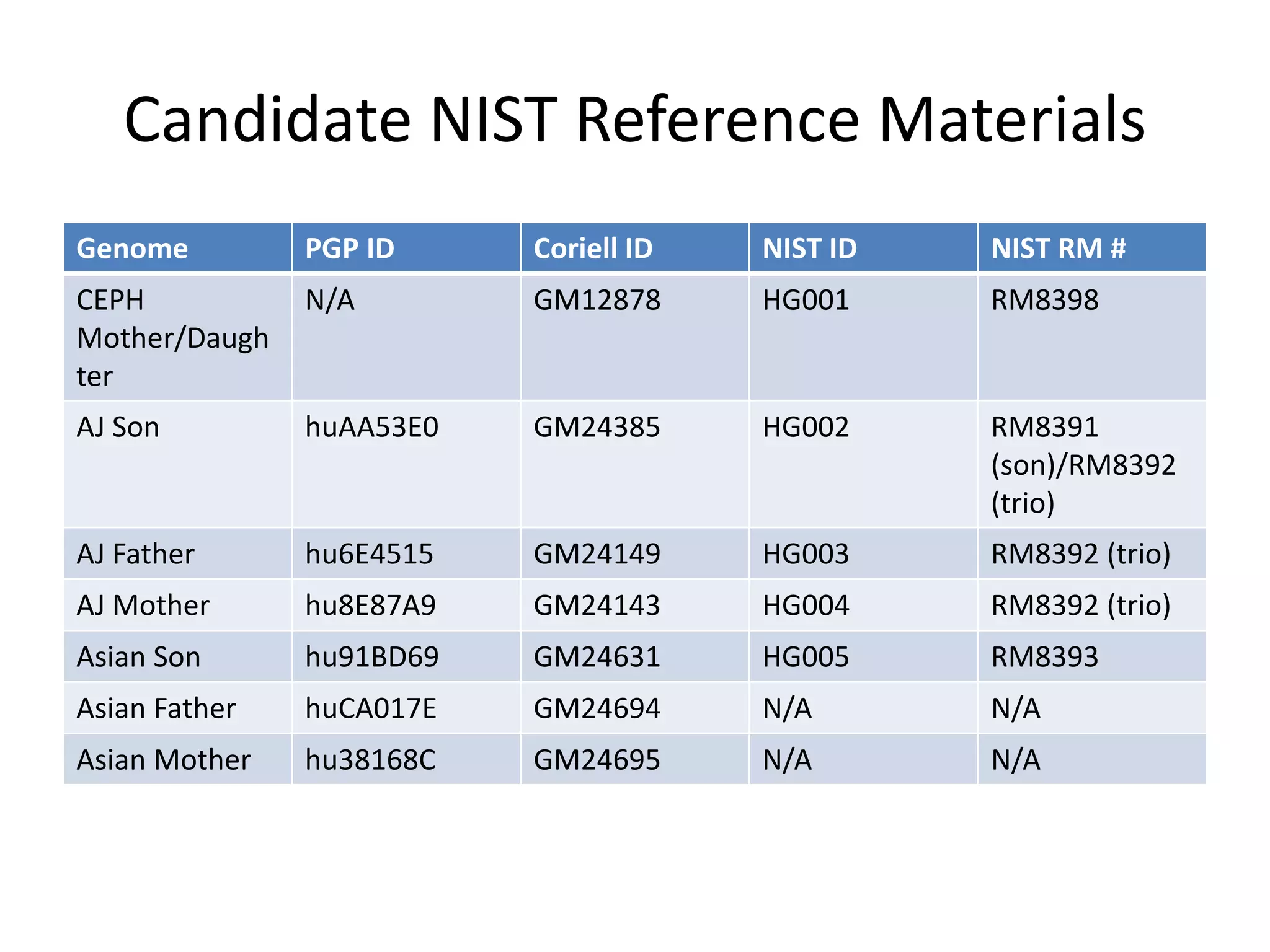
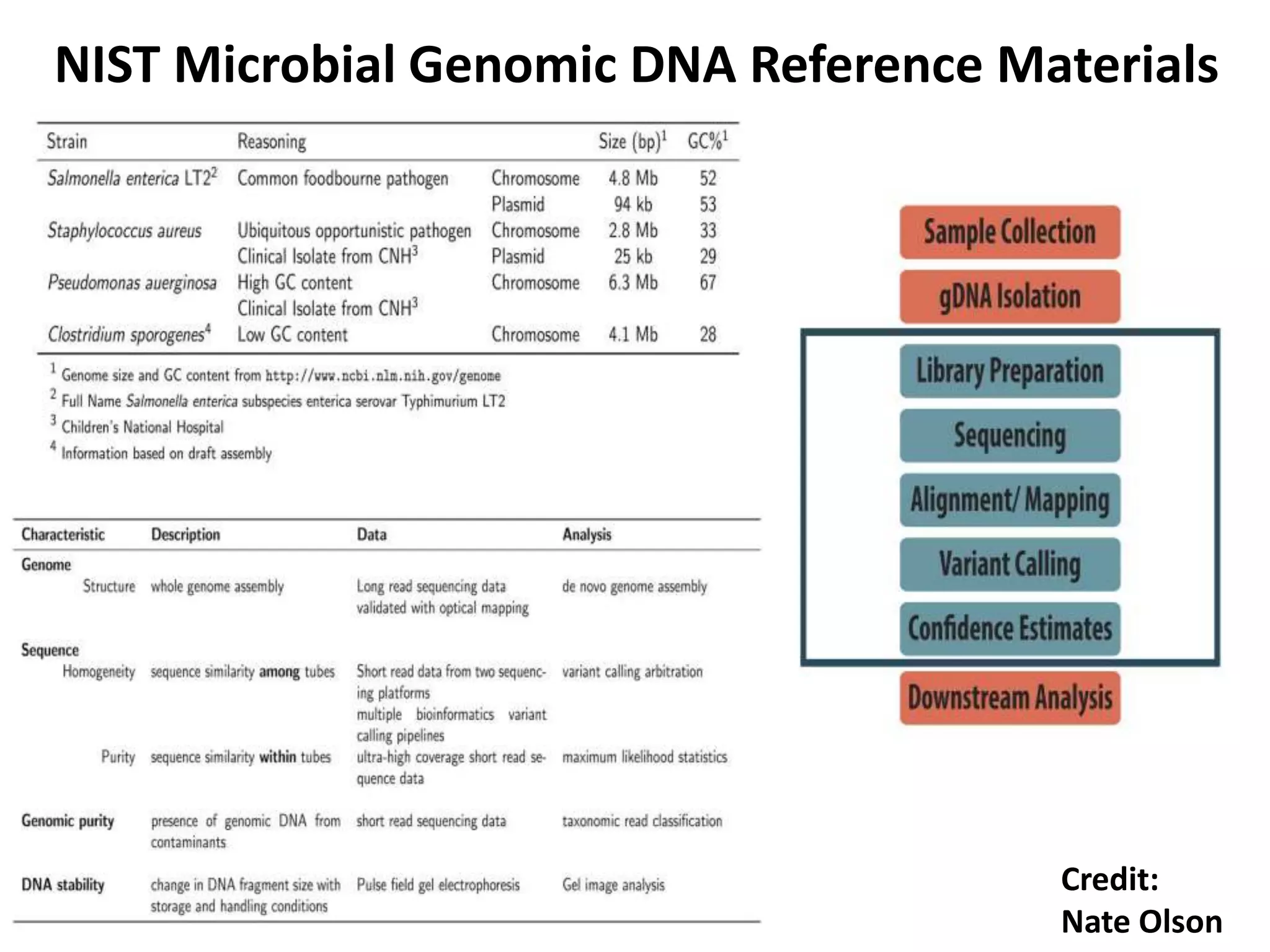
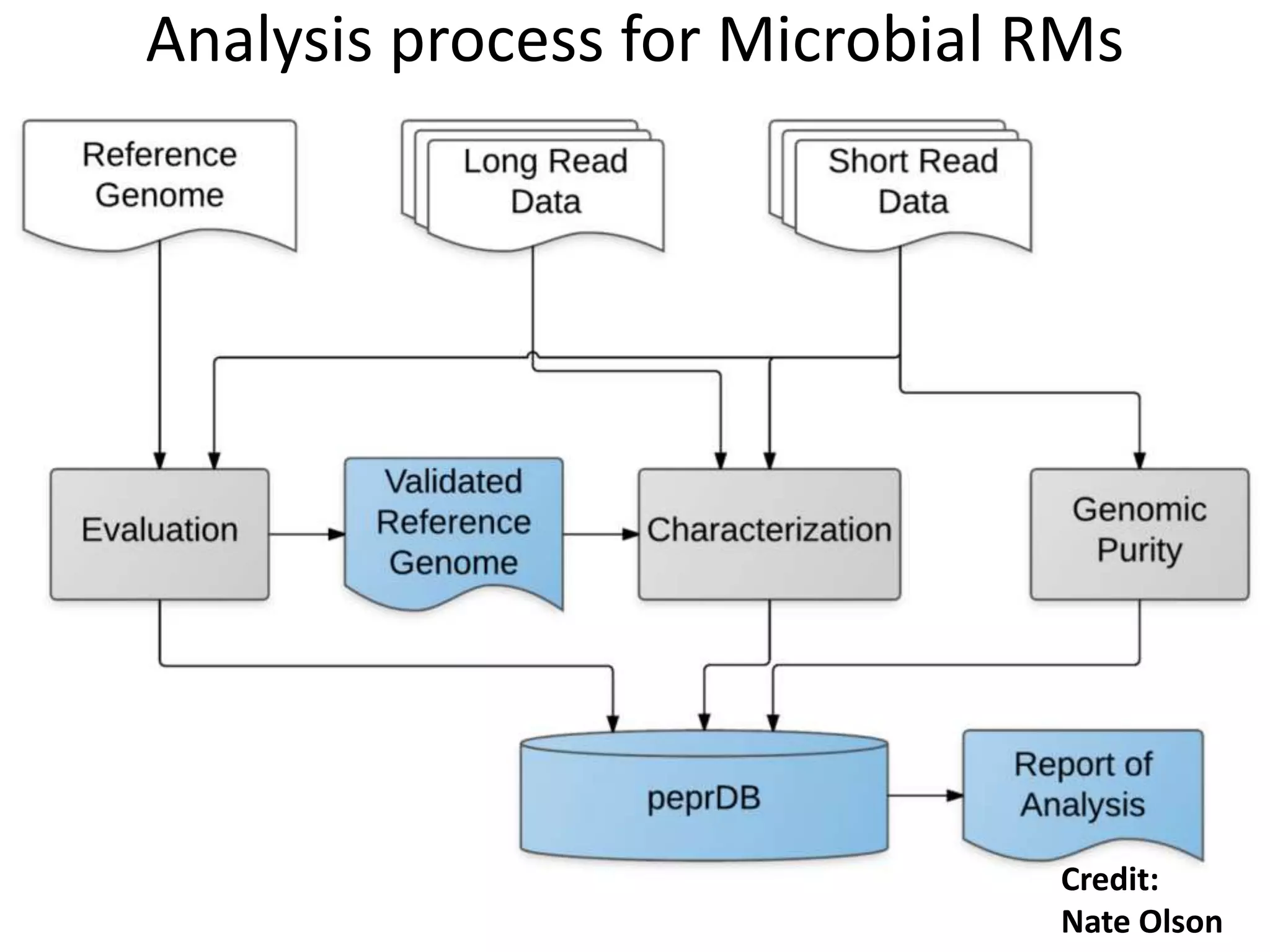
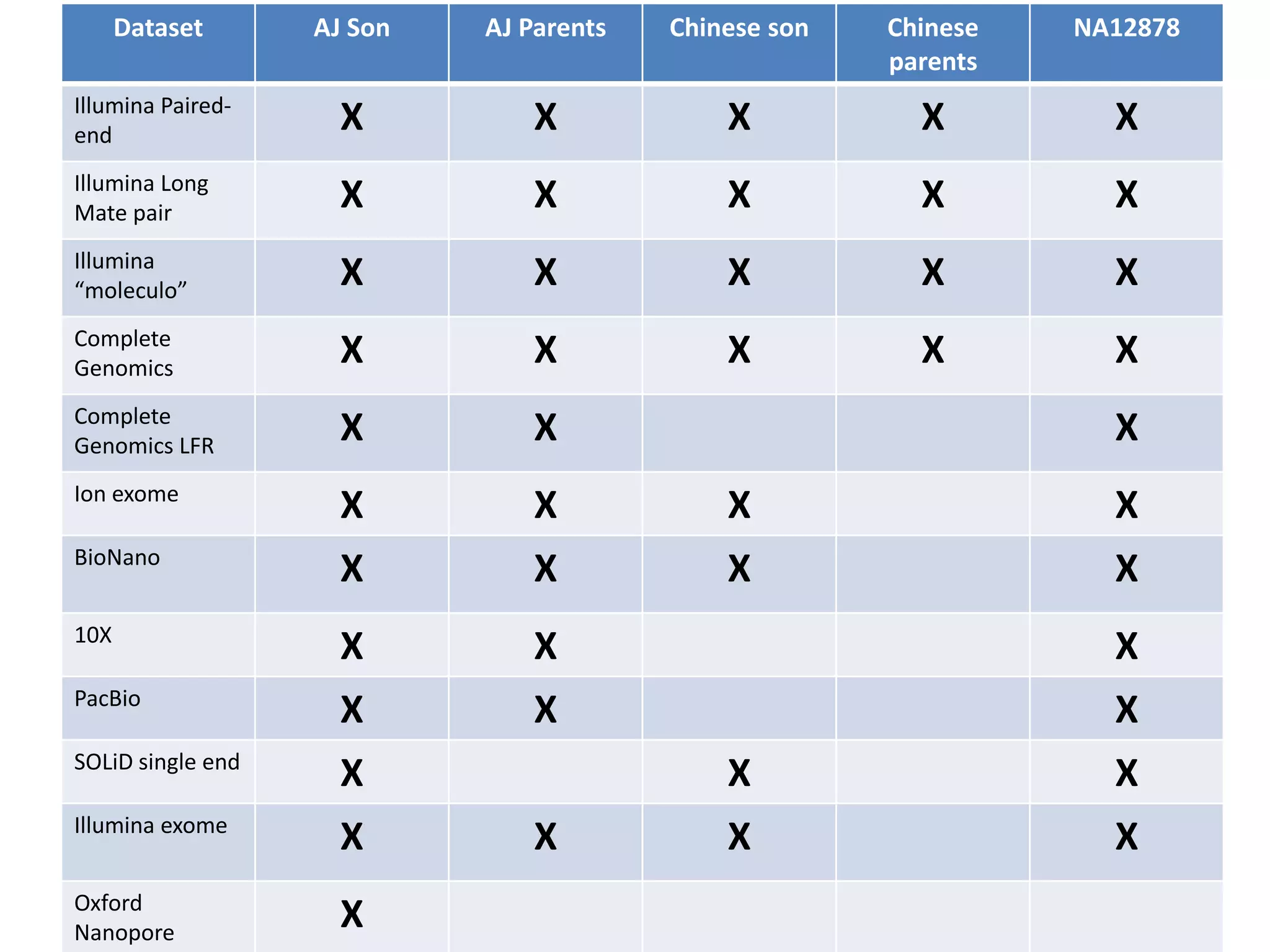
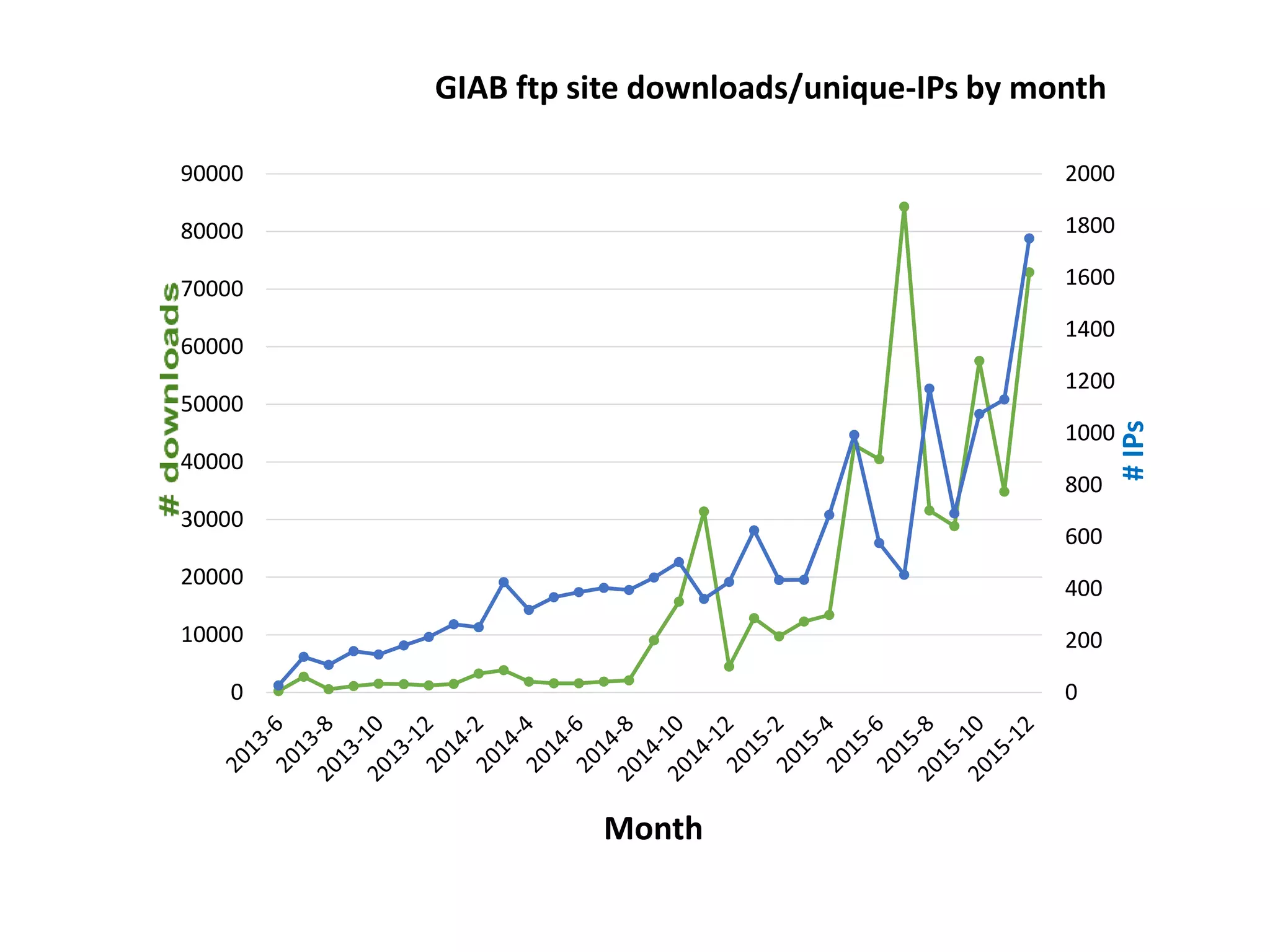
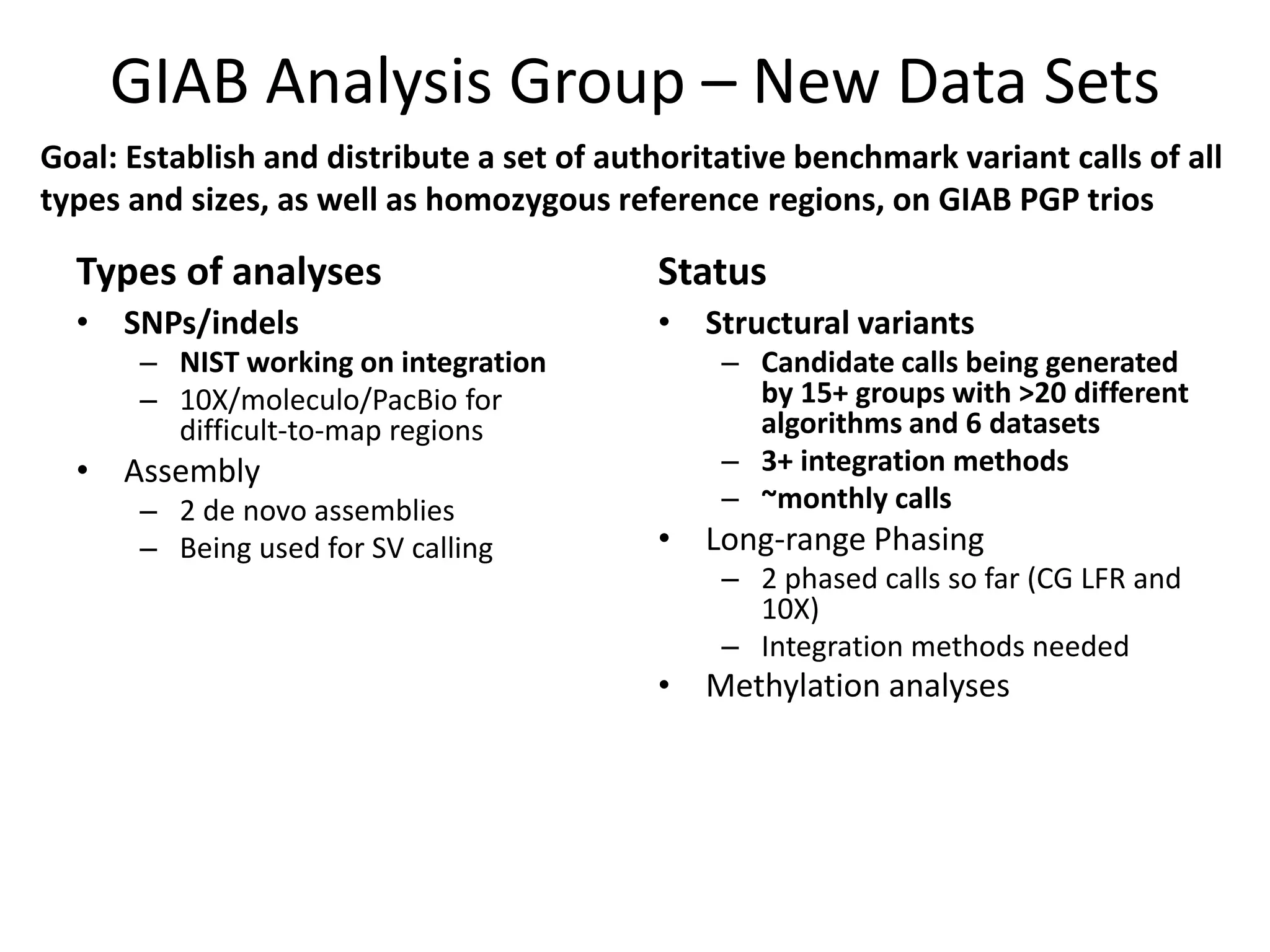
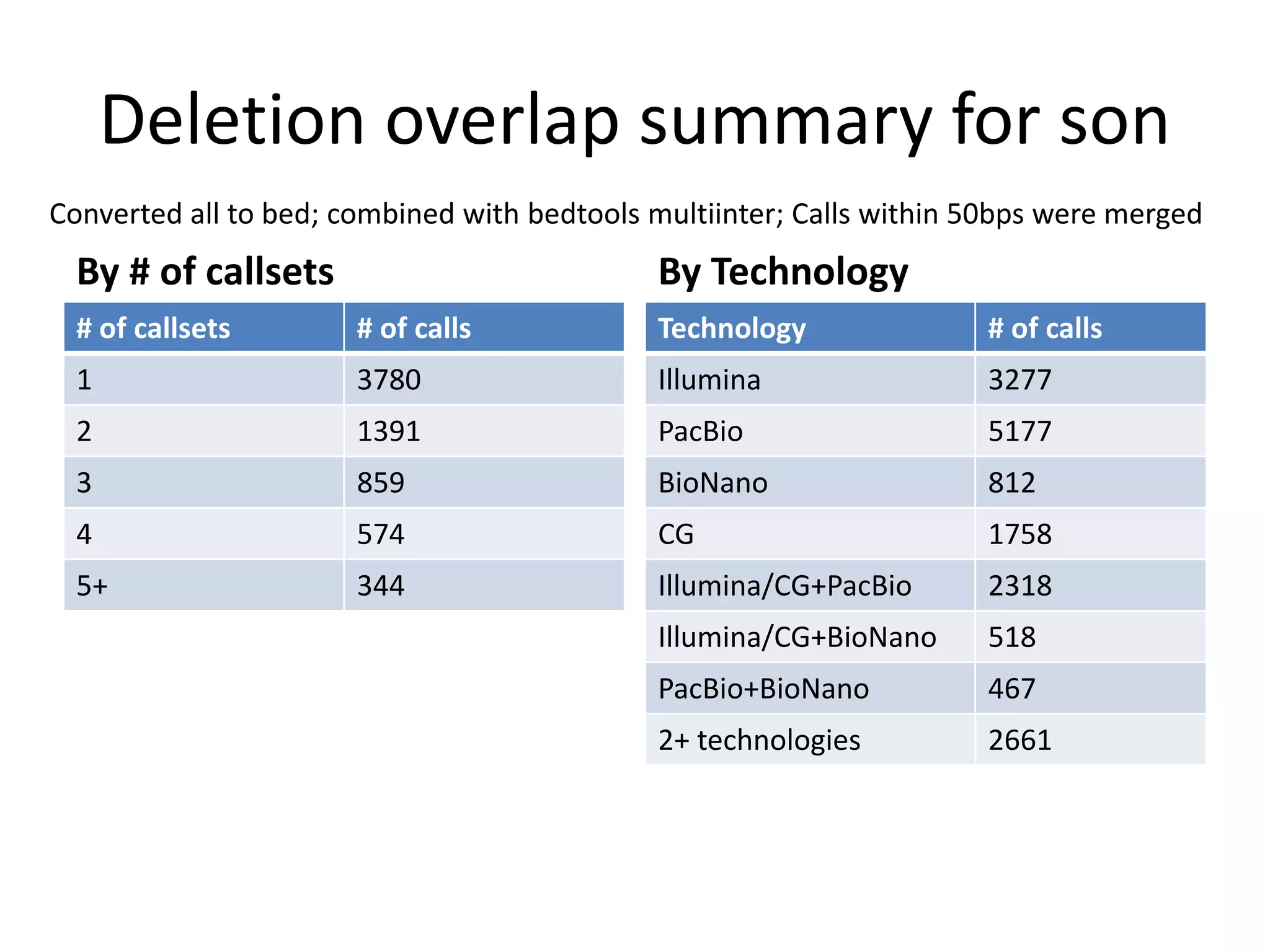
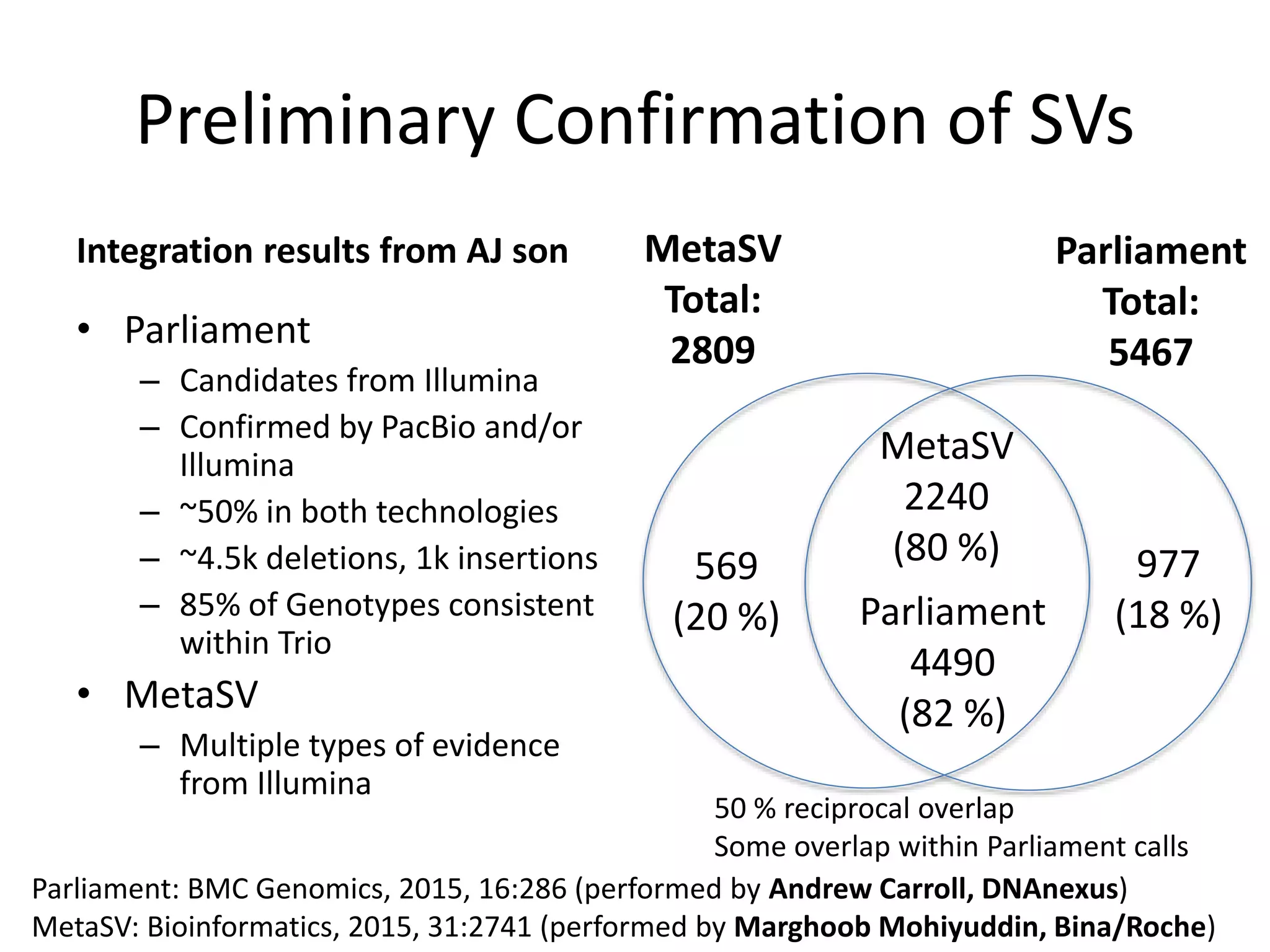
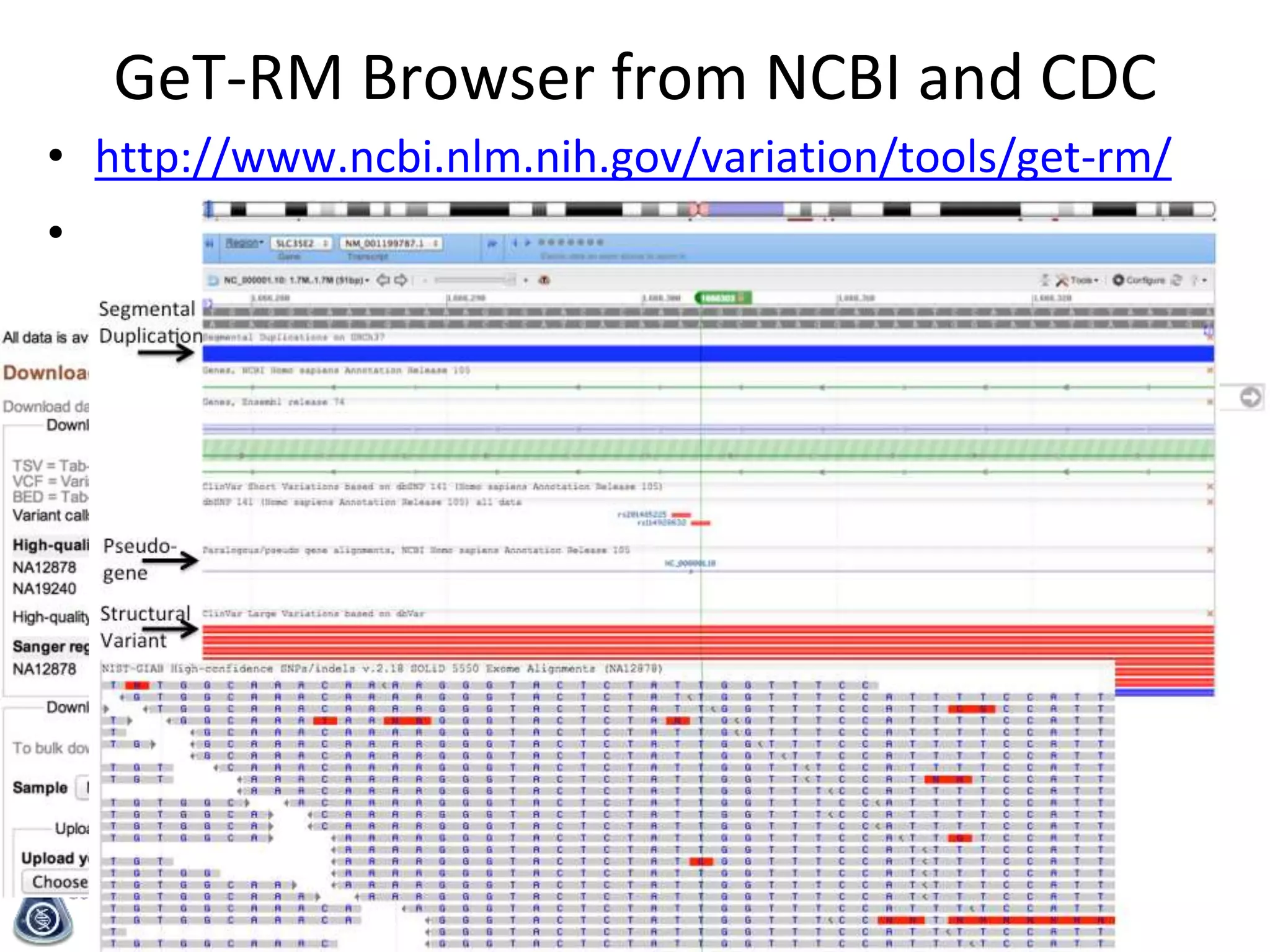
The Genome in a Bottle Consortium is developing reference materials, reference methods, and reference data to assess confidence in human whole genome variant calls. The Consortium is characterizing several human genomes including the NA12878 genome, an Ashkenazi Jewish trio, and a Chinese trio from the Personal Genome Project. Data generated for these genomes includes various sequencing technologies from Illumina, Complete Genomics, PacBio, BioNano, and others. The Consortium is developing high-confidence variant calls for SNPs, indels, structural variants, and phasing. Individual datasets and integrated variant calls will be made publicly available on the GIAB FTP site.