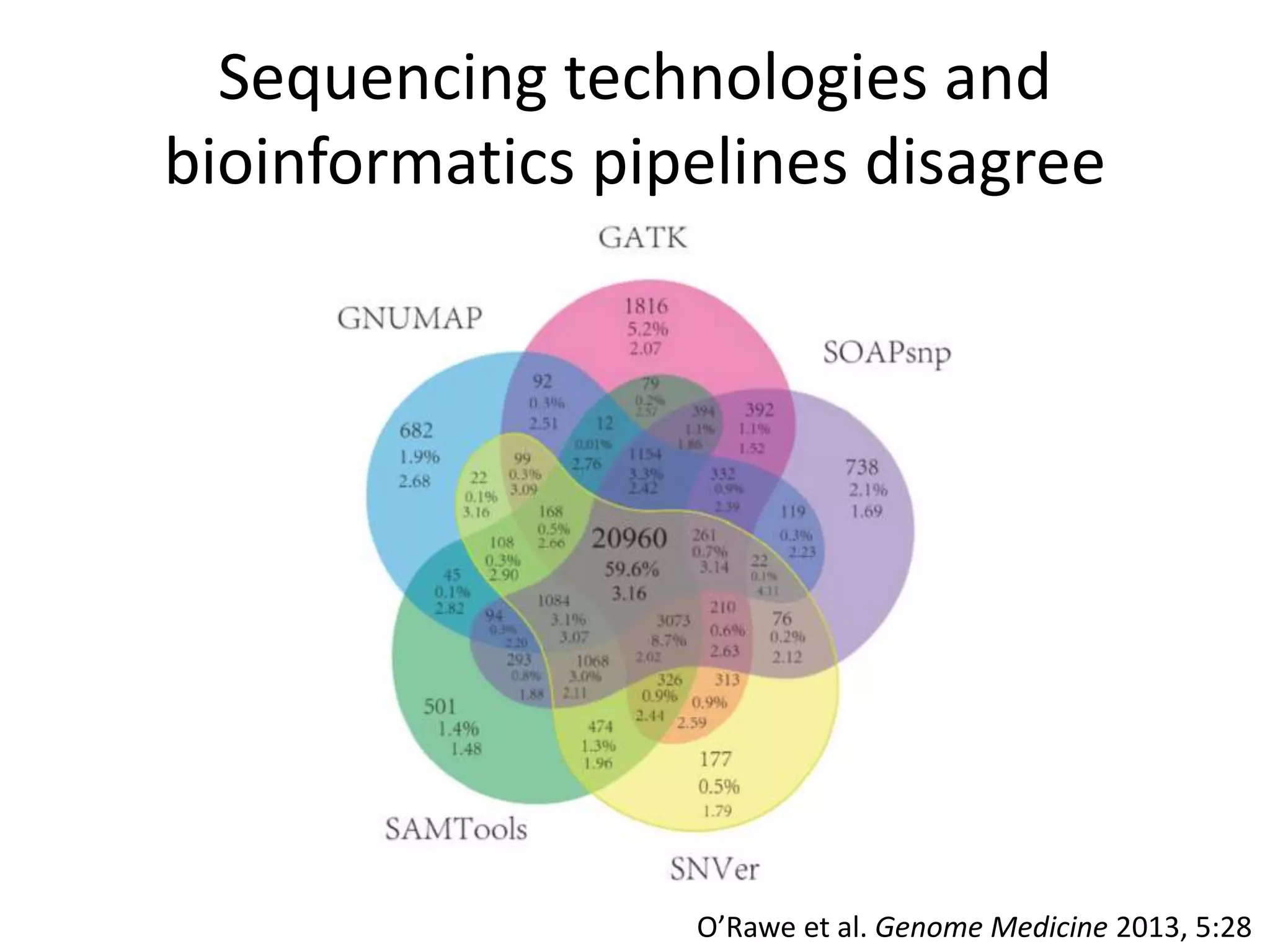
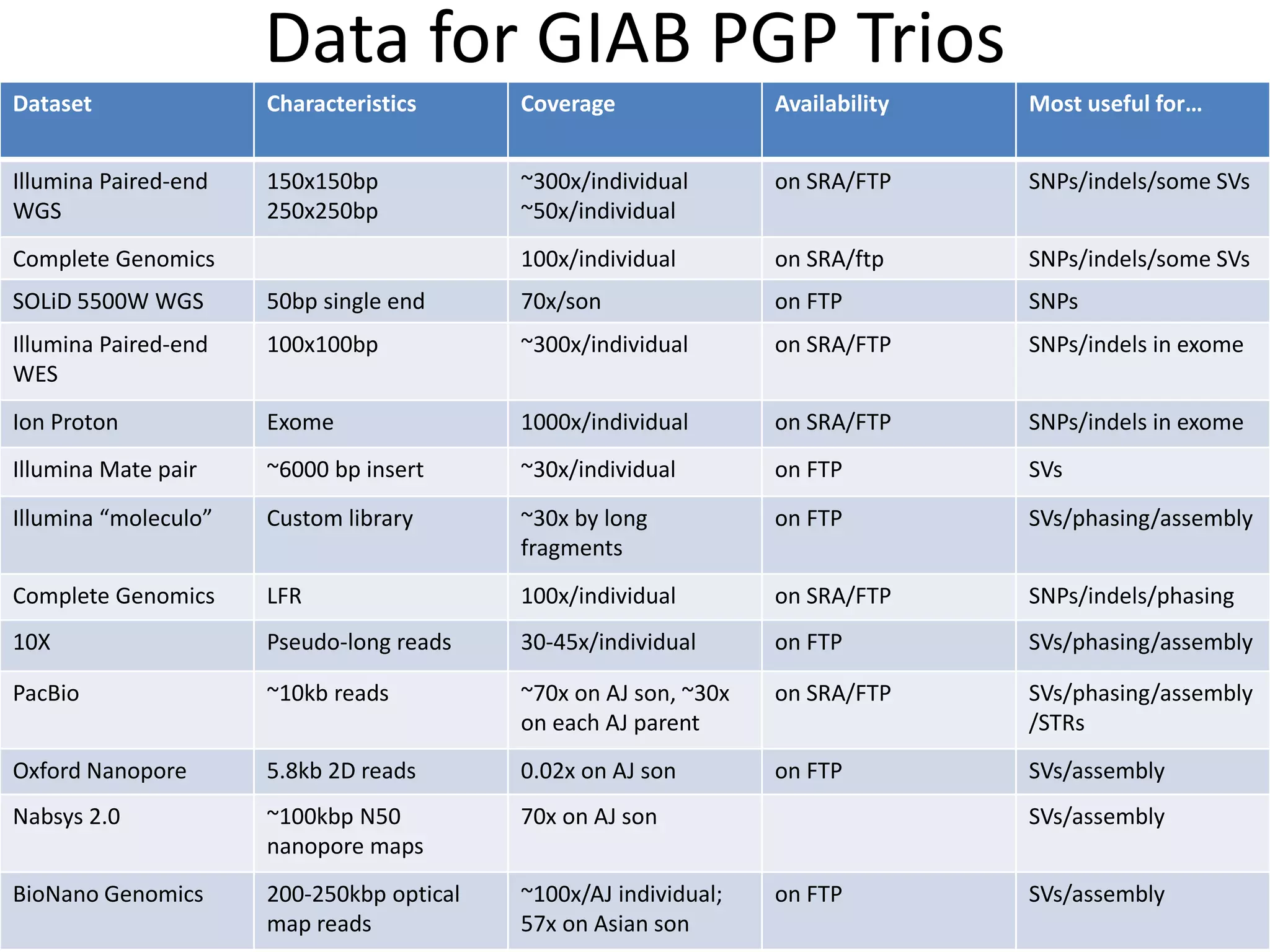
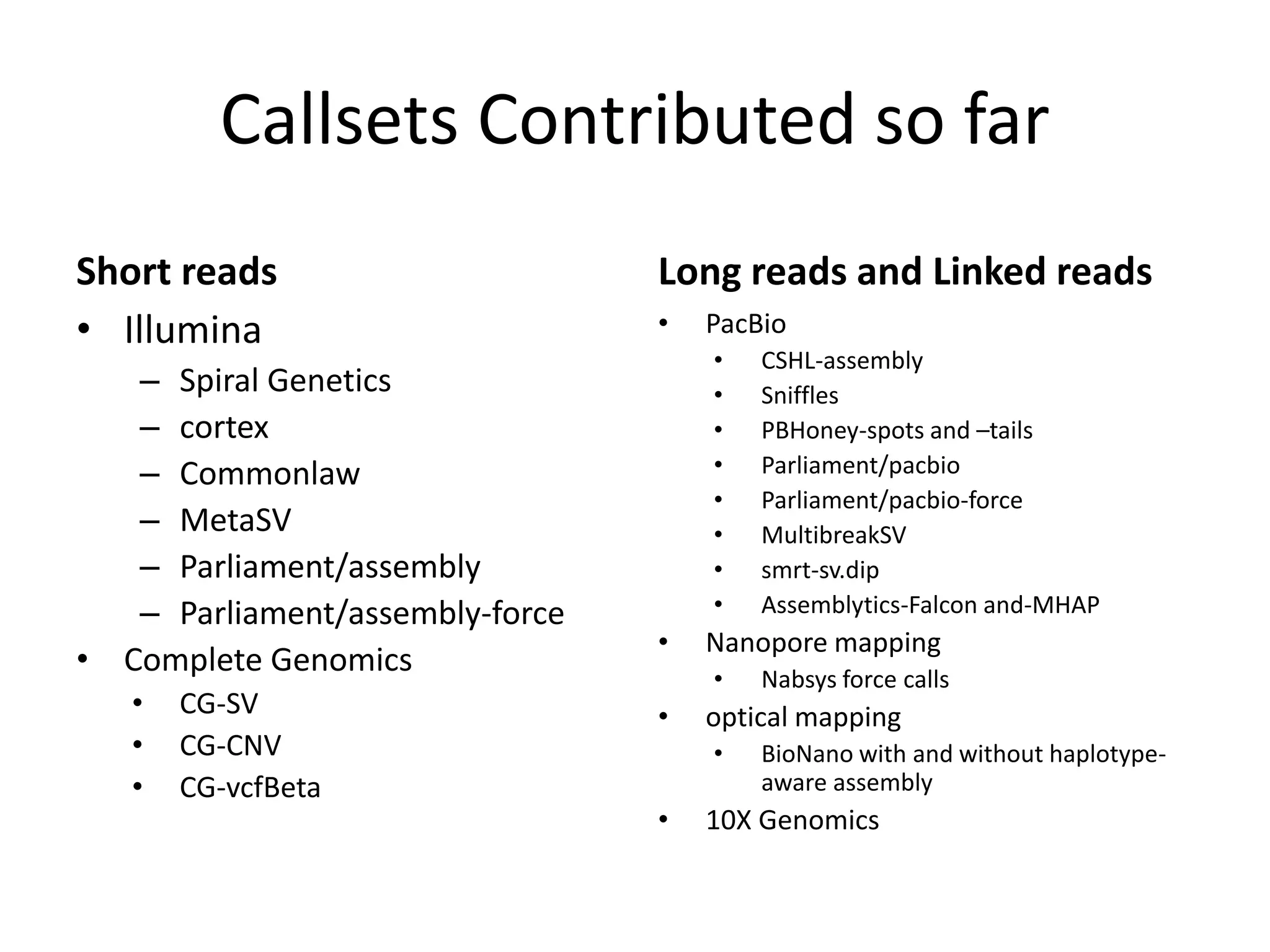
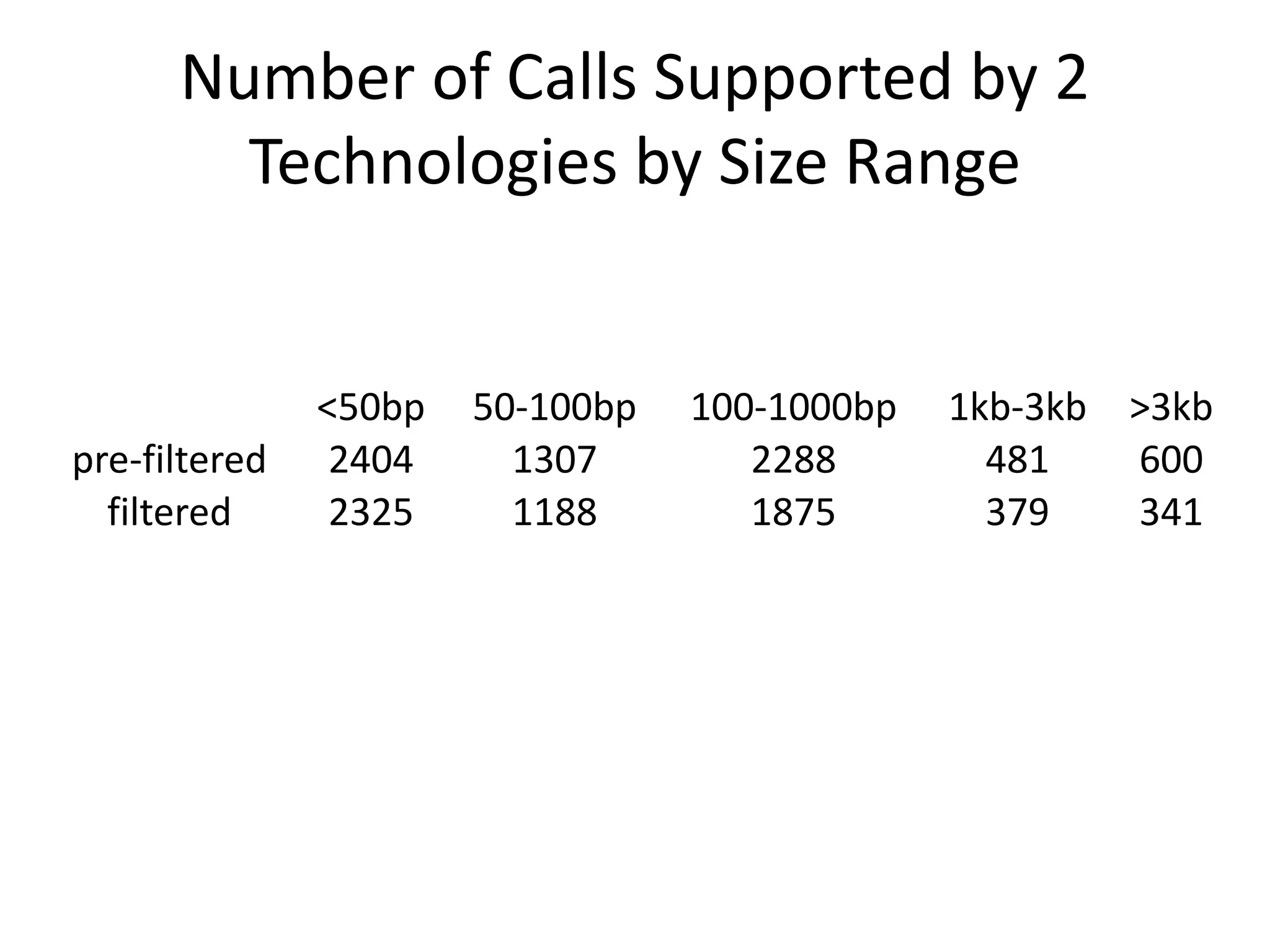
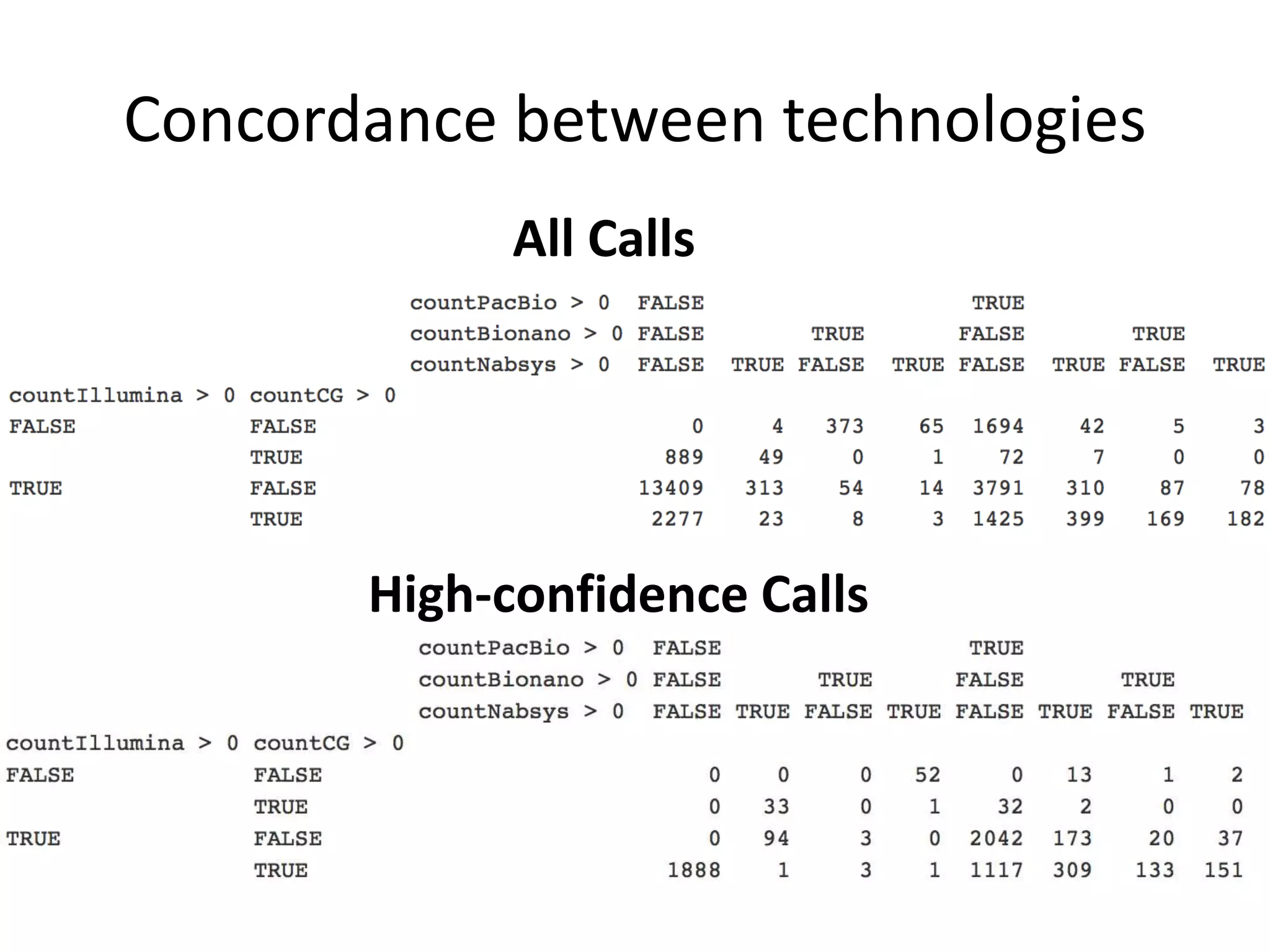
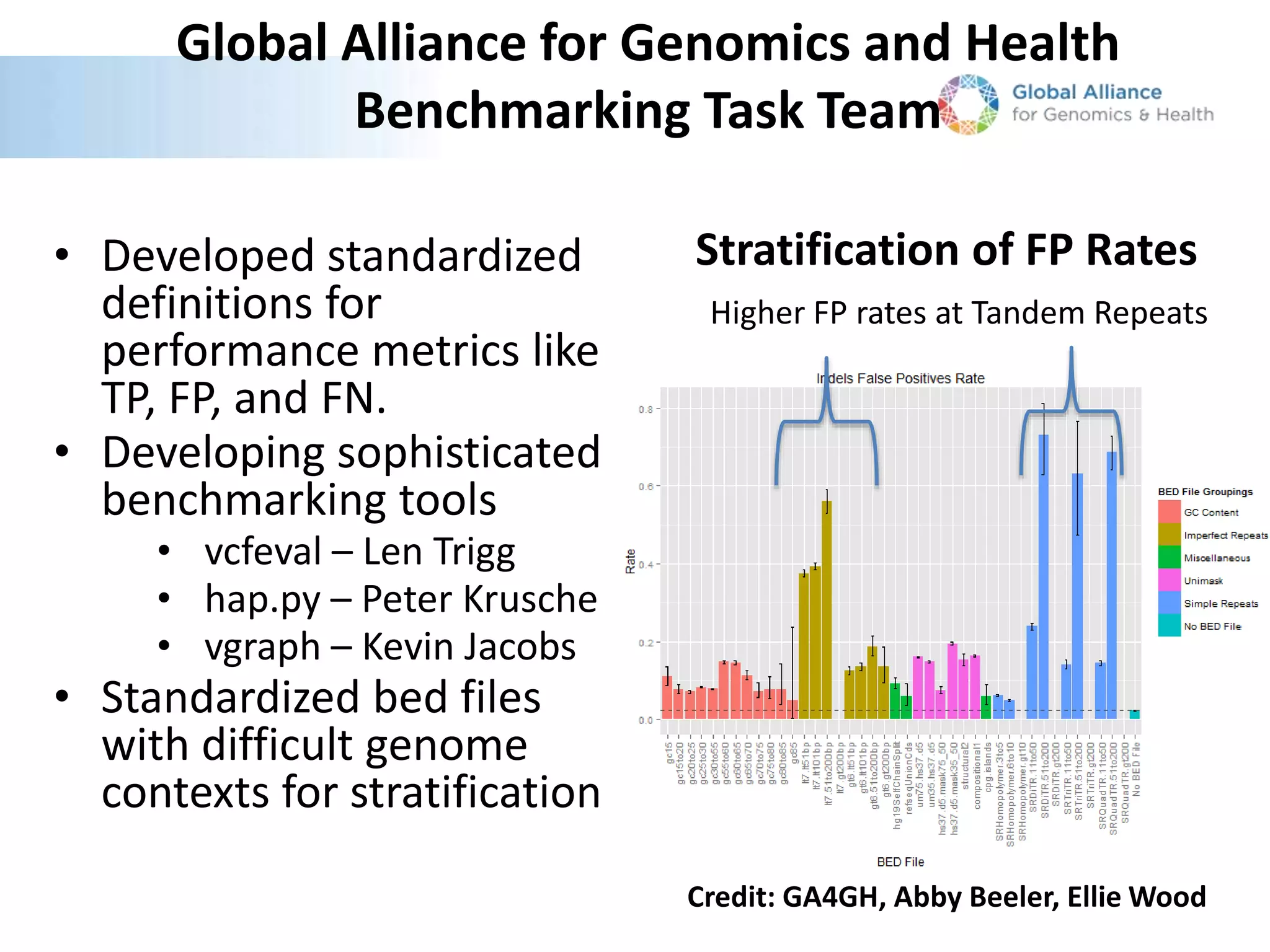
This document summarizes the process used to benchmark large deletion calls from multiple sequencing technologies and bioinformatics pipelines. Researchers merged deletion calls from 14 datasets into regions and evaluated call size accuracy. Calls supported by two or more technologies were identified as draft benchmark calls. Sensitivity to these calls was calculated for each method. The results provide insight into strengths and weaknesses of different approaches to structural variant detection.