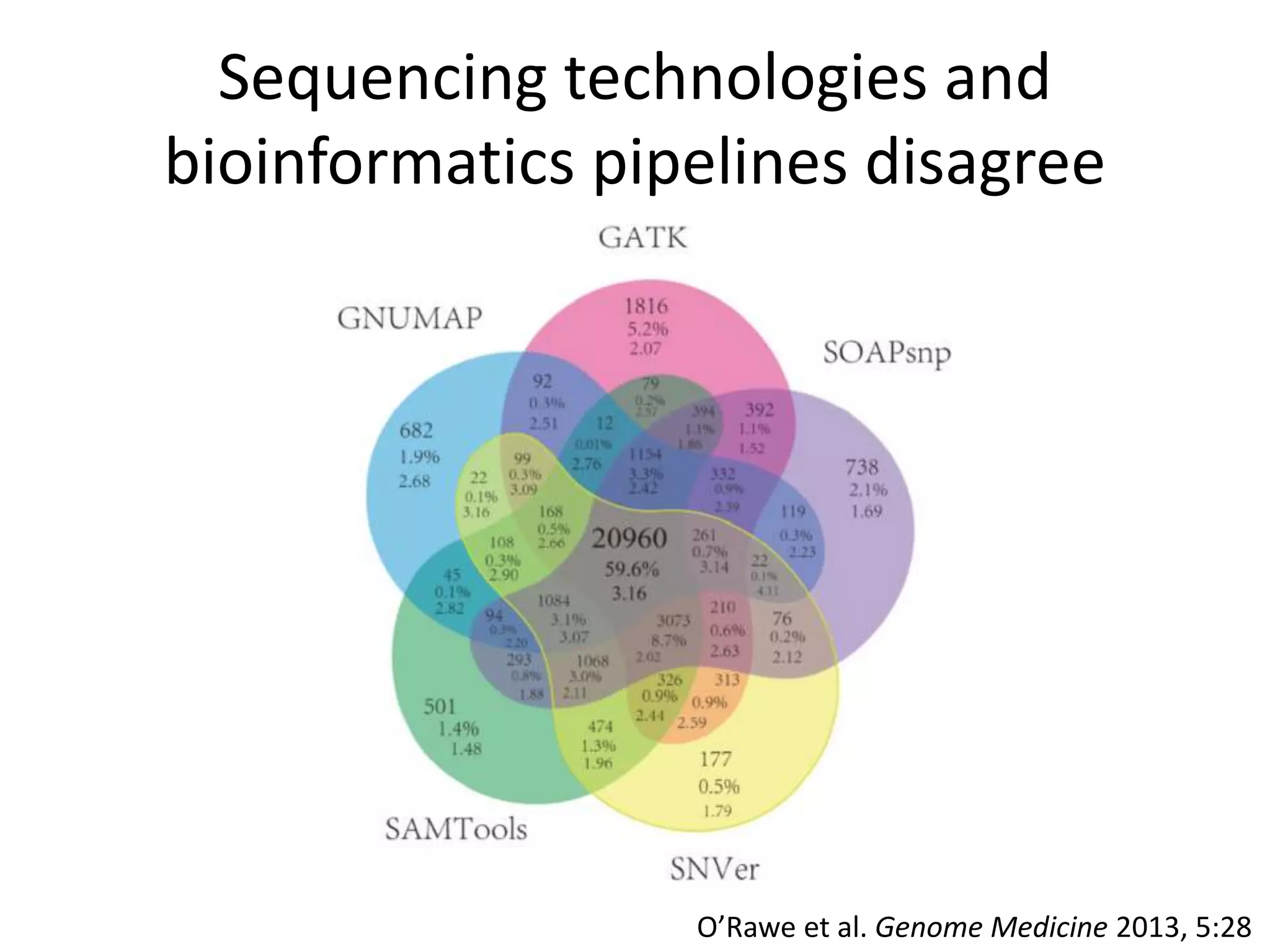
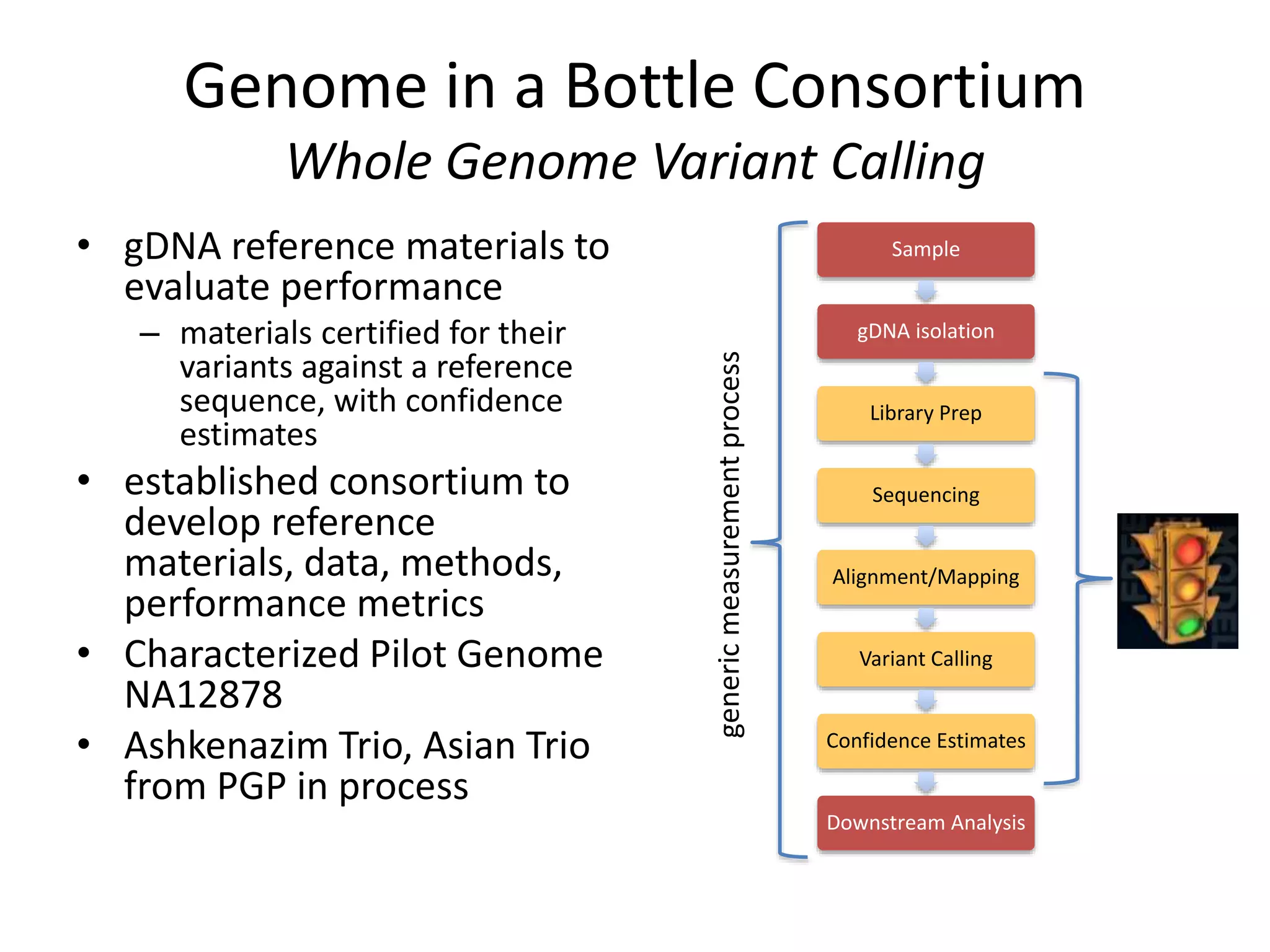
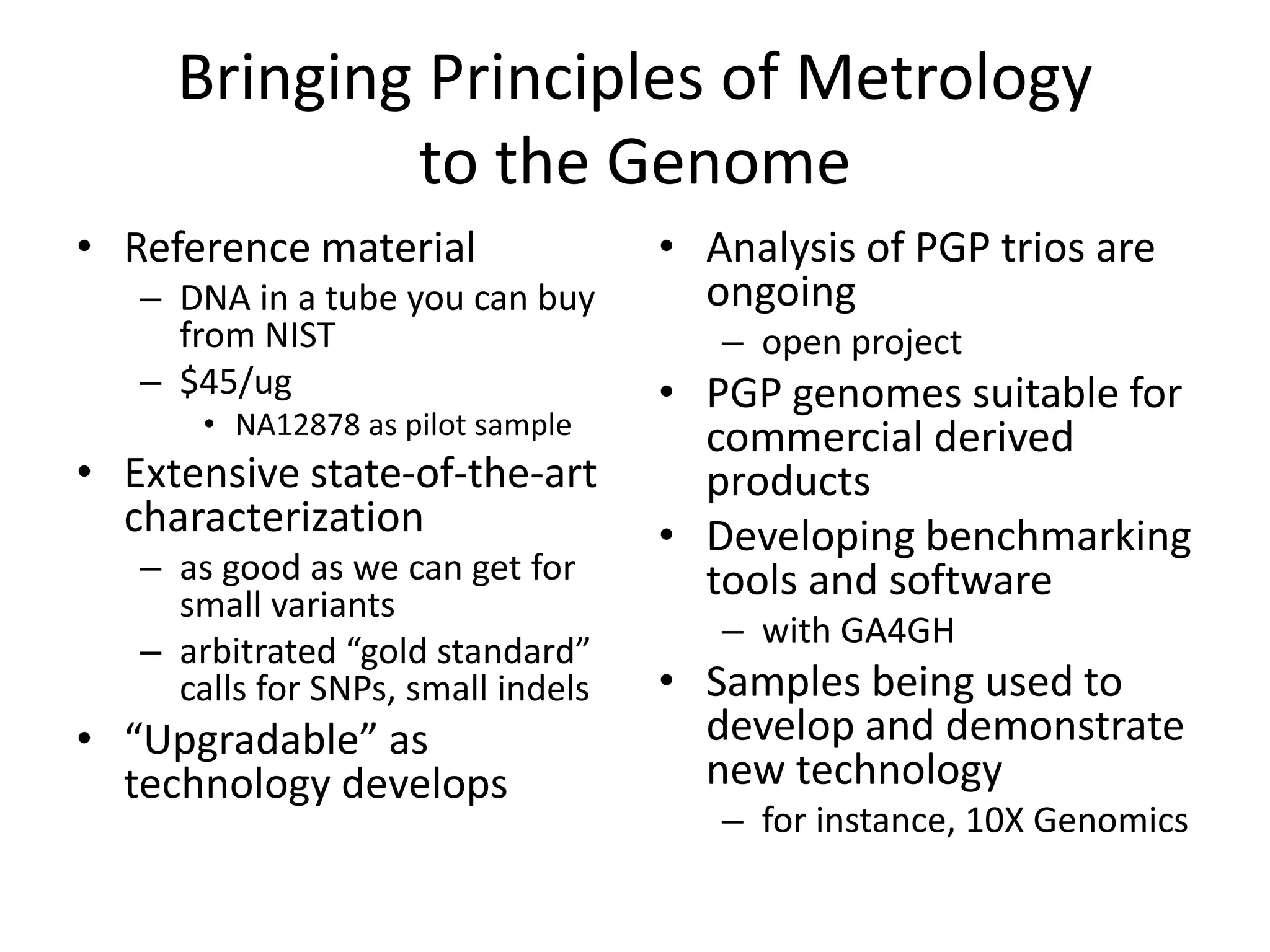
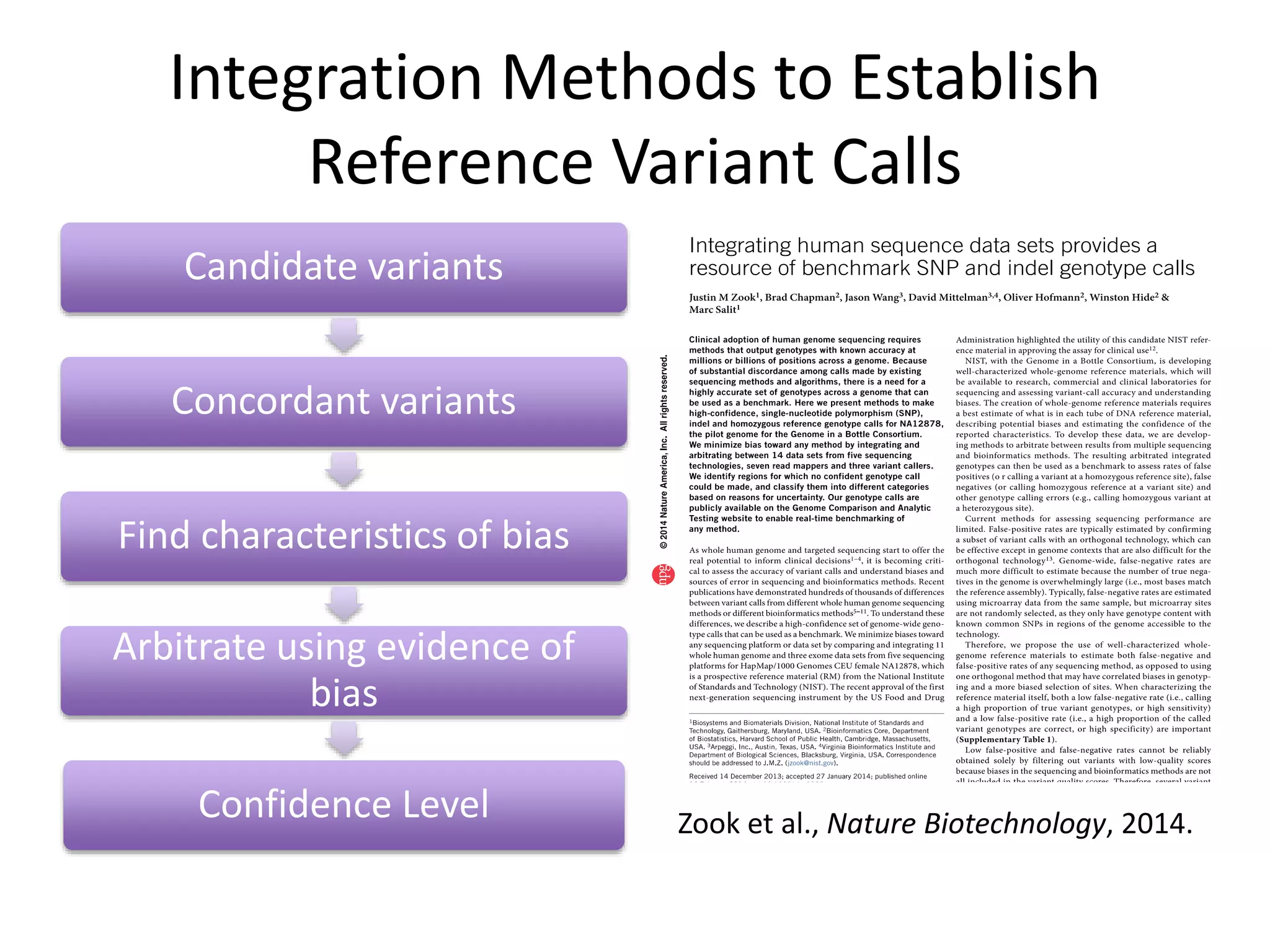
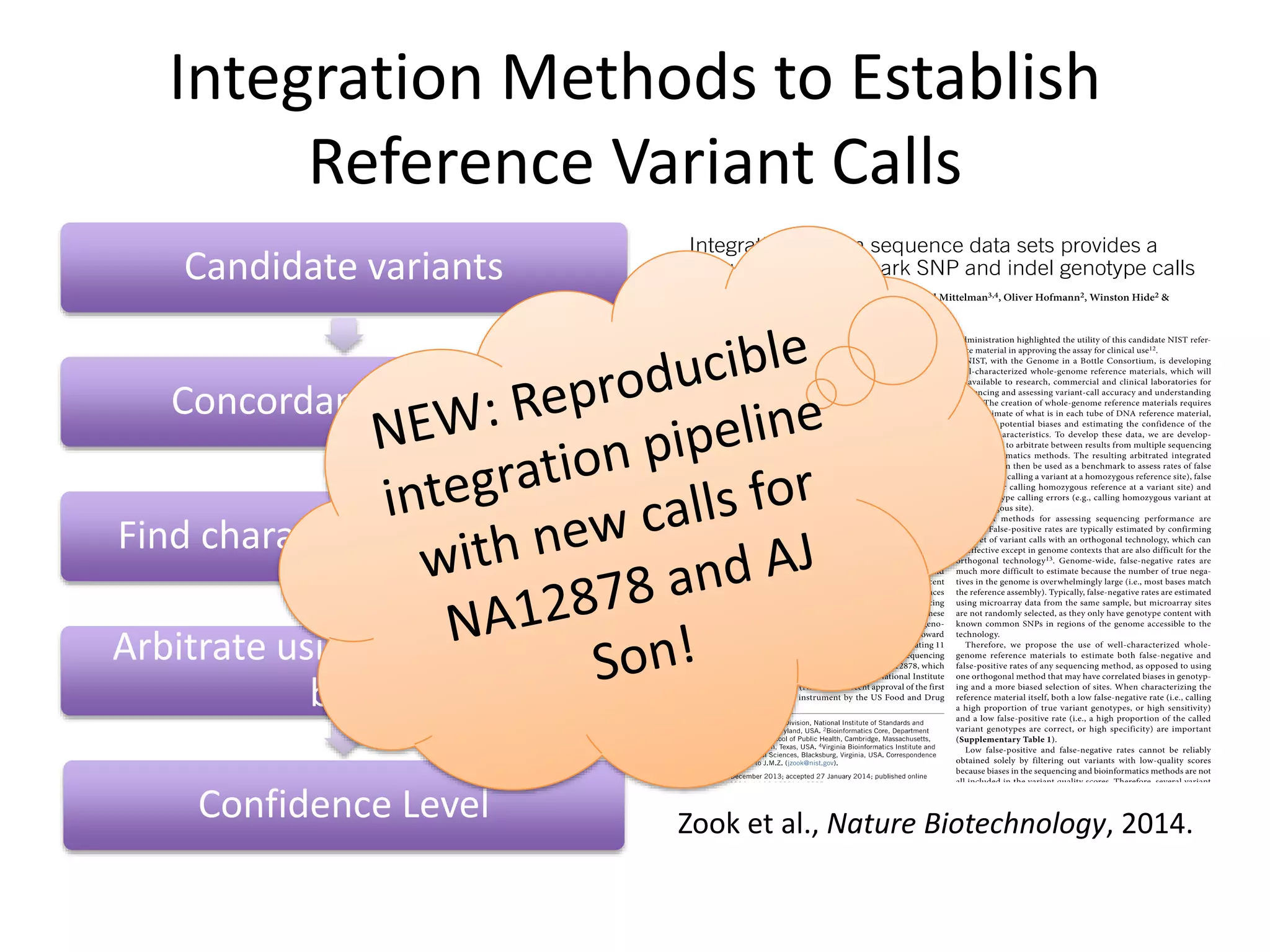
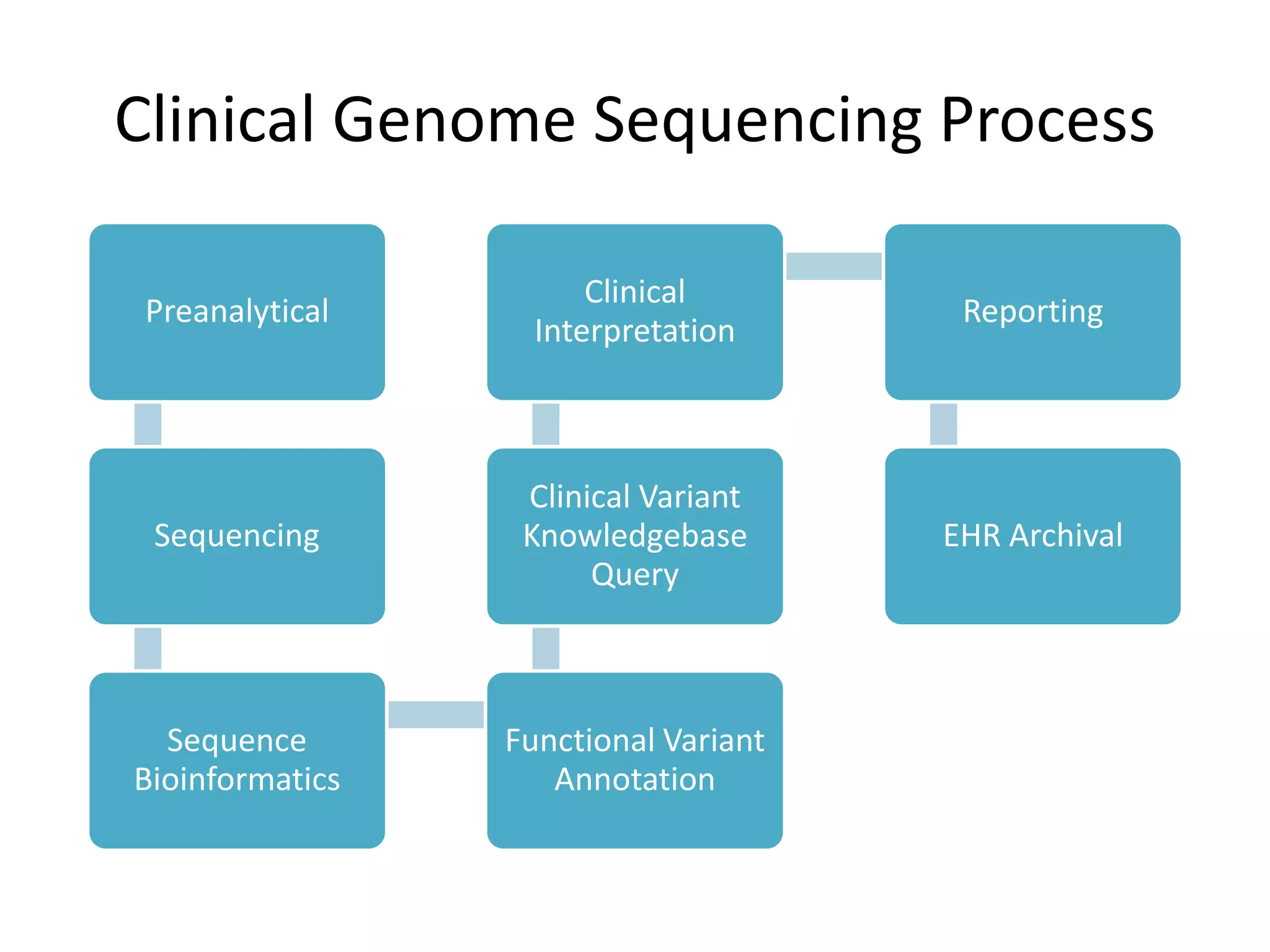
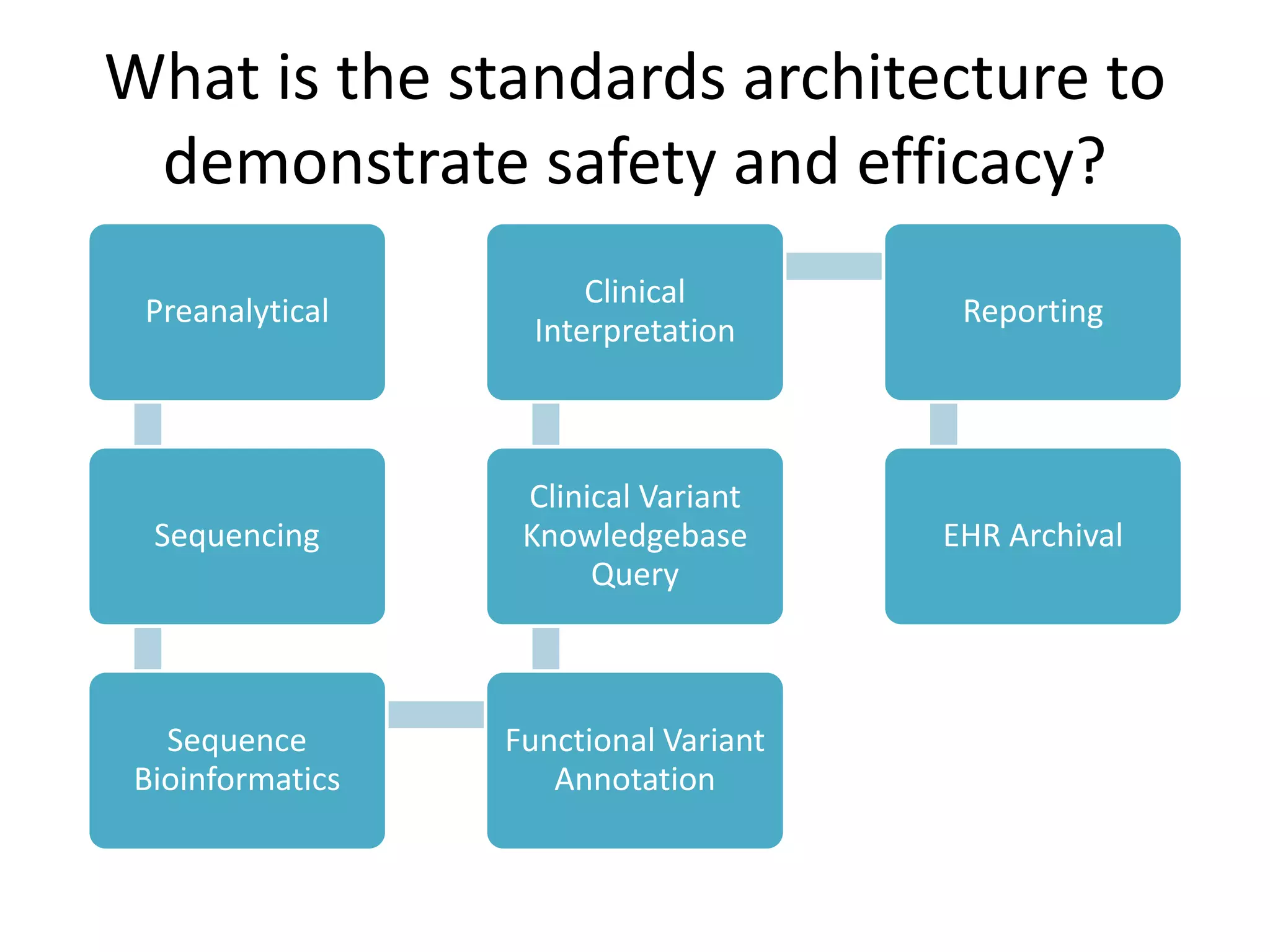
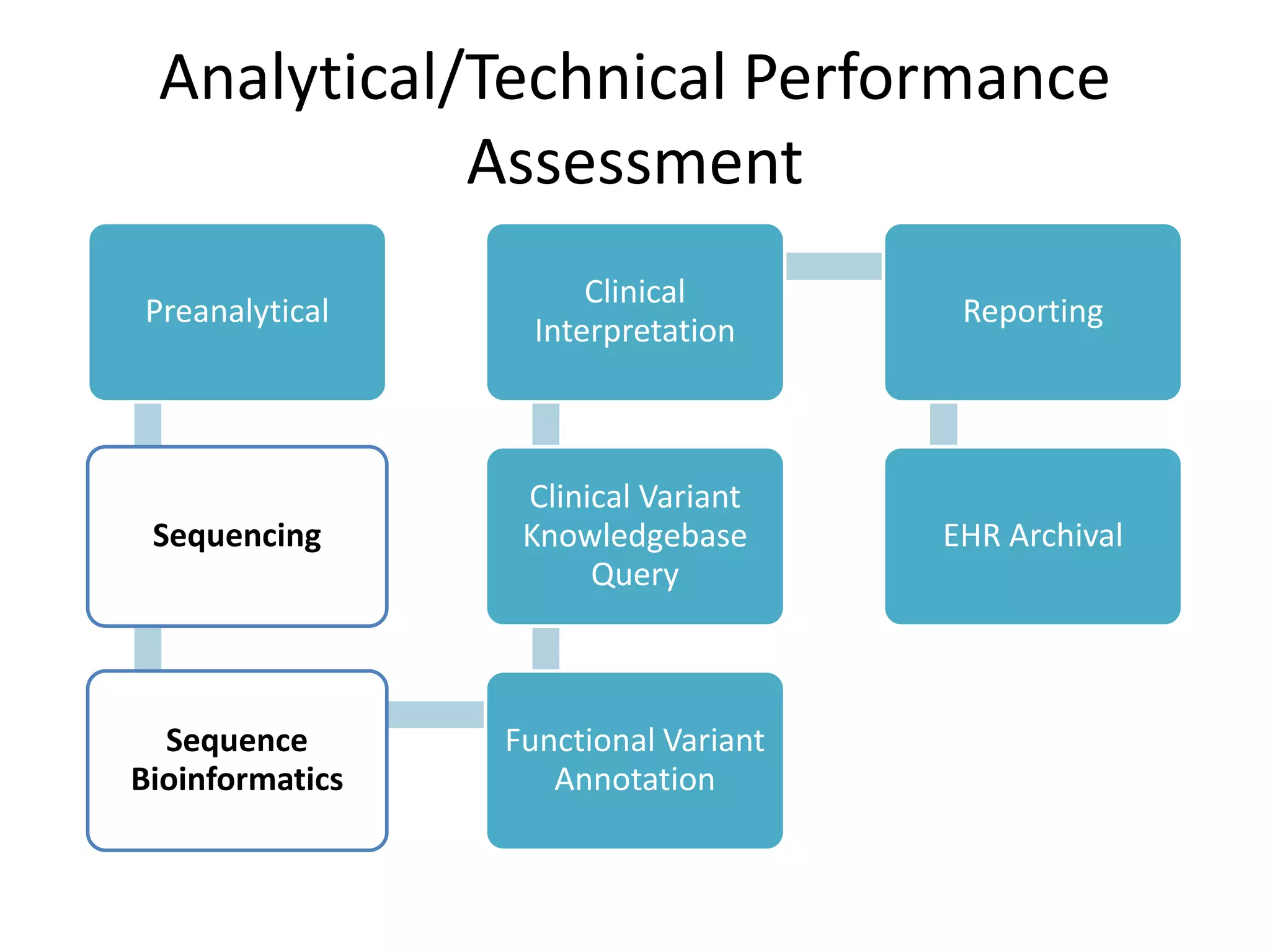
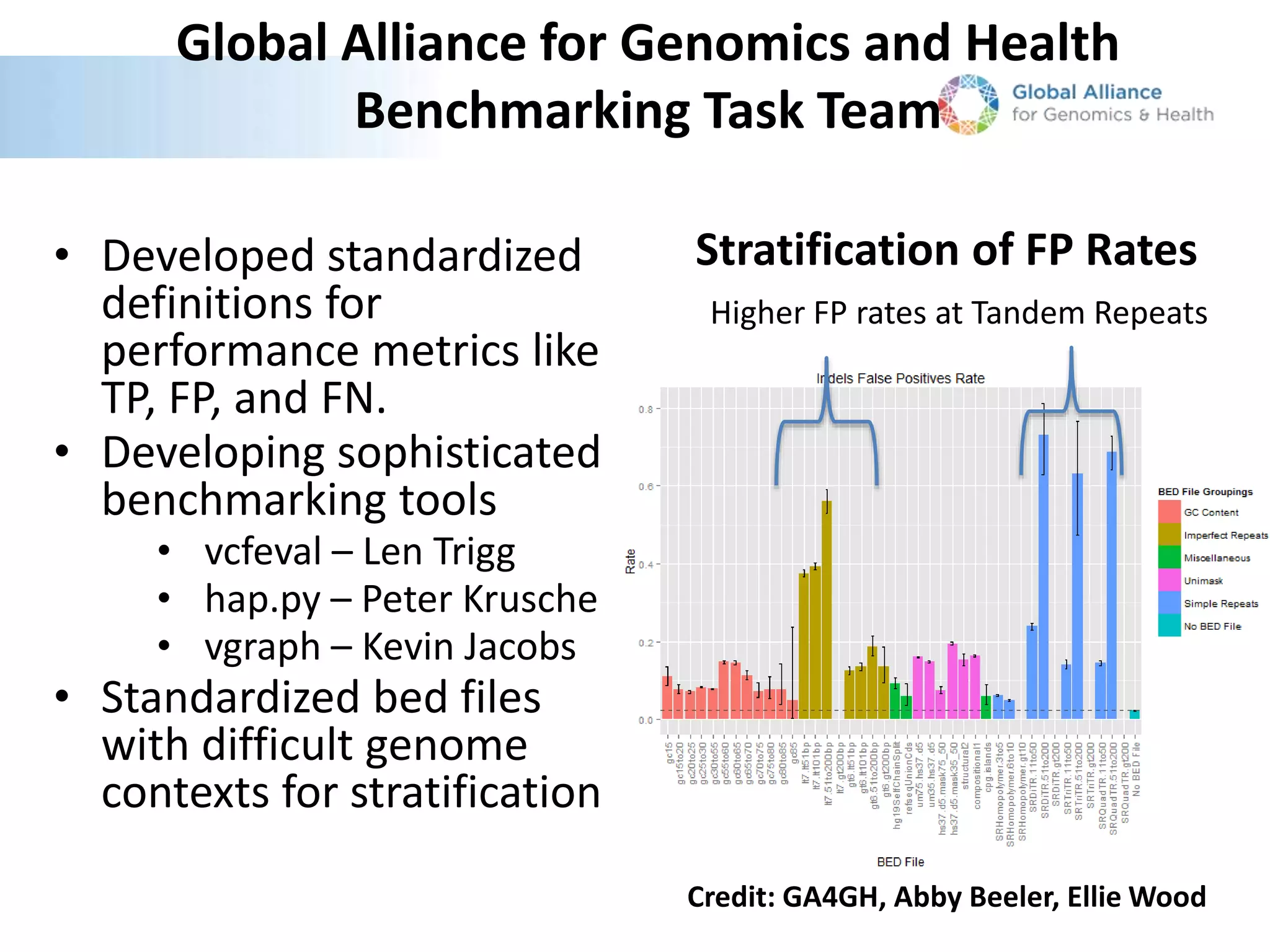
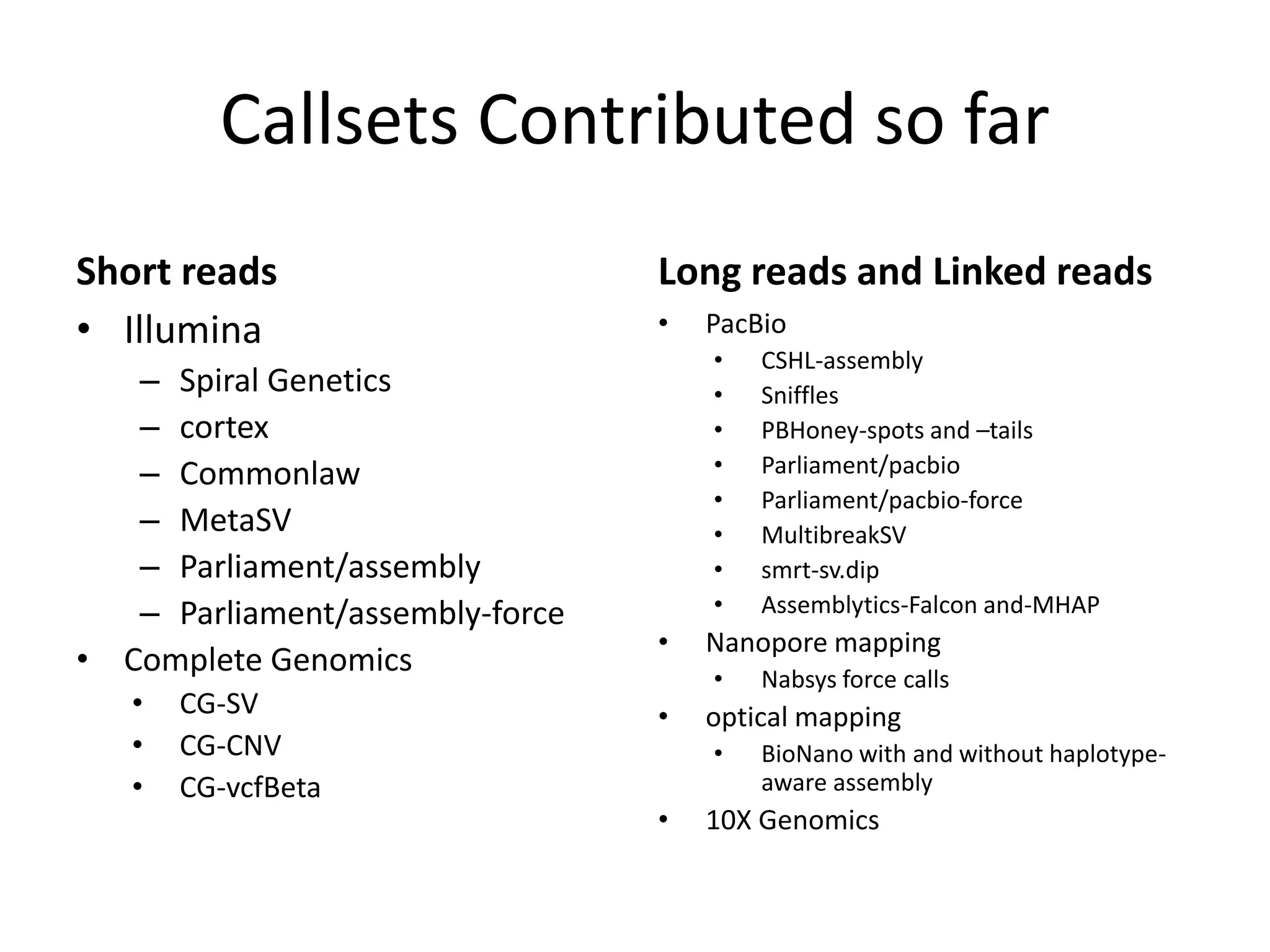
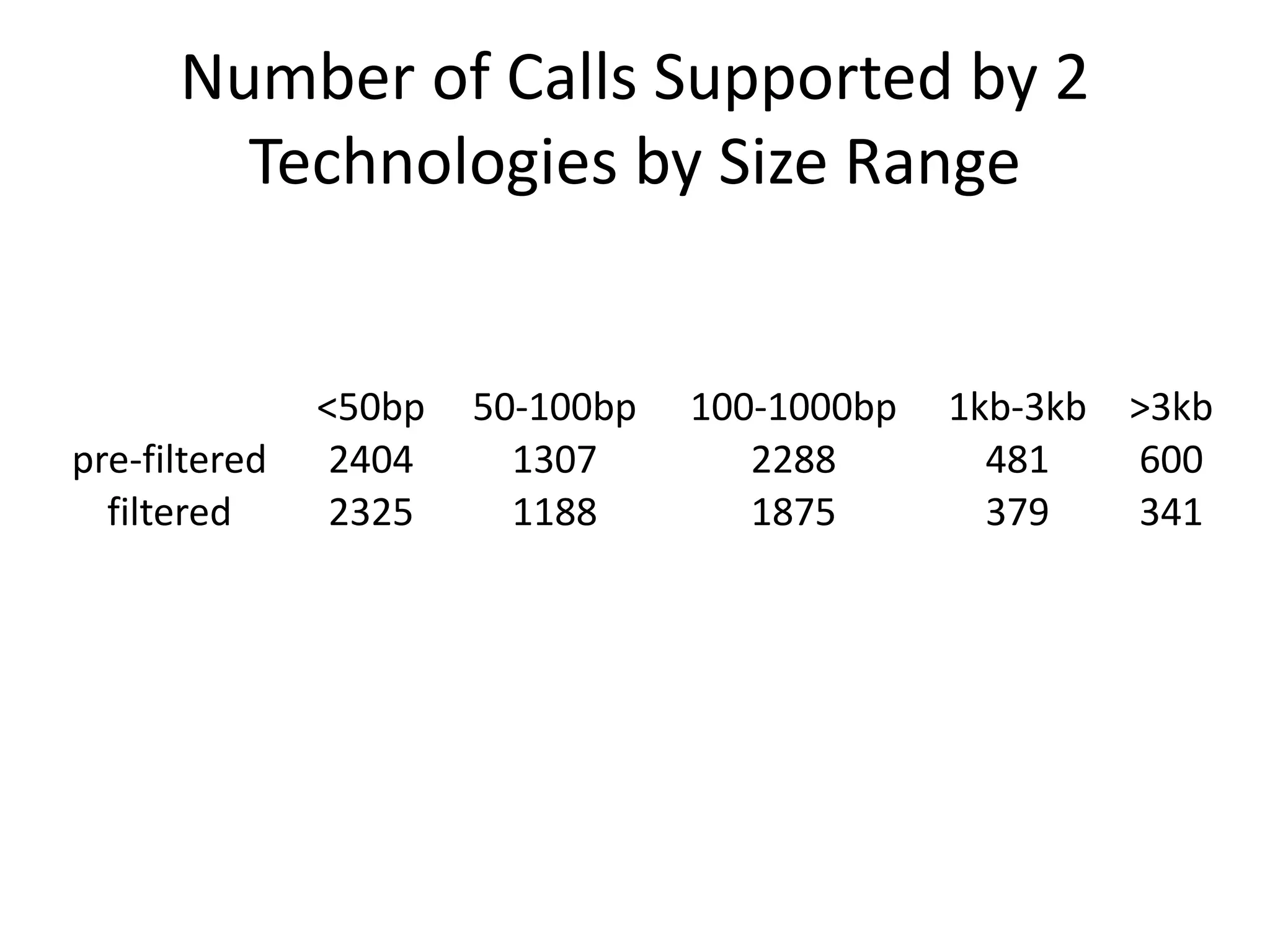
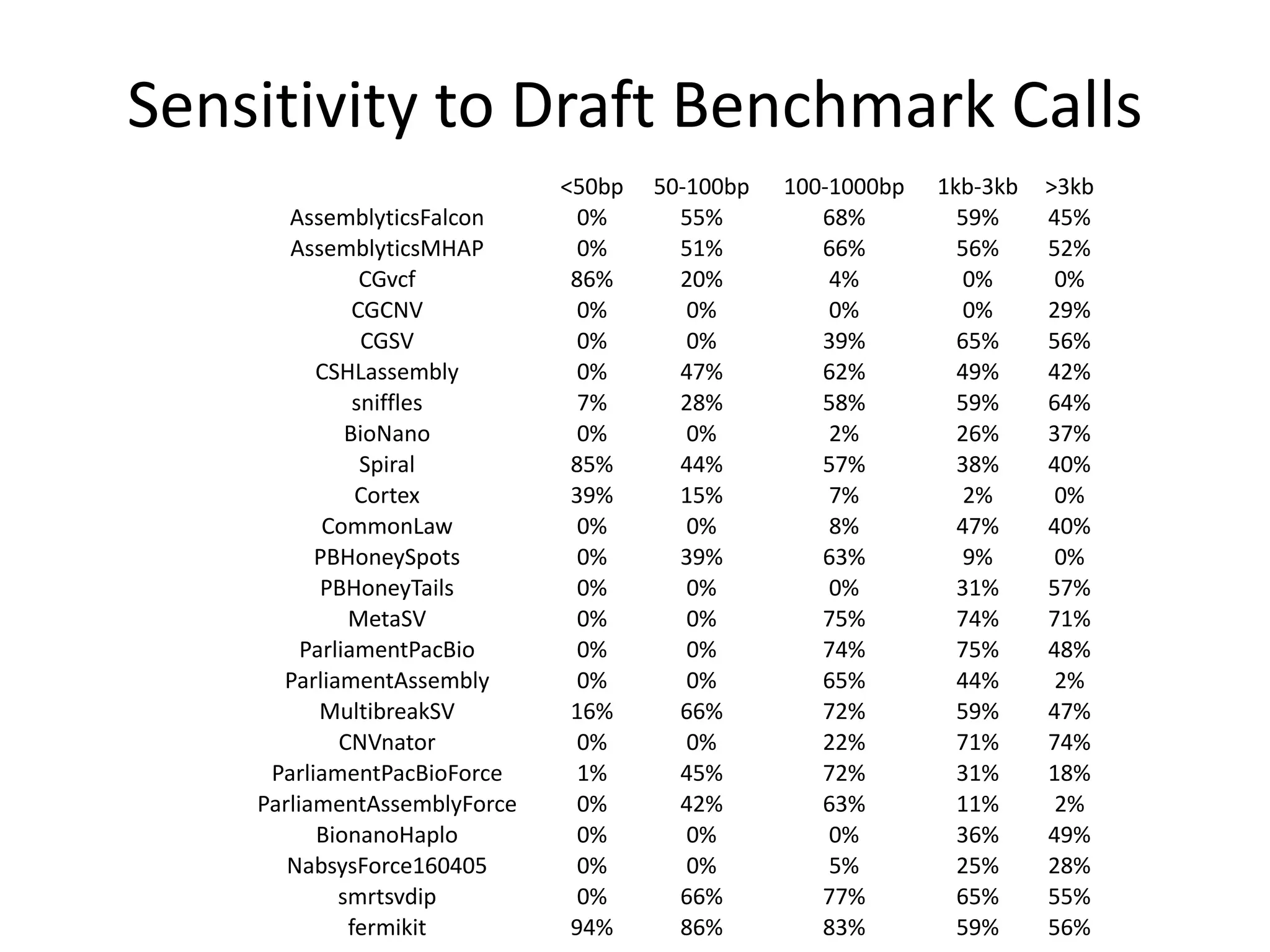
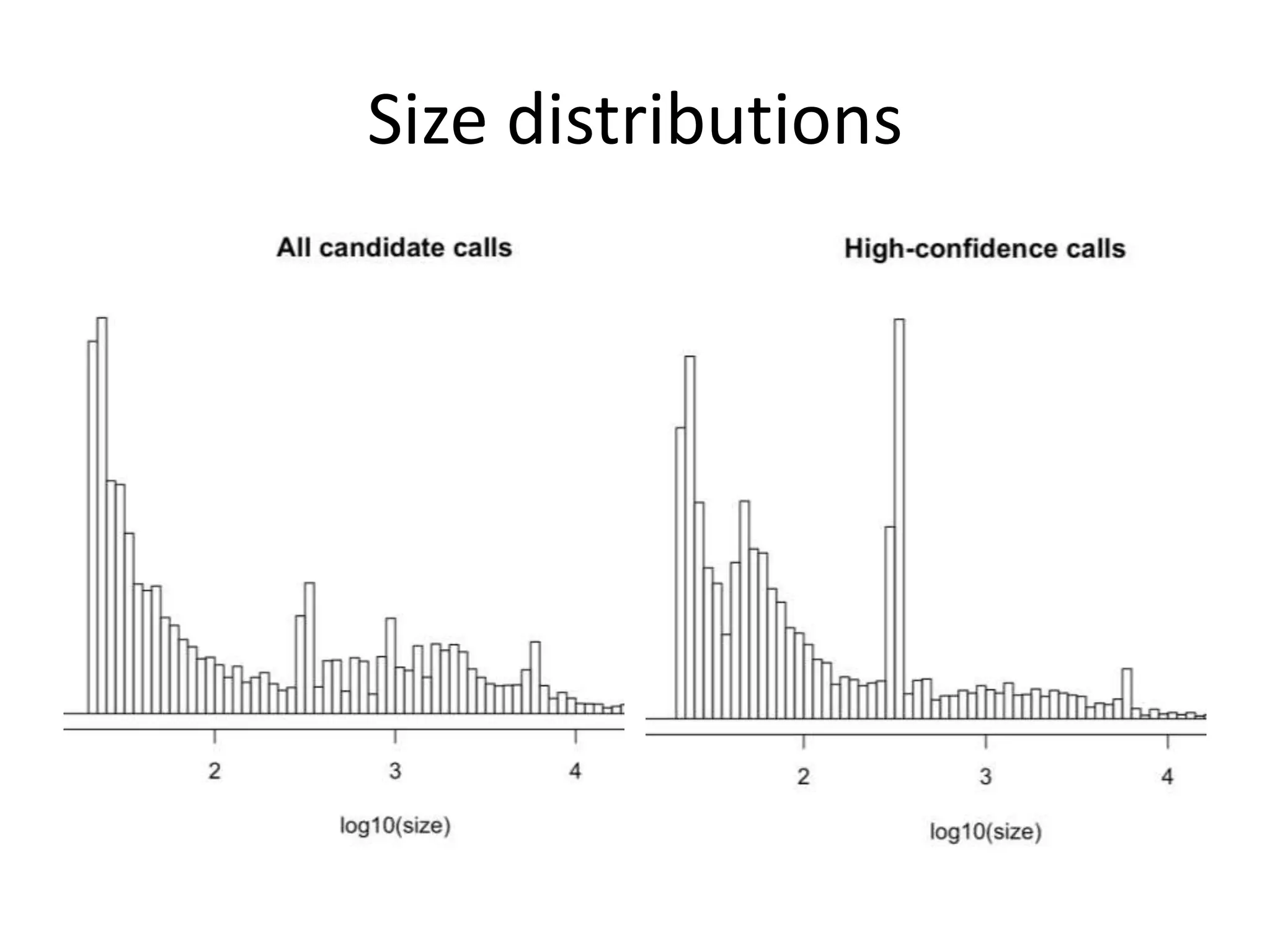
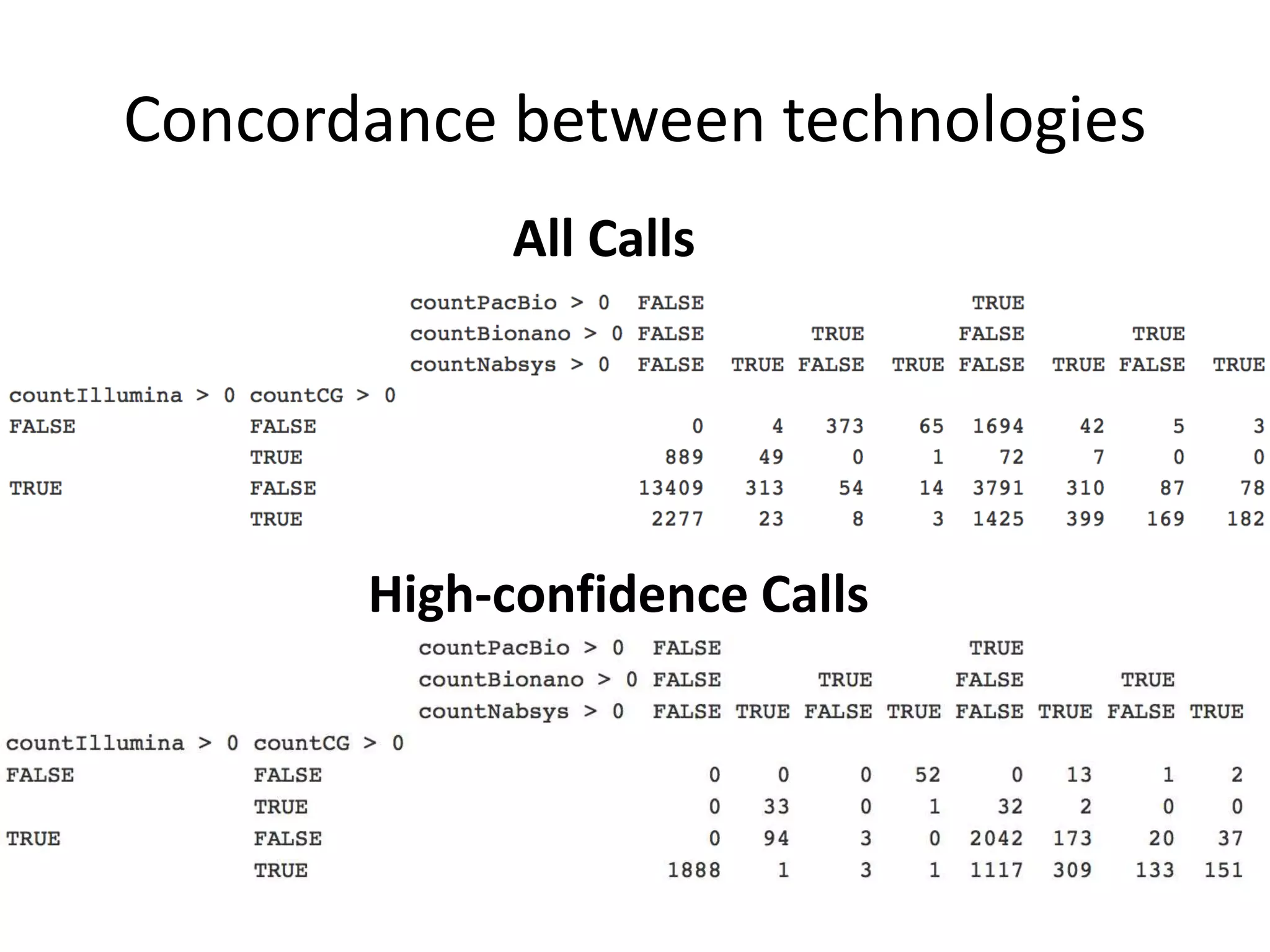
This document summarizes the work of the Genome in a Bottle Consortium to develop reference materials and methods for benchmarking genome sequencing and variant calling. The Consortium has extensively characterized the genome of the NA12878 sample to create a "gold standard" set of variant calls that can be used to evaluate sequencing platforms and bioinformatics pipelines. They are also analyzing additional samples to generate reference materials that will enable standardized testing and validation of clinical genome sequencing. The Consortium aims to develop benchmarking tools and strategies with the Global Alliance for Genomics and Health to facilitate regulatory approval and clinical application of genome sequencing.