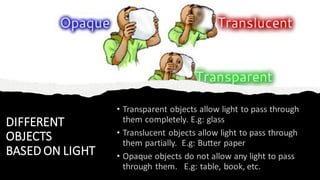
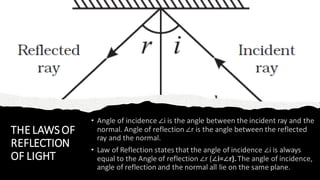
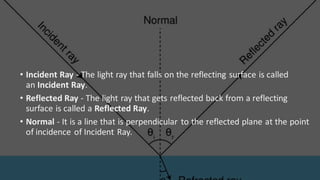
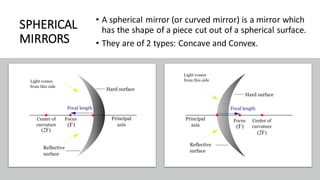
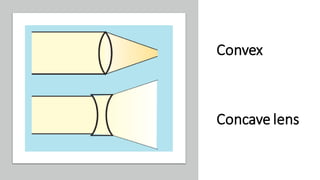
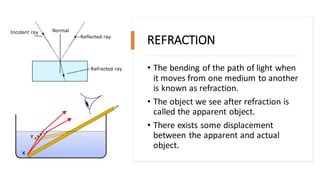
Light travels in a straight line and can be reflected, refracted, or absorbed when it hits different materials and surfaces. Reflection occurs when light bounces off a surface like a mirror, following the laws of reflection. Refraction is when light changes direction as it passes from one medium to another, like from air to water. Lenses and curved mirrors can form real or virtual images by refracting or reflecting light rays. Prisms disperse white light into a spectrum due to refraction, demonstrating that light is made of different colors.