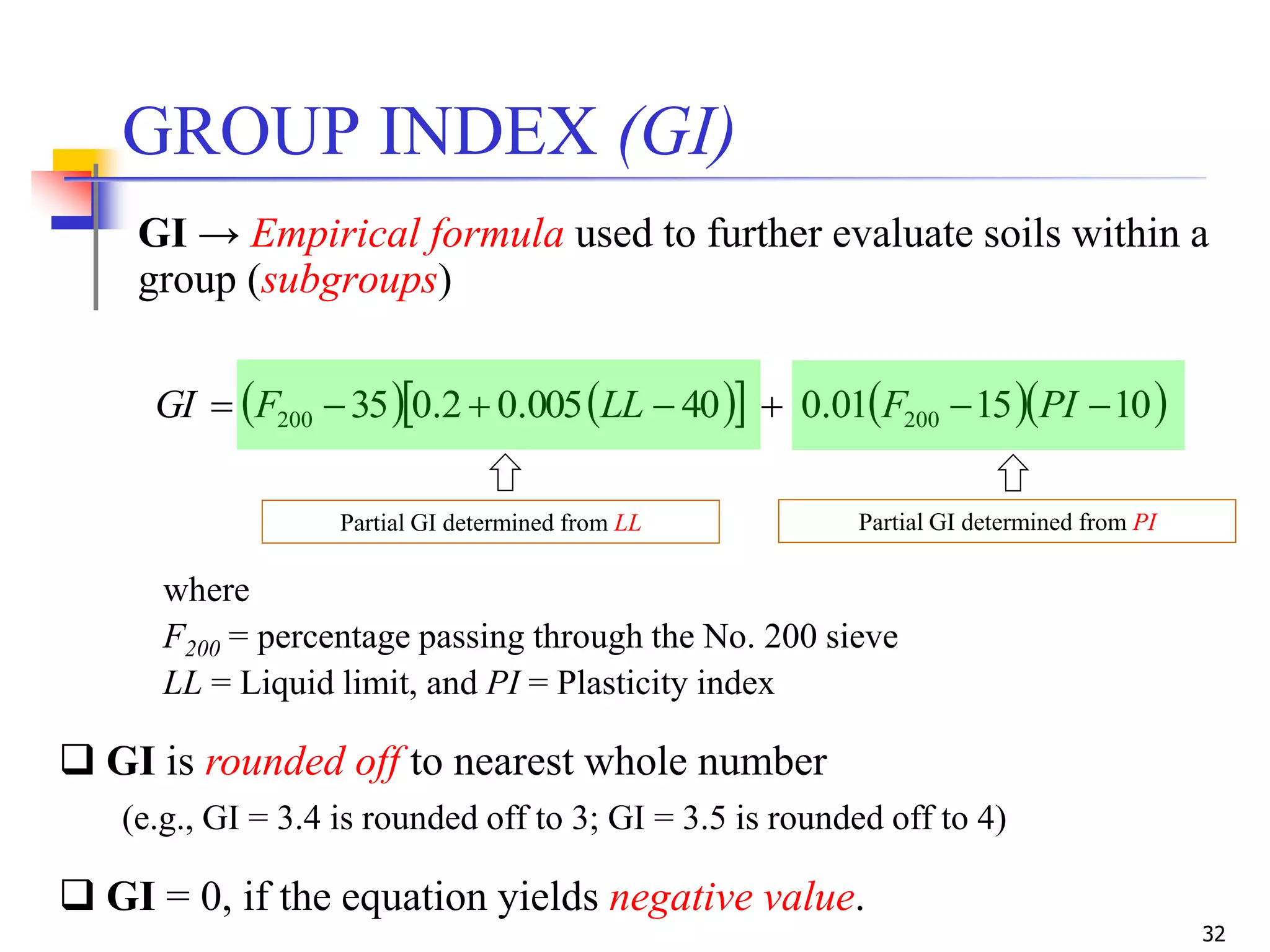
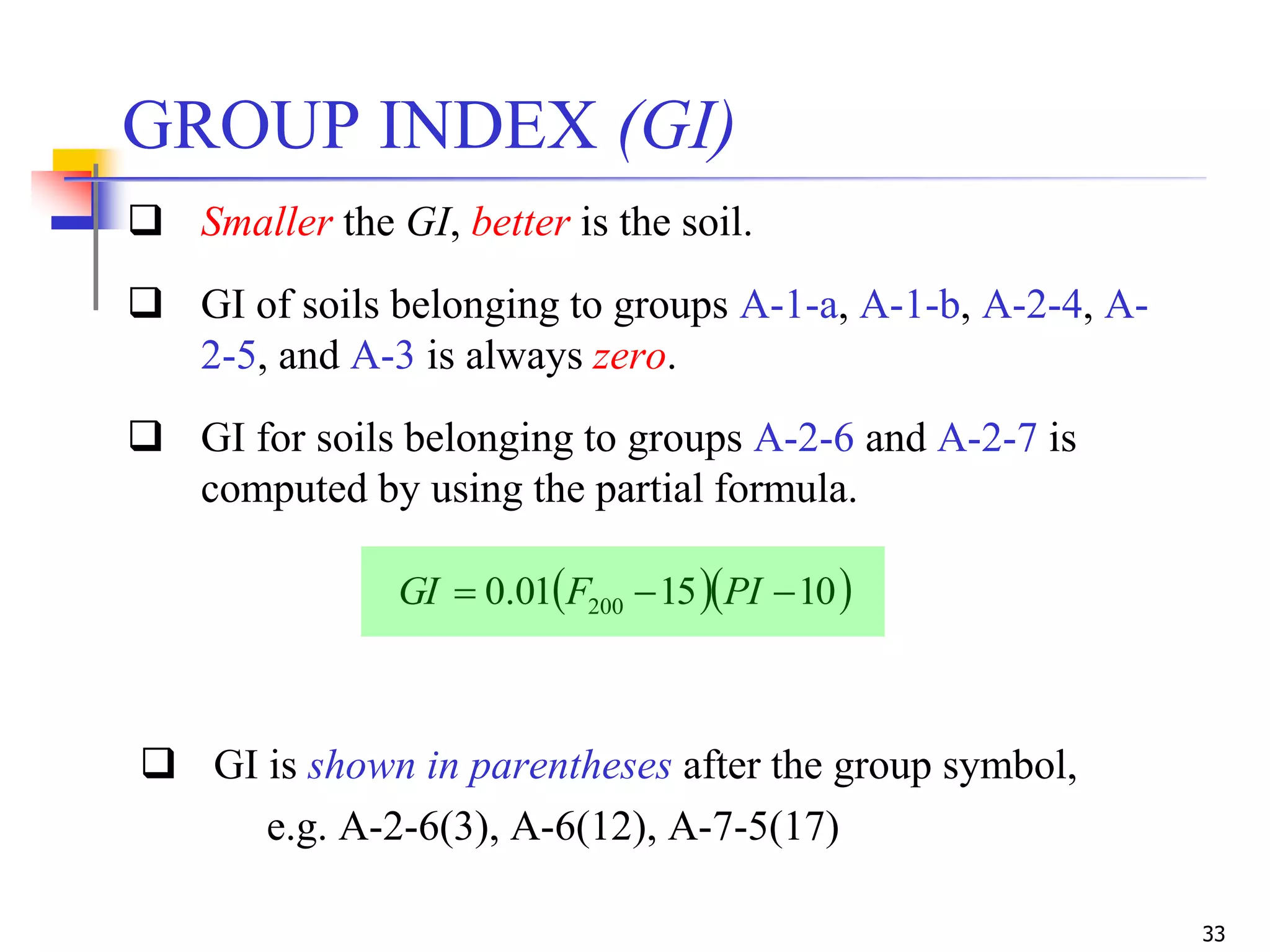
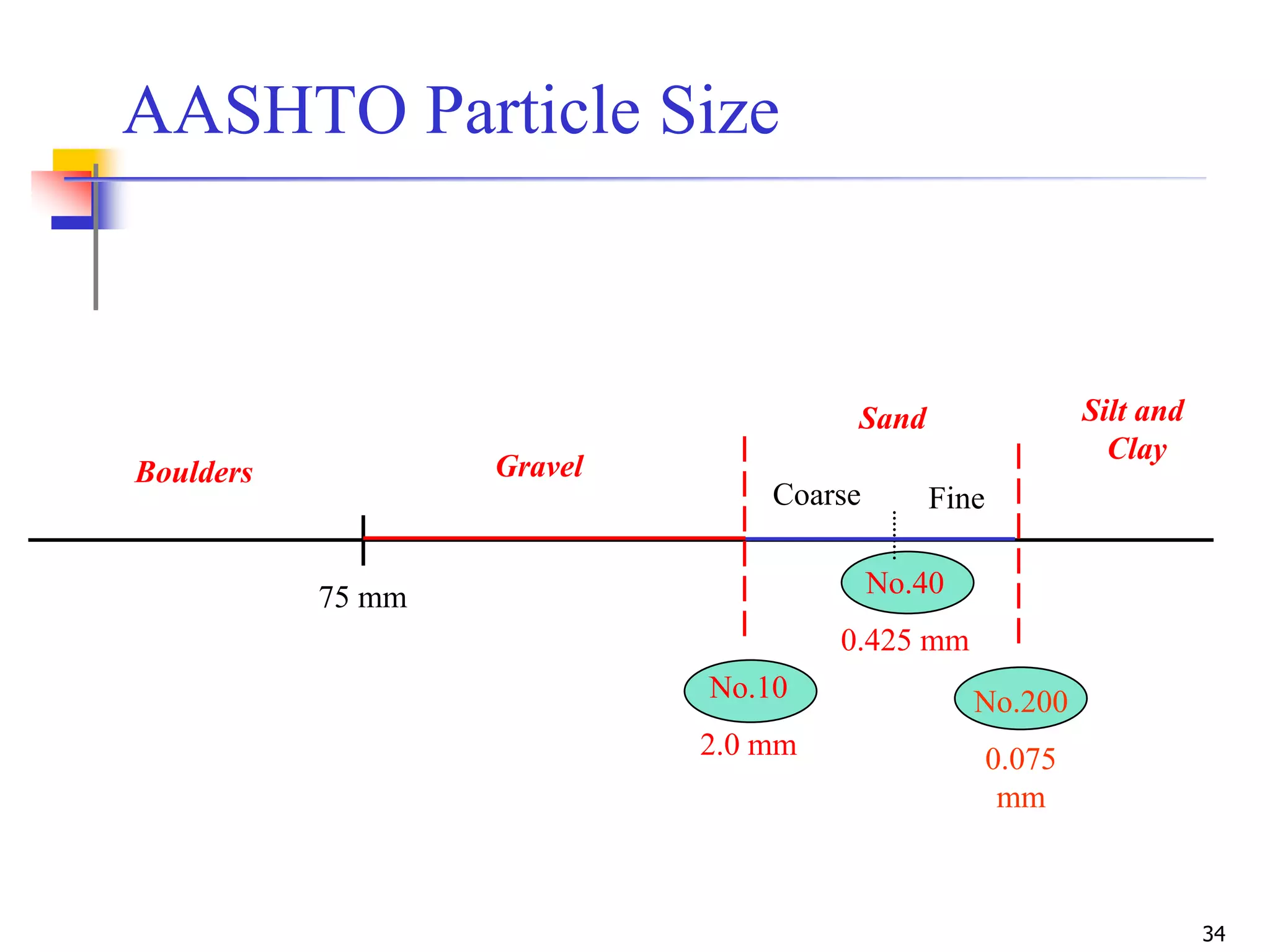
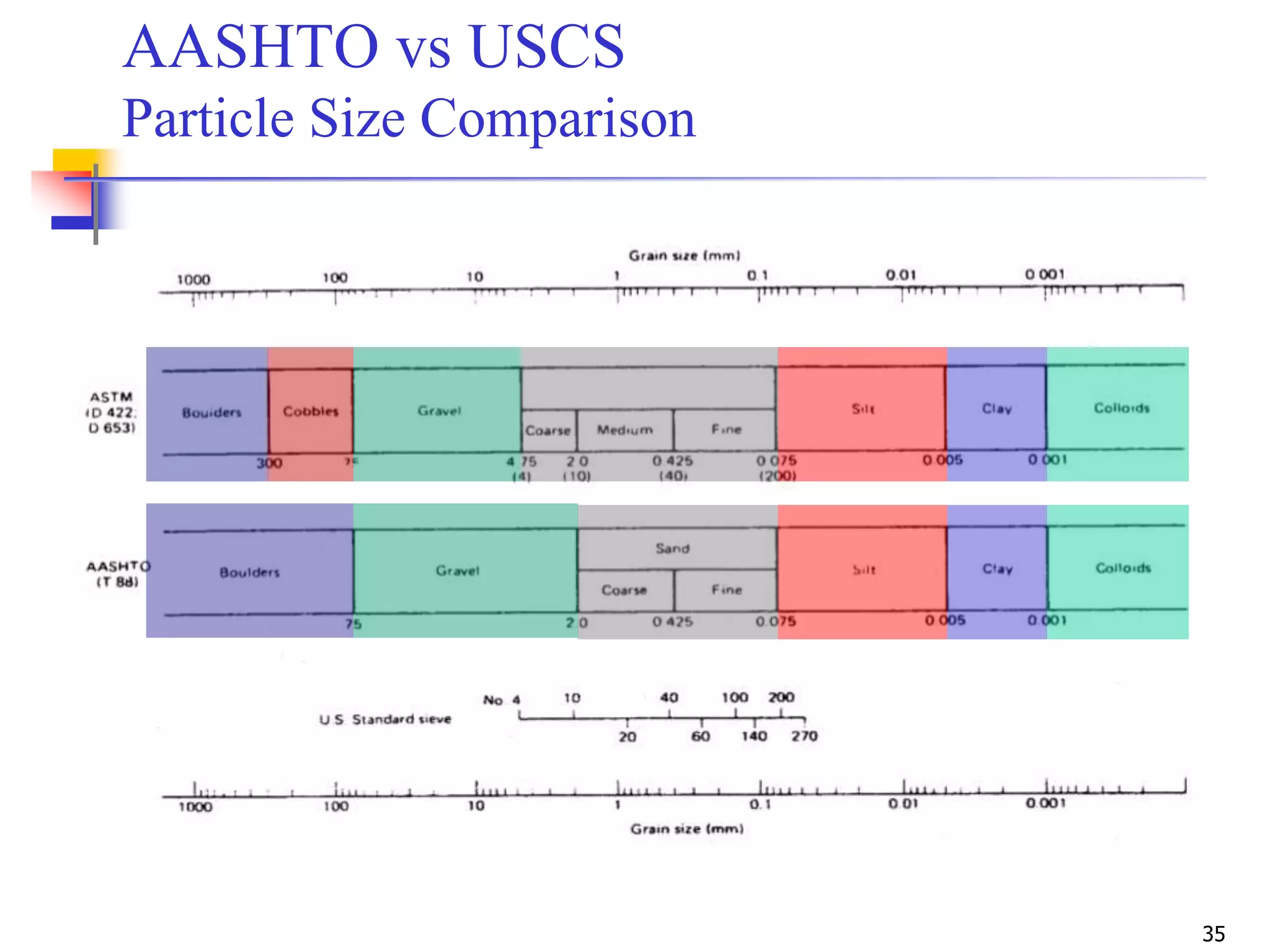
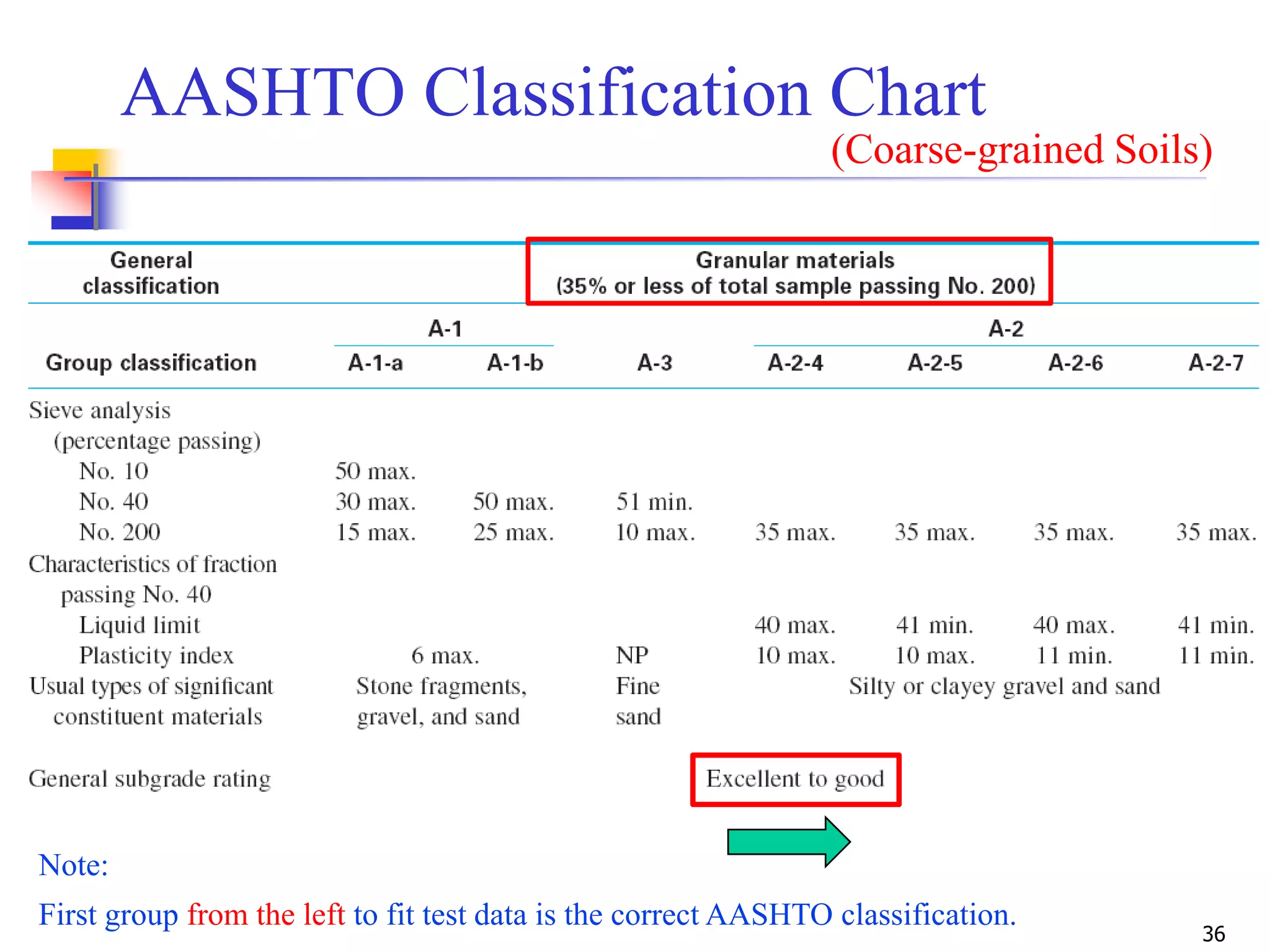
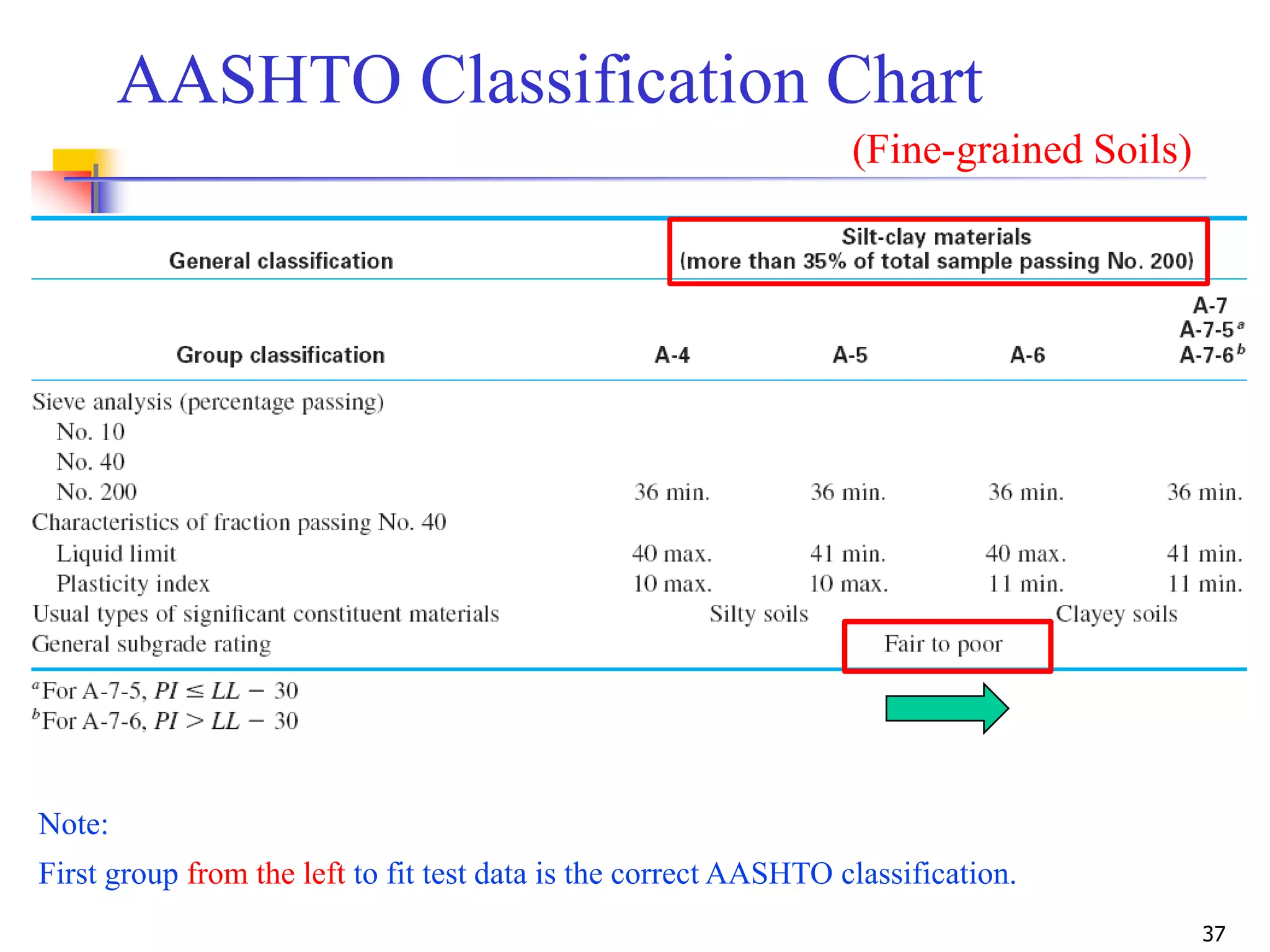
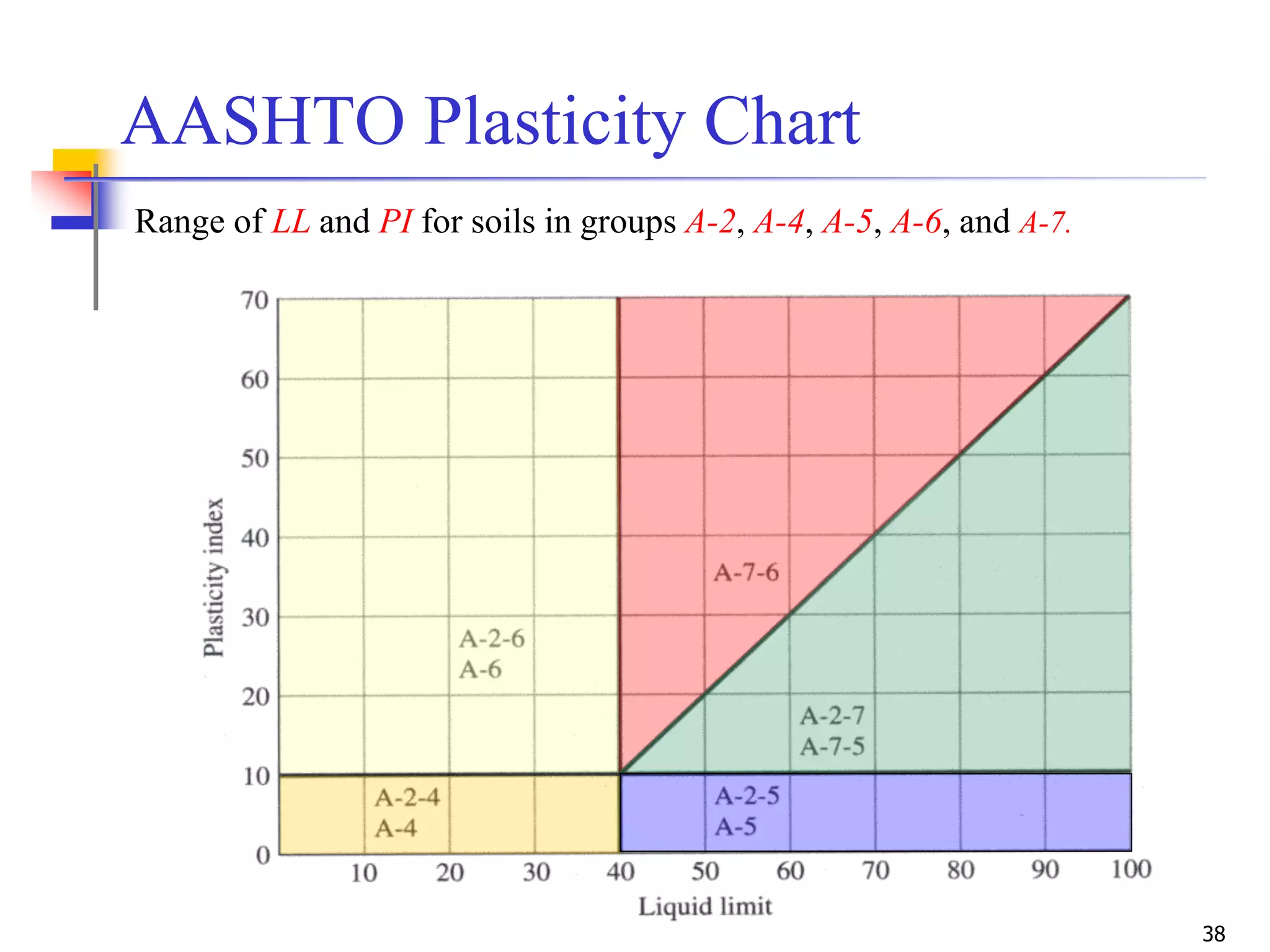
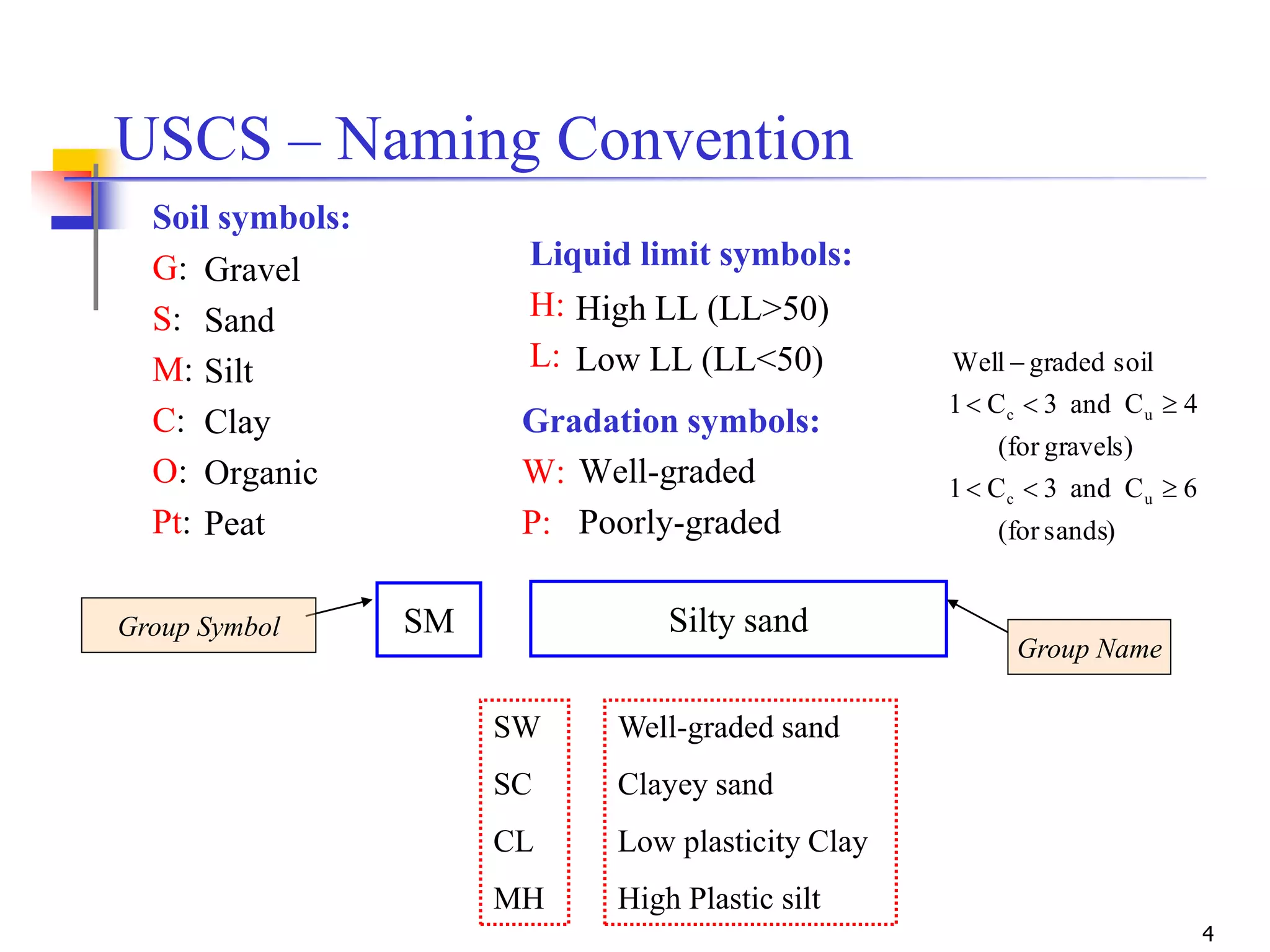
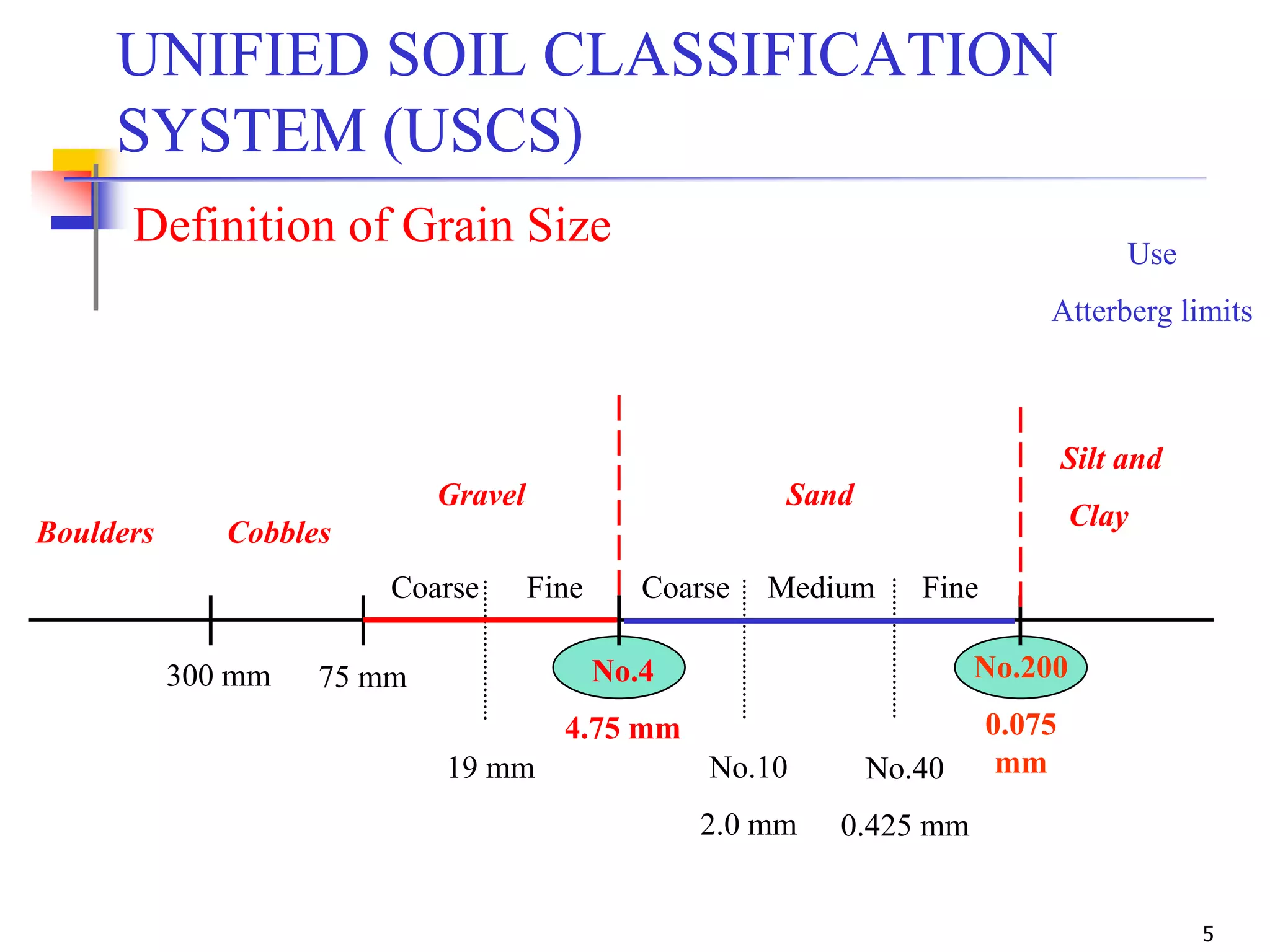
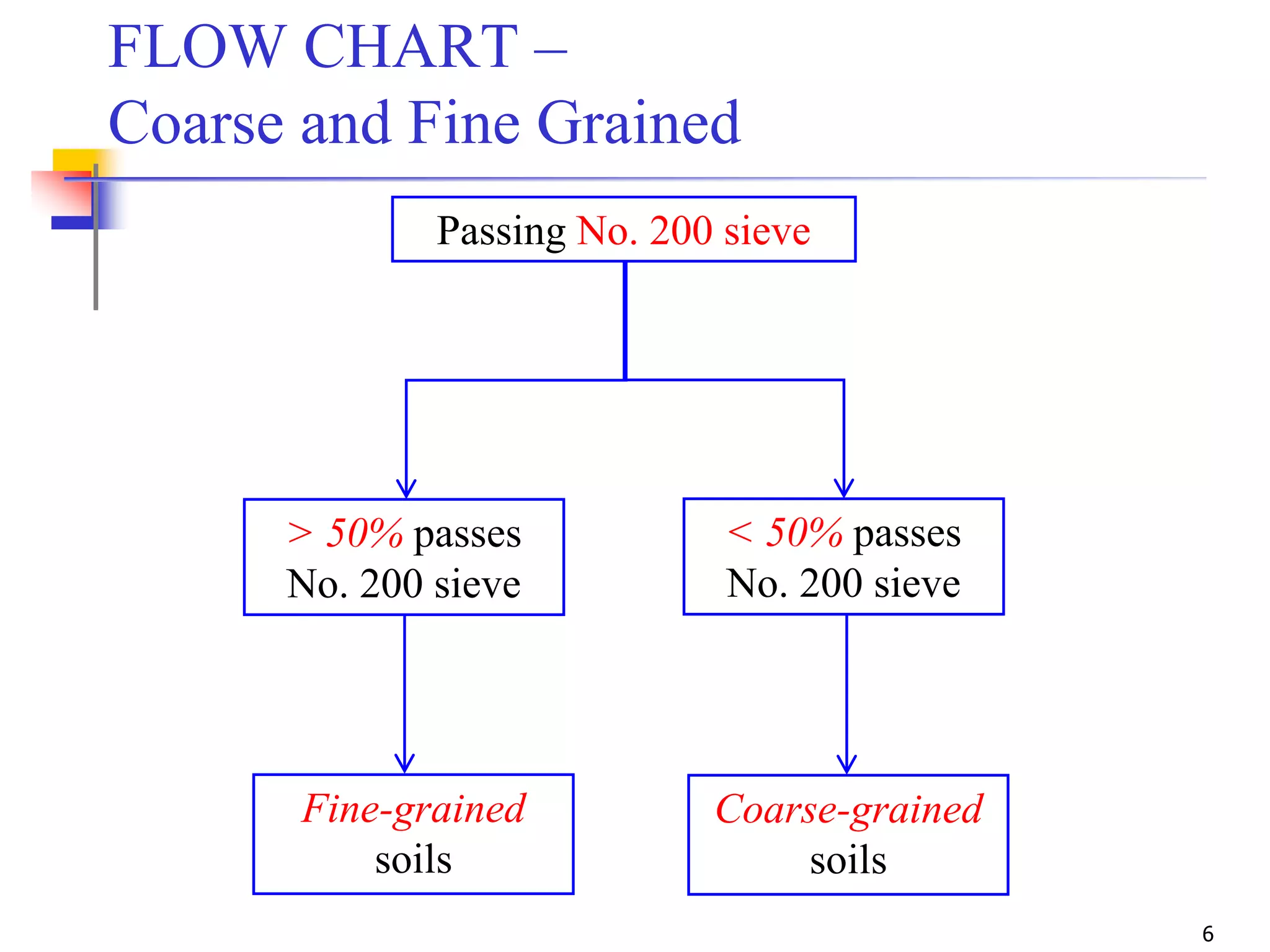
The document provides lecture notes on geotechnical engineering, focusing on two primary soil classification systems: the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) and the AASHTO system. It details the categories of soils based on grain size and plasticity, along with flow charts and practice problems for classifying soils. The content emphasizes the importance of these systems in categorizing soils for engineering applications.
![1
Geotechnical Engineering–I [CE-221]
BSc Civil Engineering – 4th Semester
by
Dr. Muhammad Irfan
Assistant Professor
Civil Engg. Dept. – UET Lahore
Email: mirfan1@msn.com
Lecture Handouts: https://groups.google.com/d/forum/2016session-geotech-i
Lecture # 11
27-Feb-2018](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-180923183816/75/Geotechnical-Engineering-I-Lec-11-USCS-AASHTO-1-2048.jpg)


![24
24
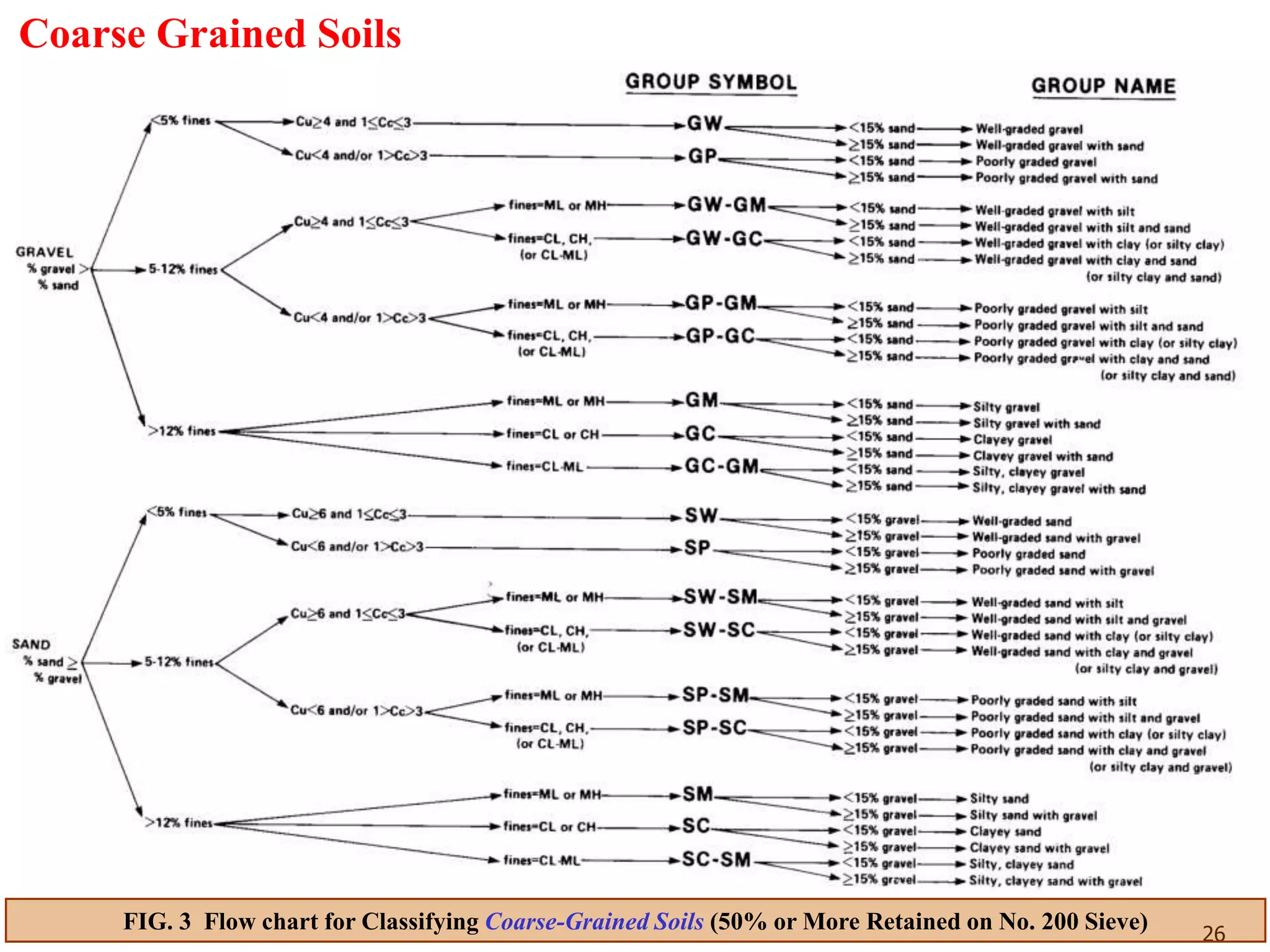
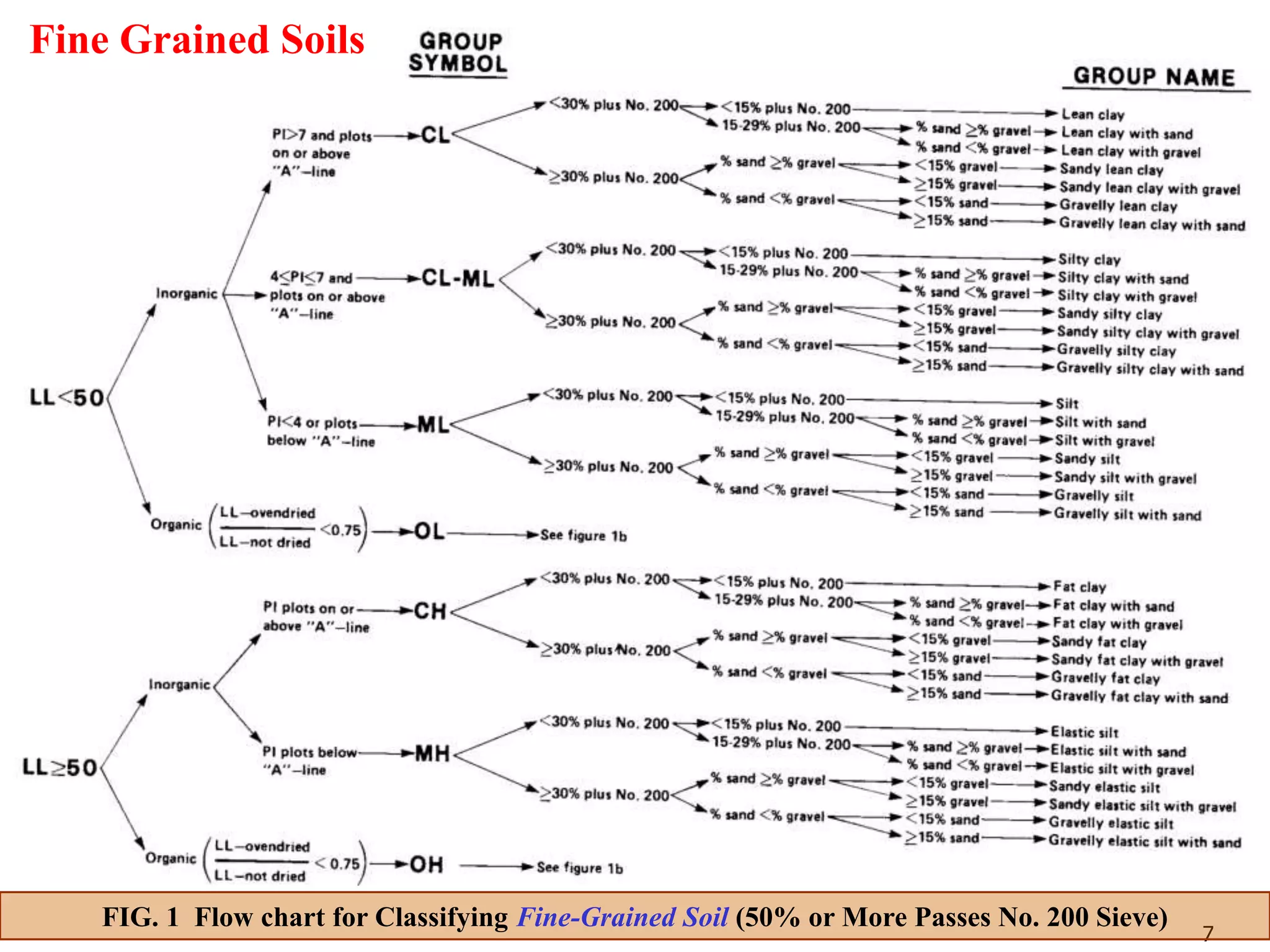
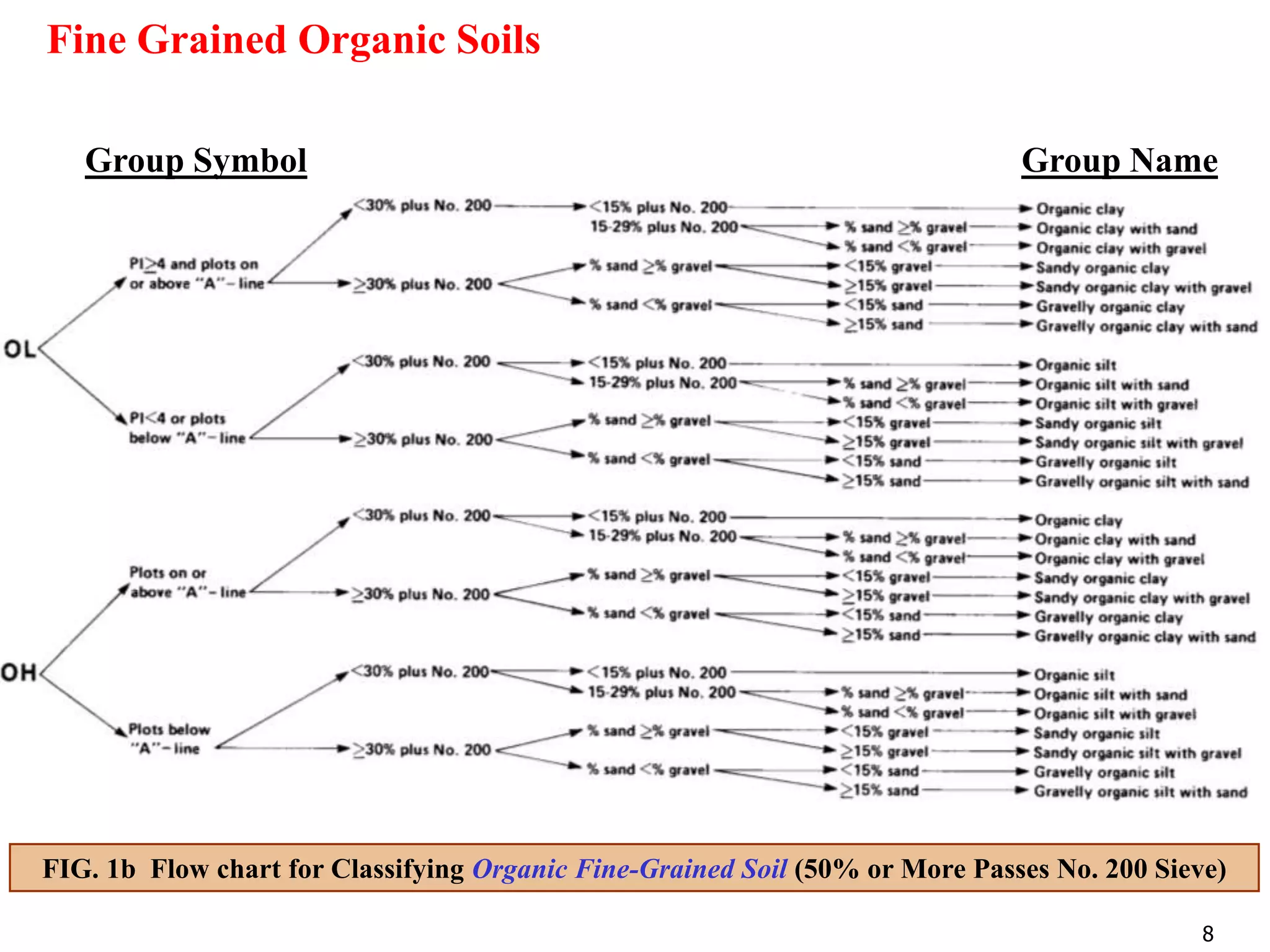
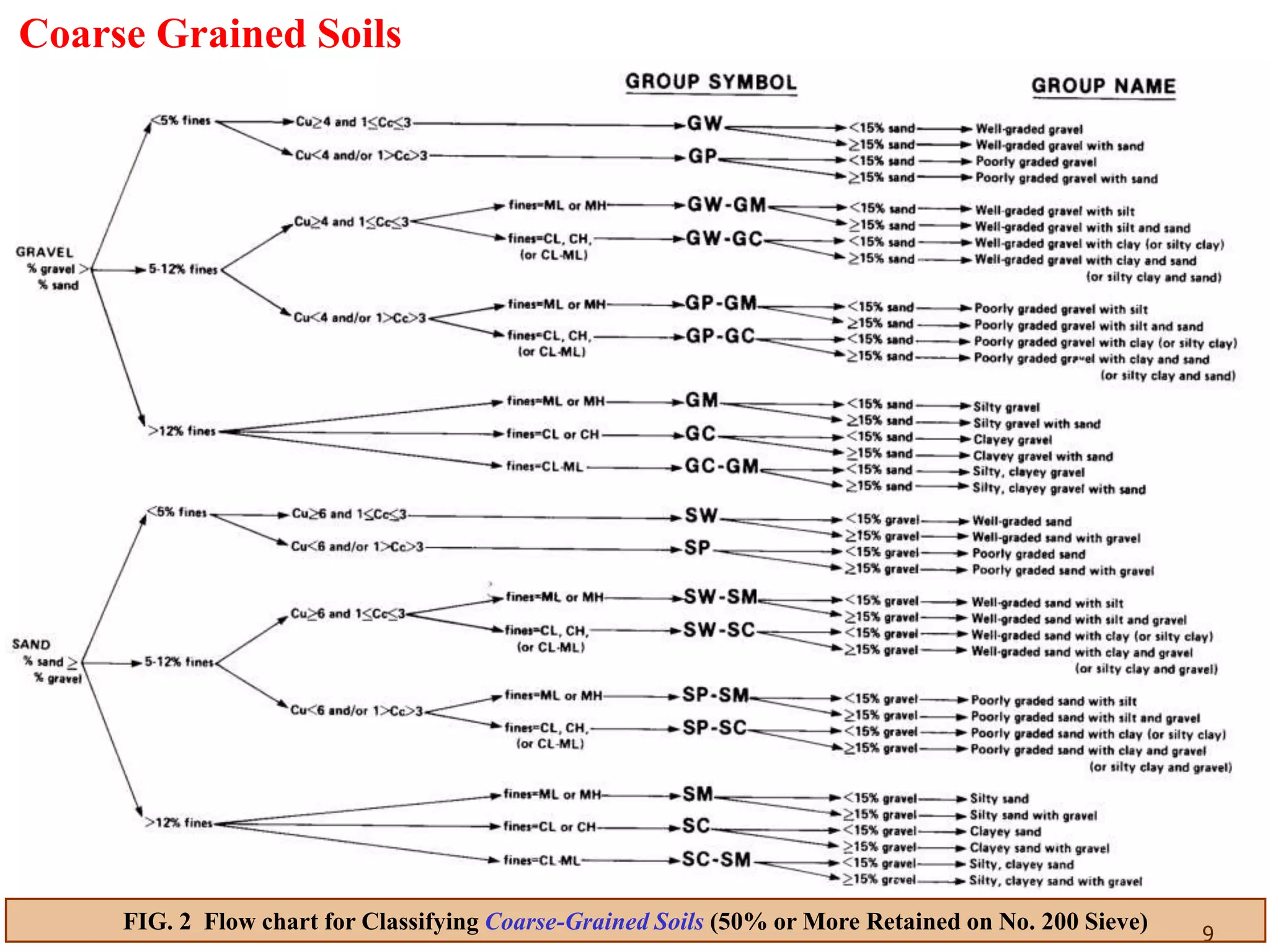
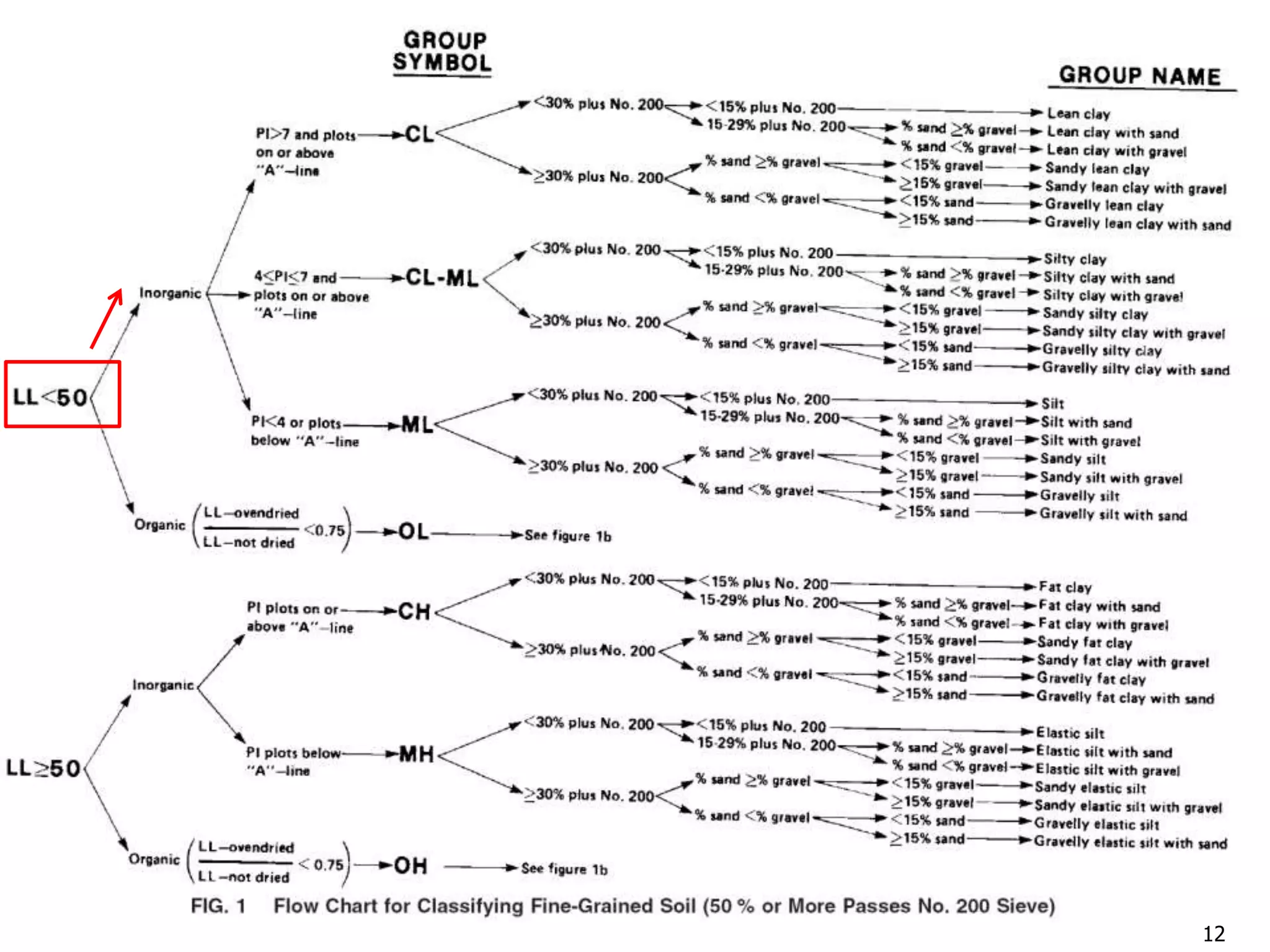
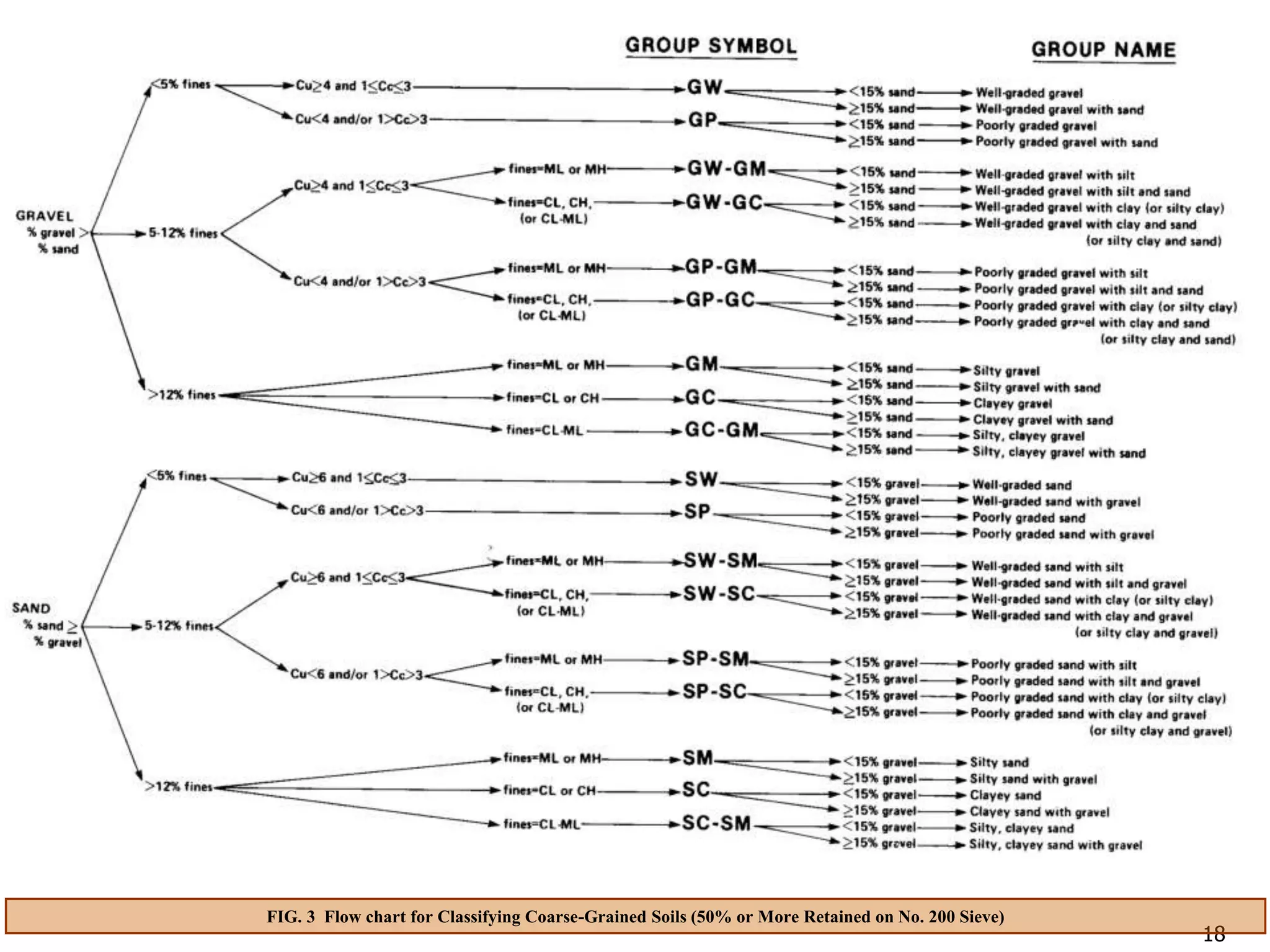
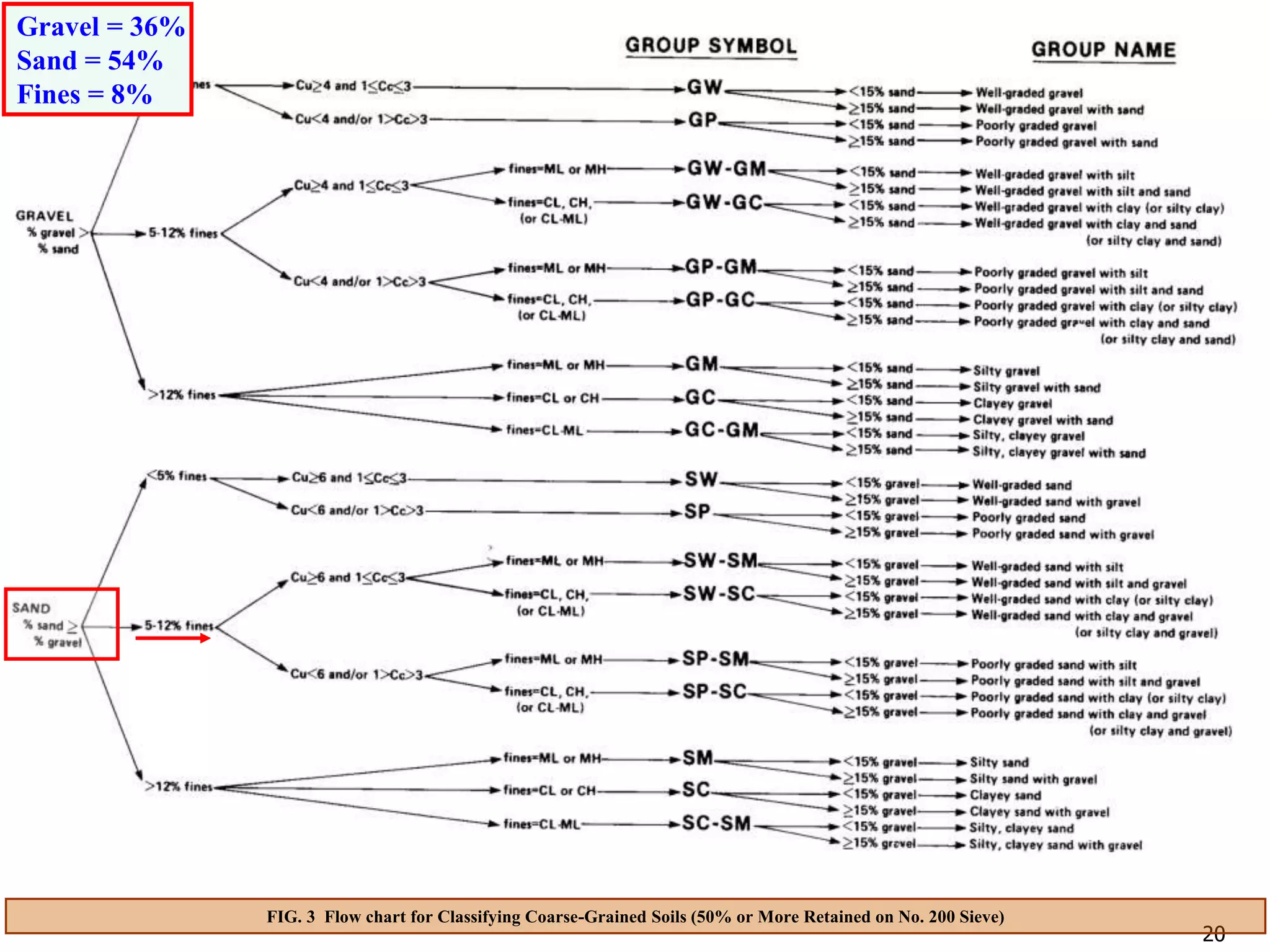
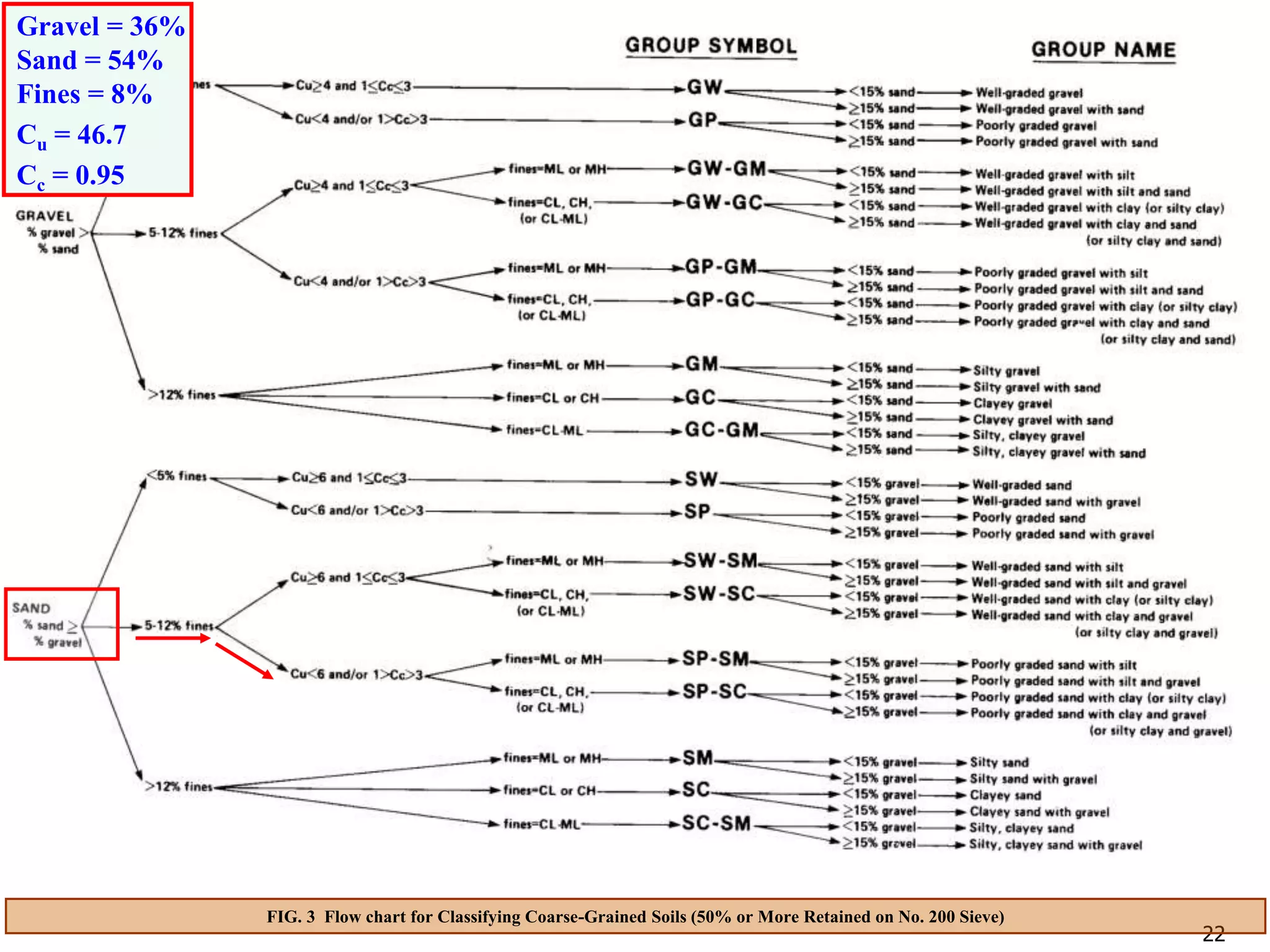
FIG. 3 Flow chart for Classifying Coarse-Grained Soils (50% or More Retained on No. 200 Sieve)
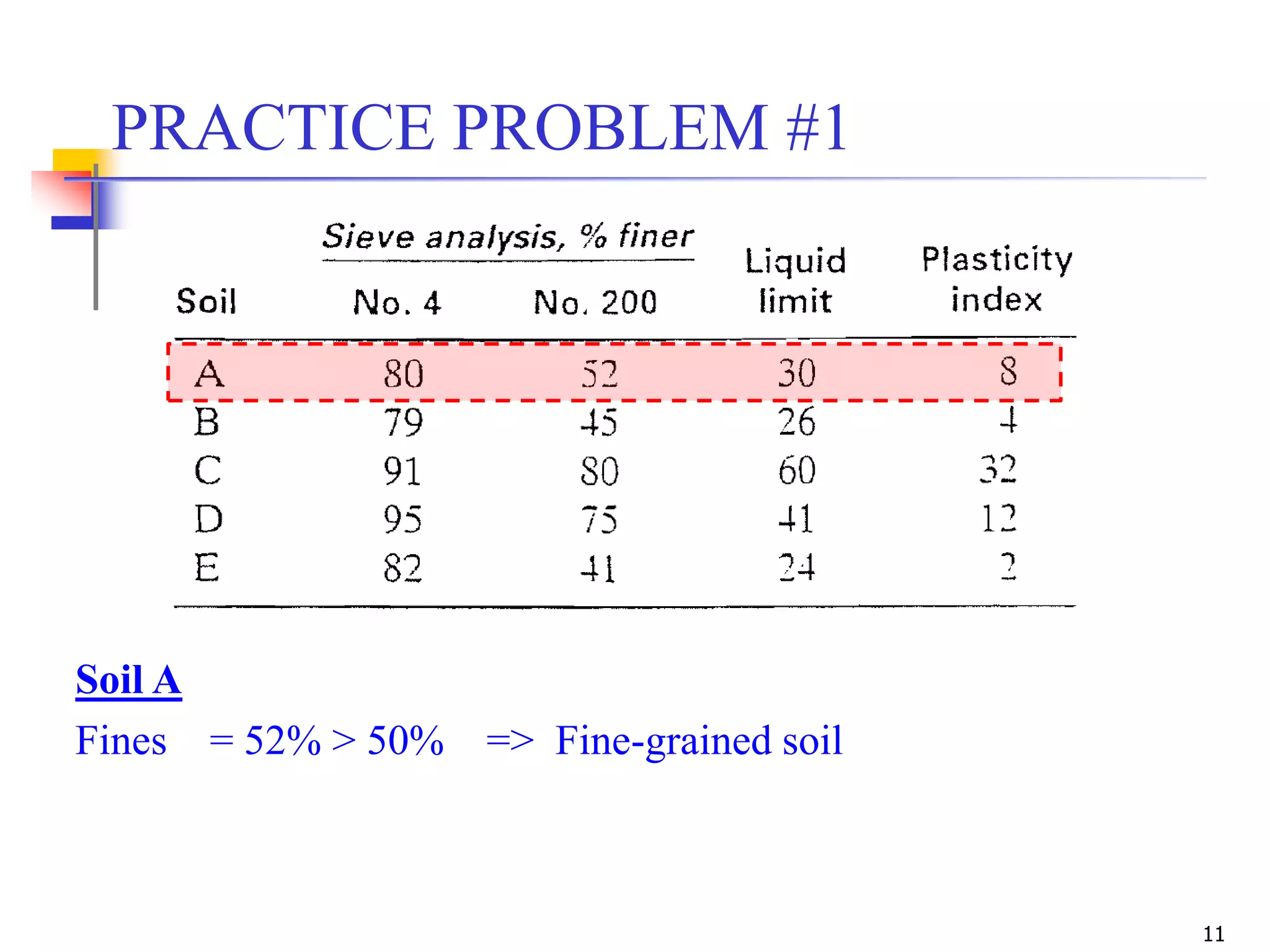
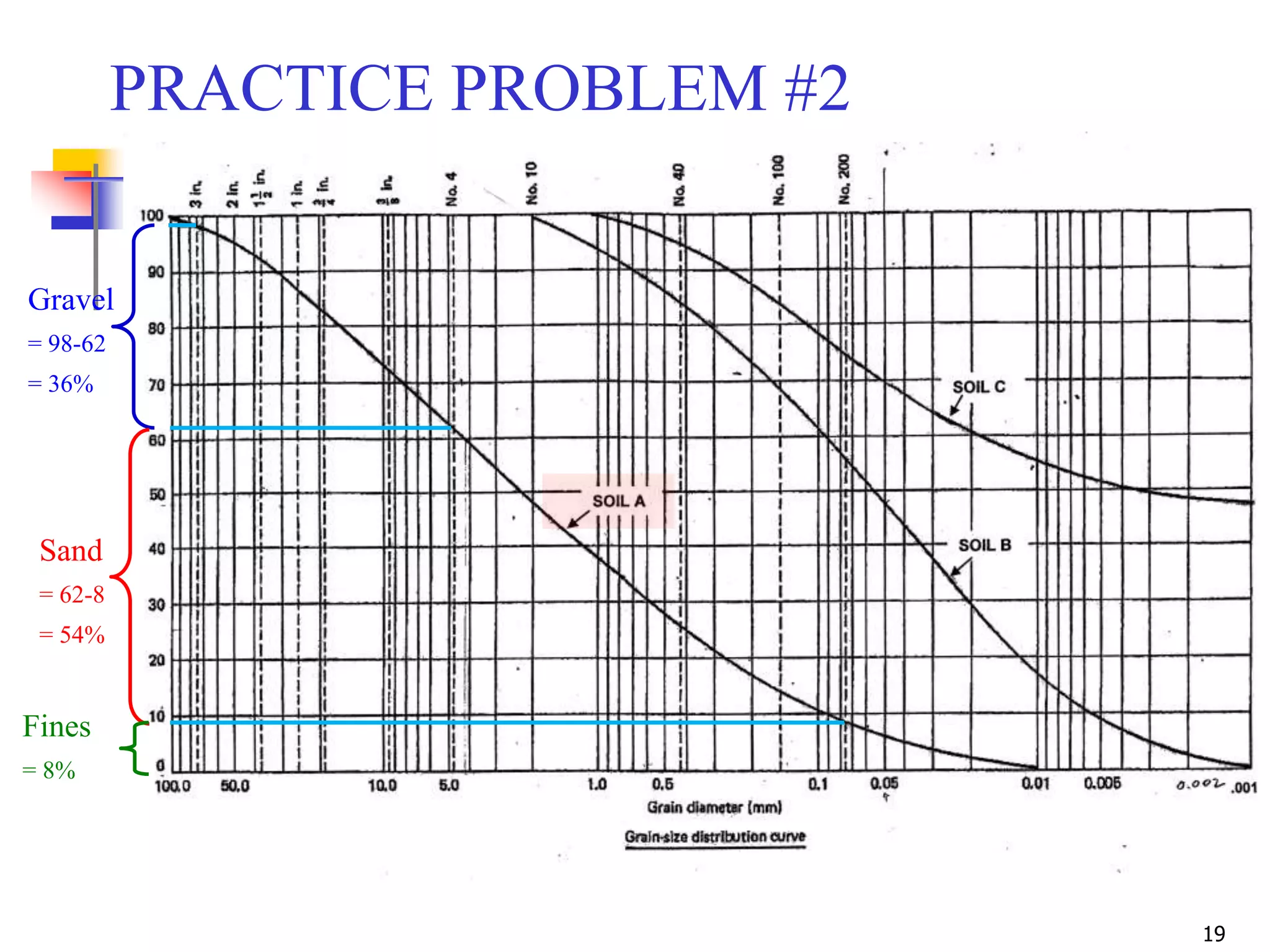
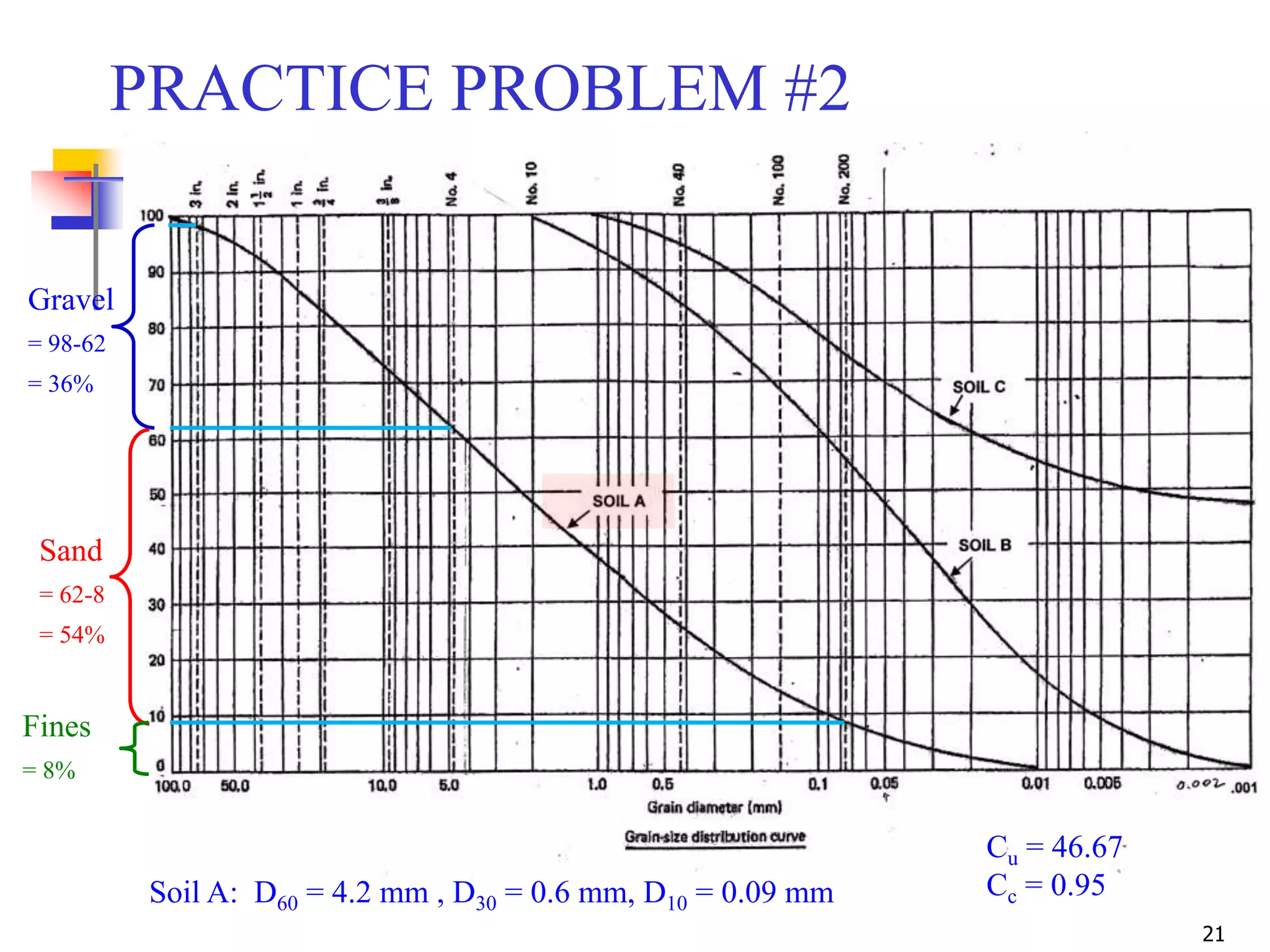
Gravel = 36%
Sand = 54%
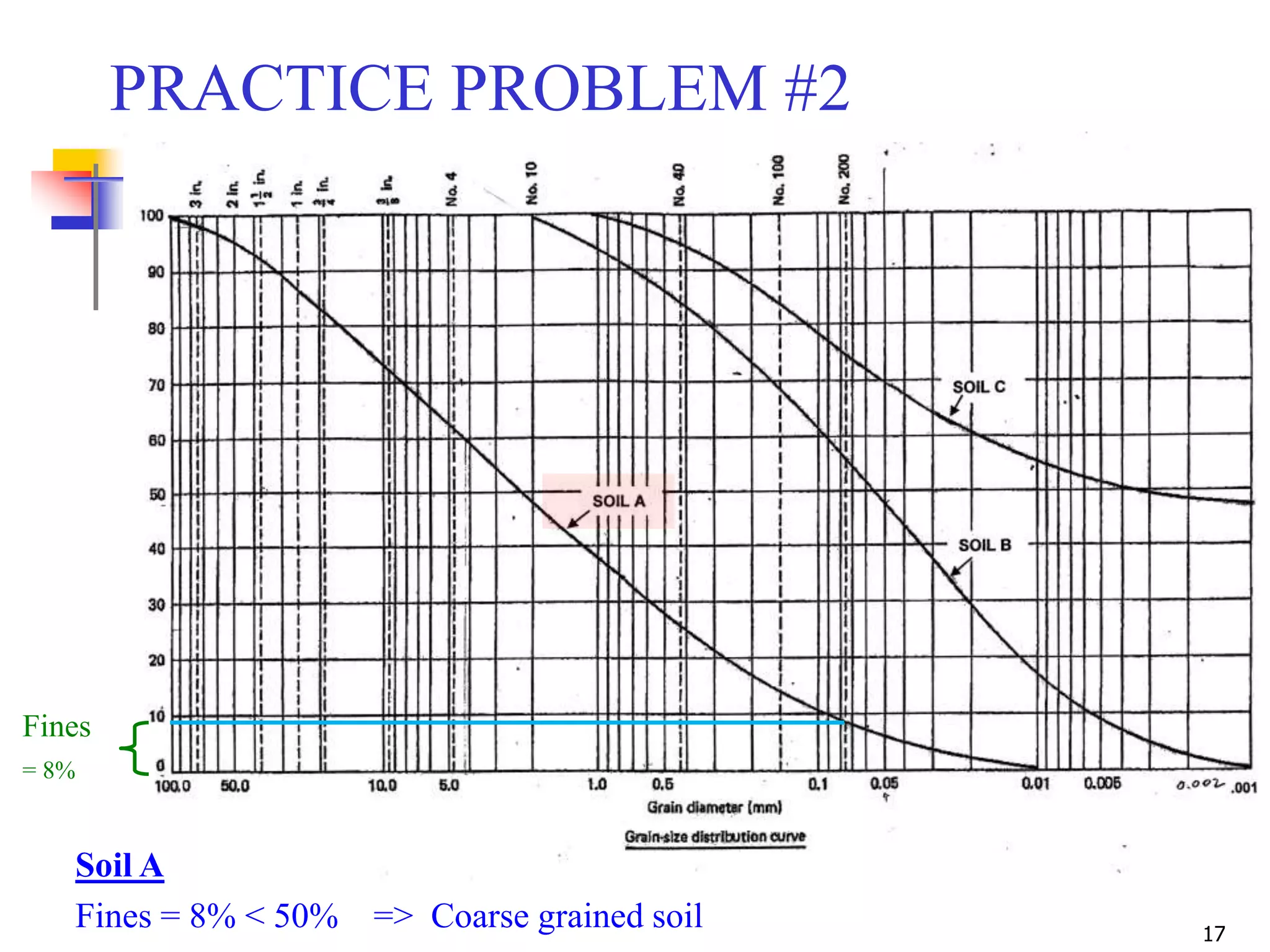
Fines = 8%
Cu = 46.7
Cc = 0.95
Soil A is classified as [SP-SM: Poorly-graded sand with silt and gravel]
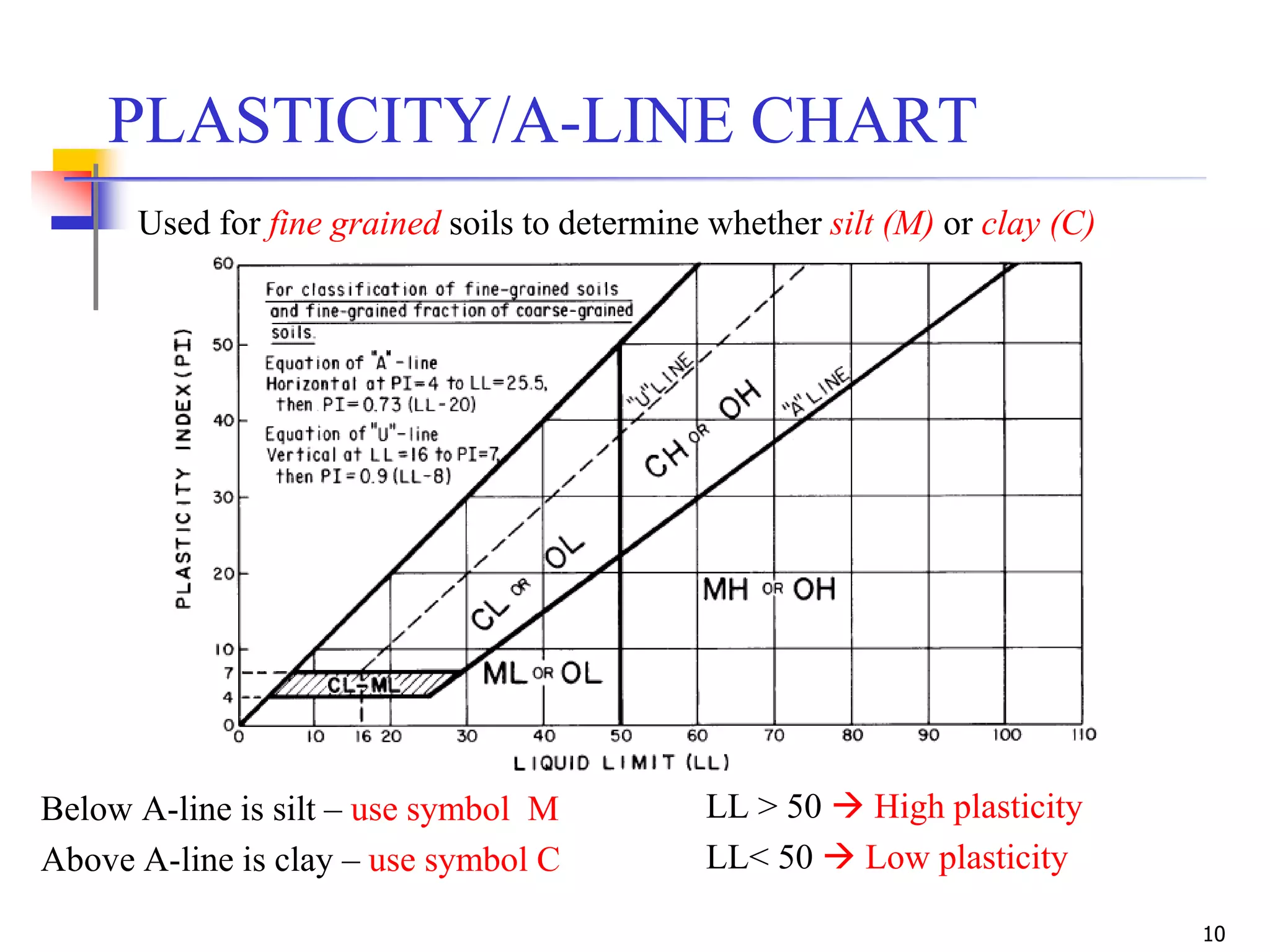
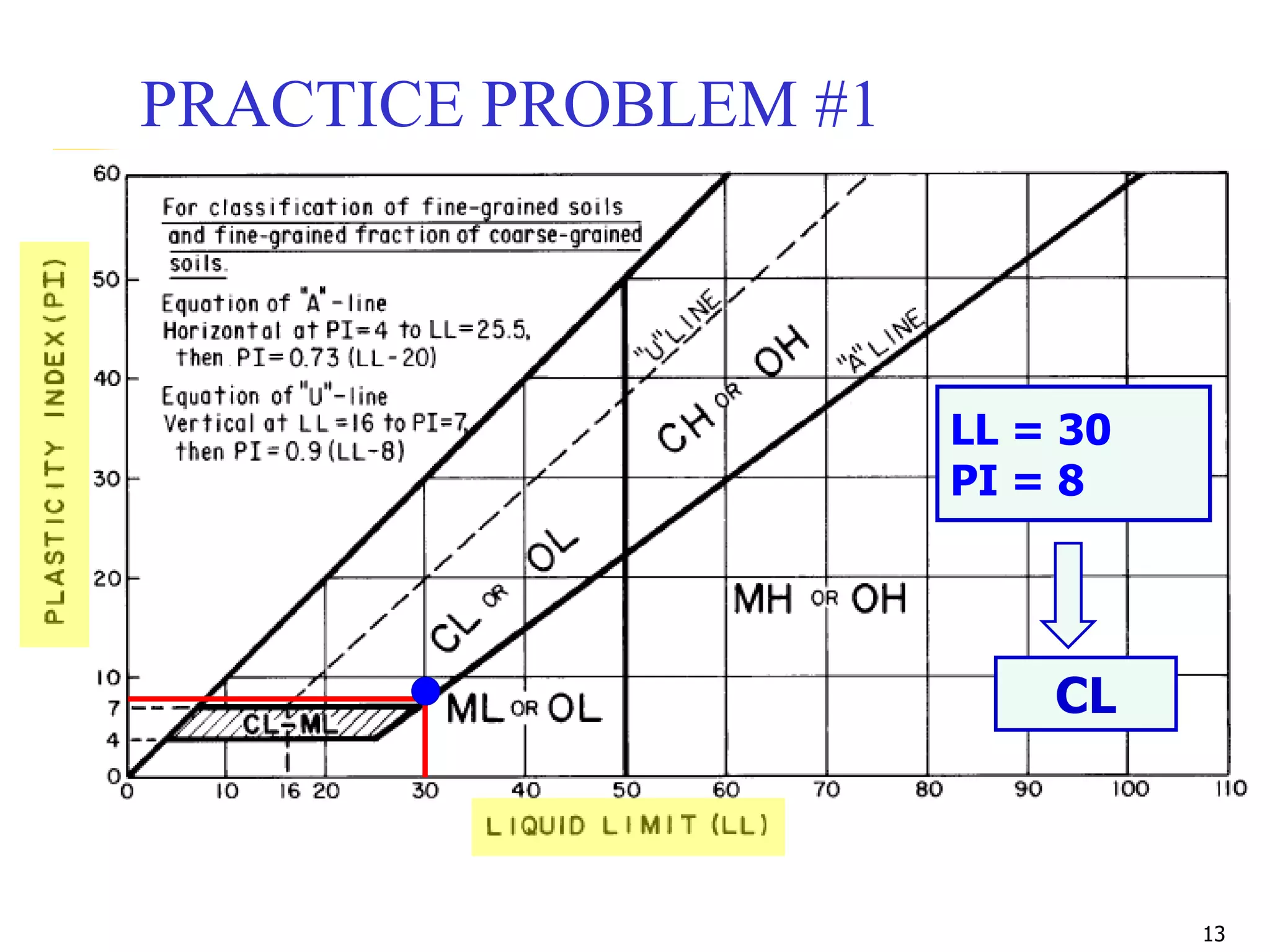
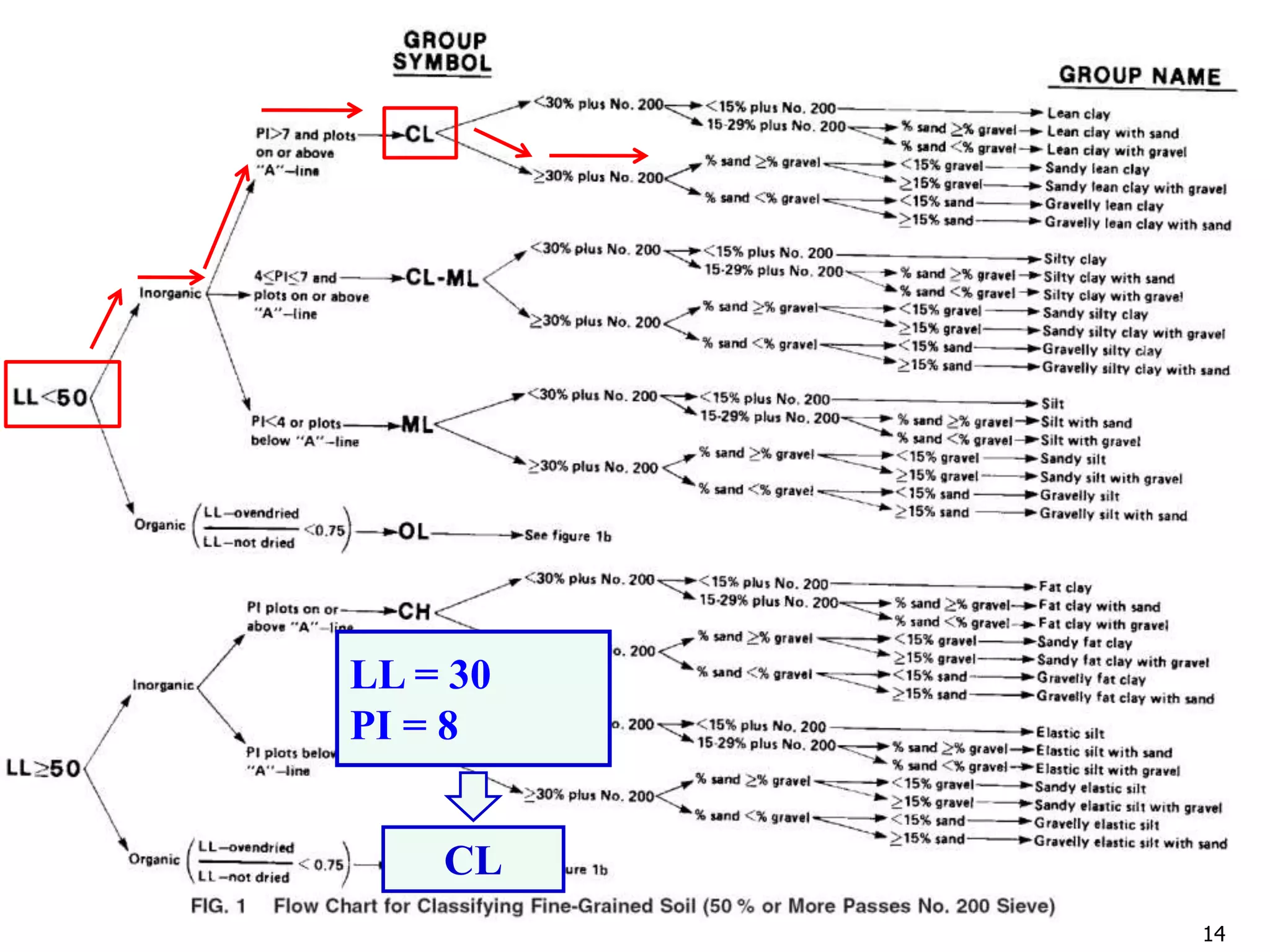
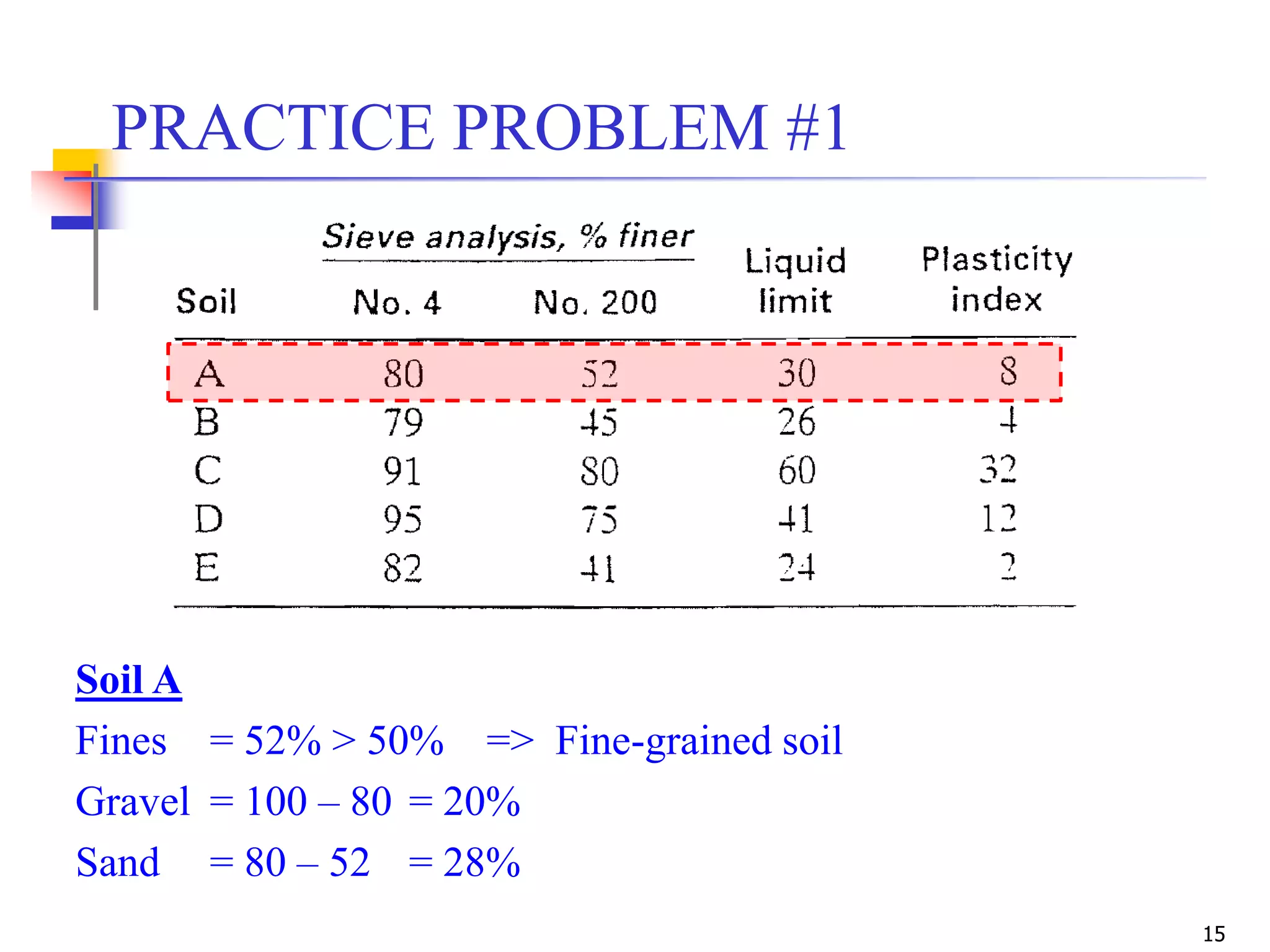
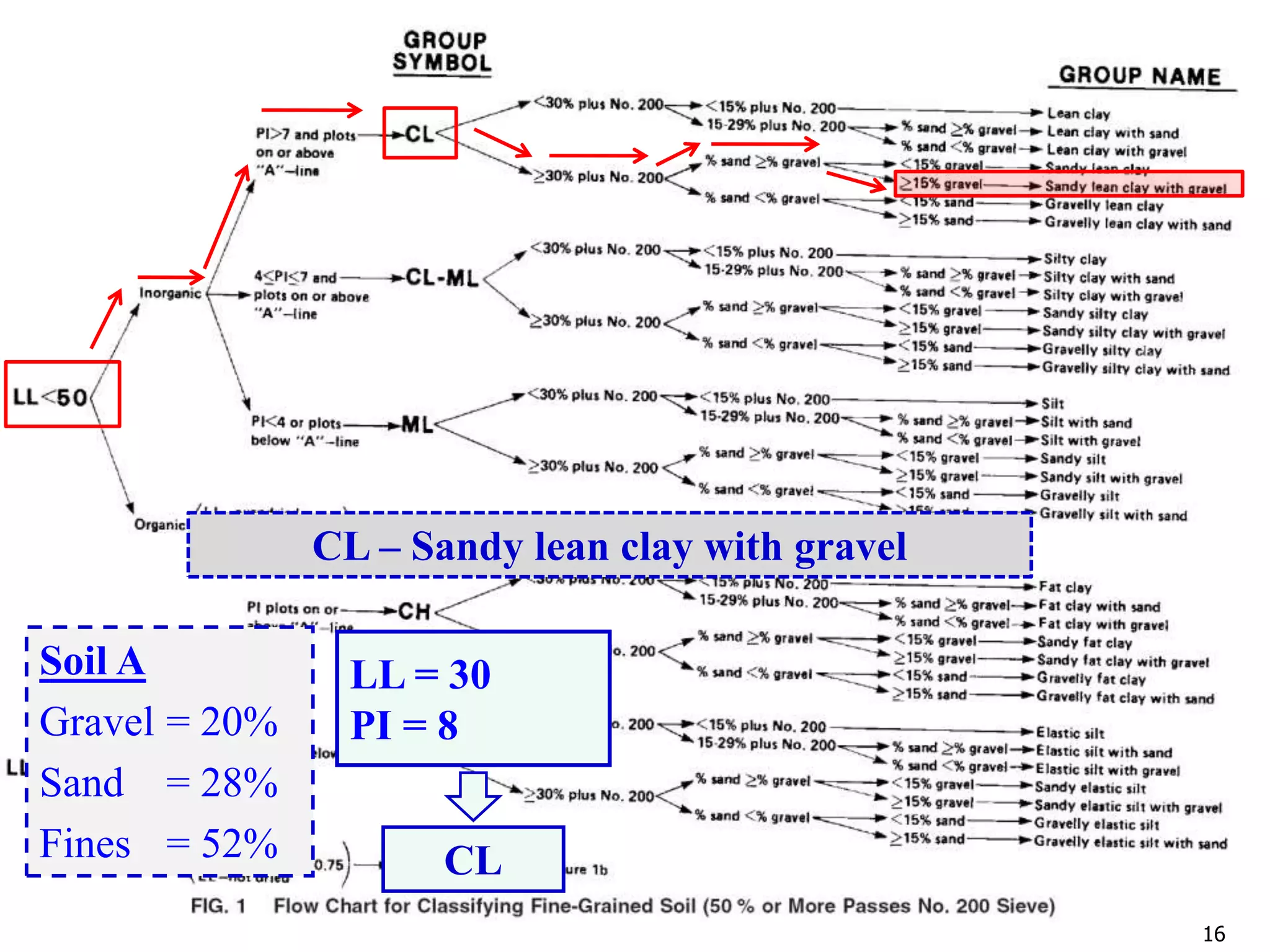
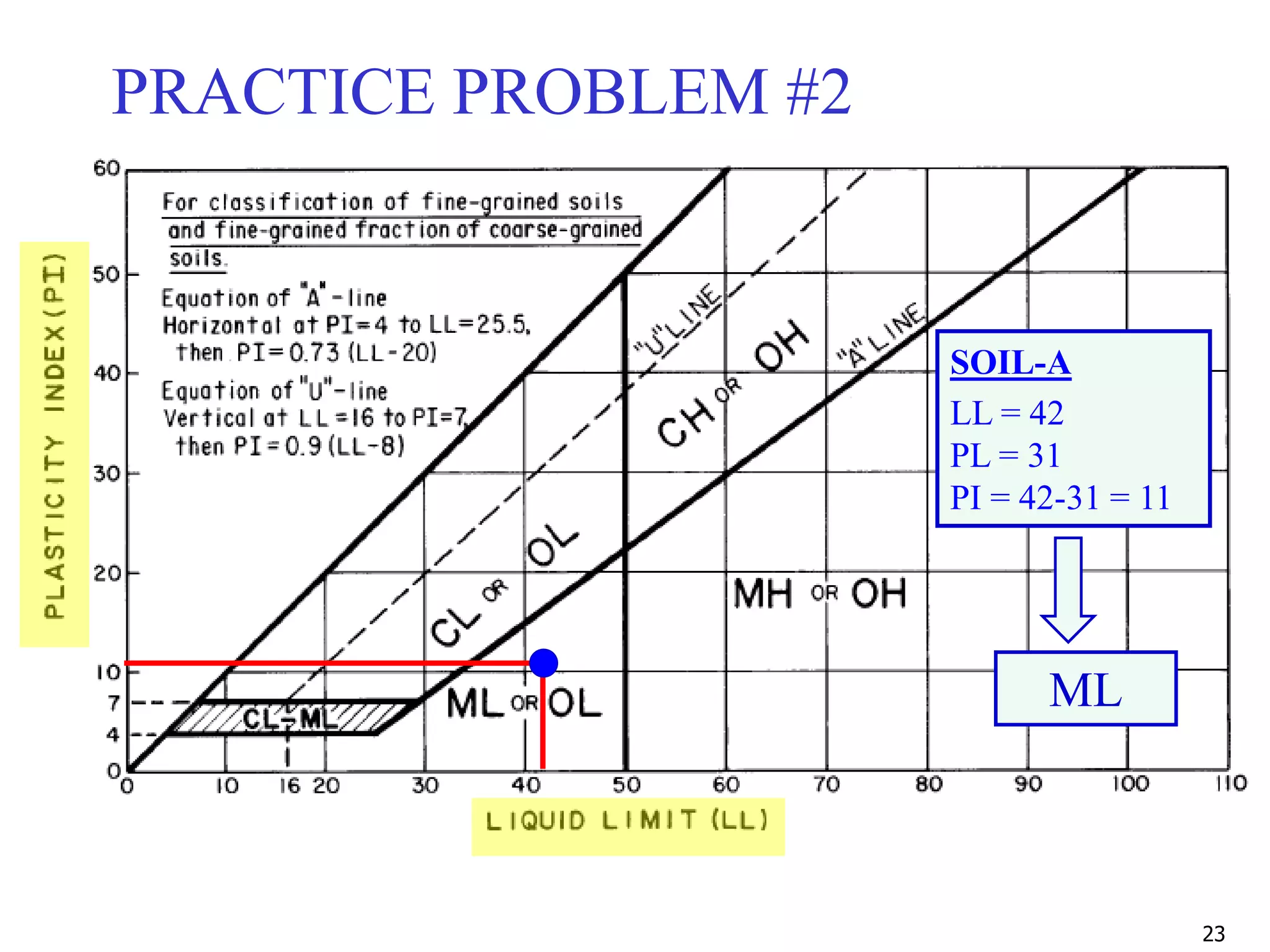
LL = 42
PL = 31
PI = 42-31 = 11
ML](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-180923183816/75/Geotechnical-Engineering-I-Lec-11-USCS-AASHTO-24-2048.jpg)