Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

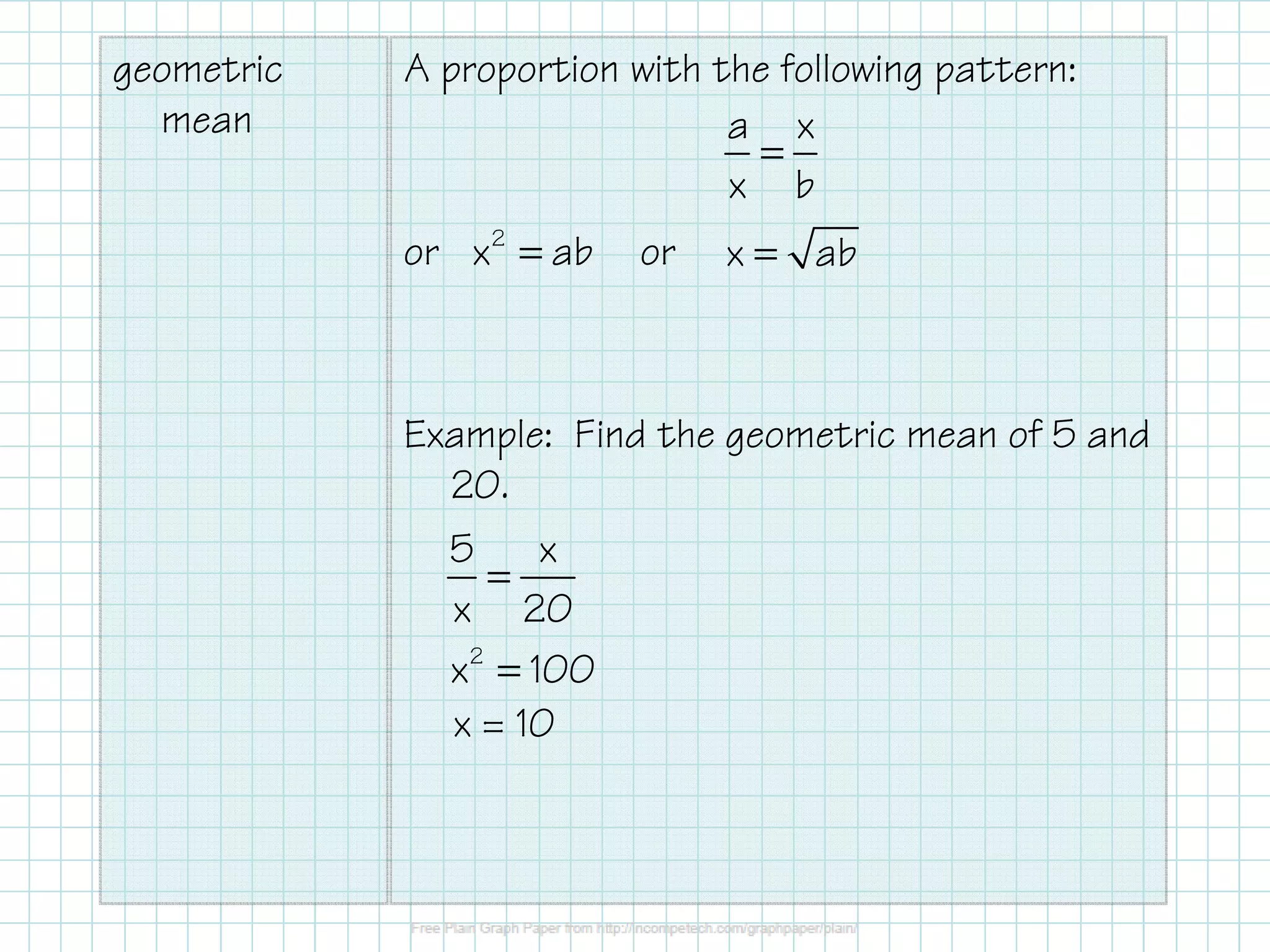
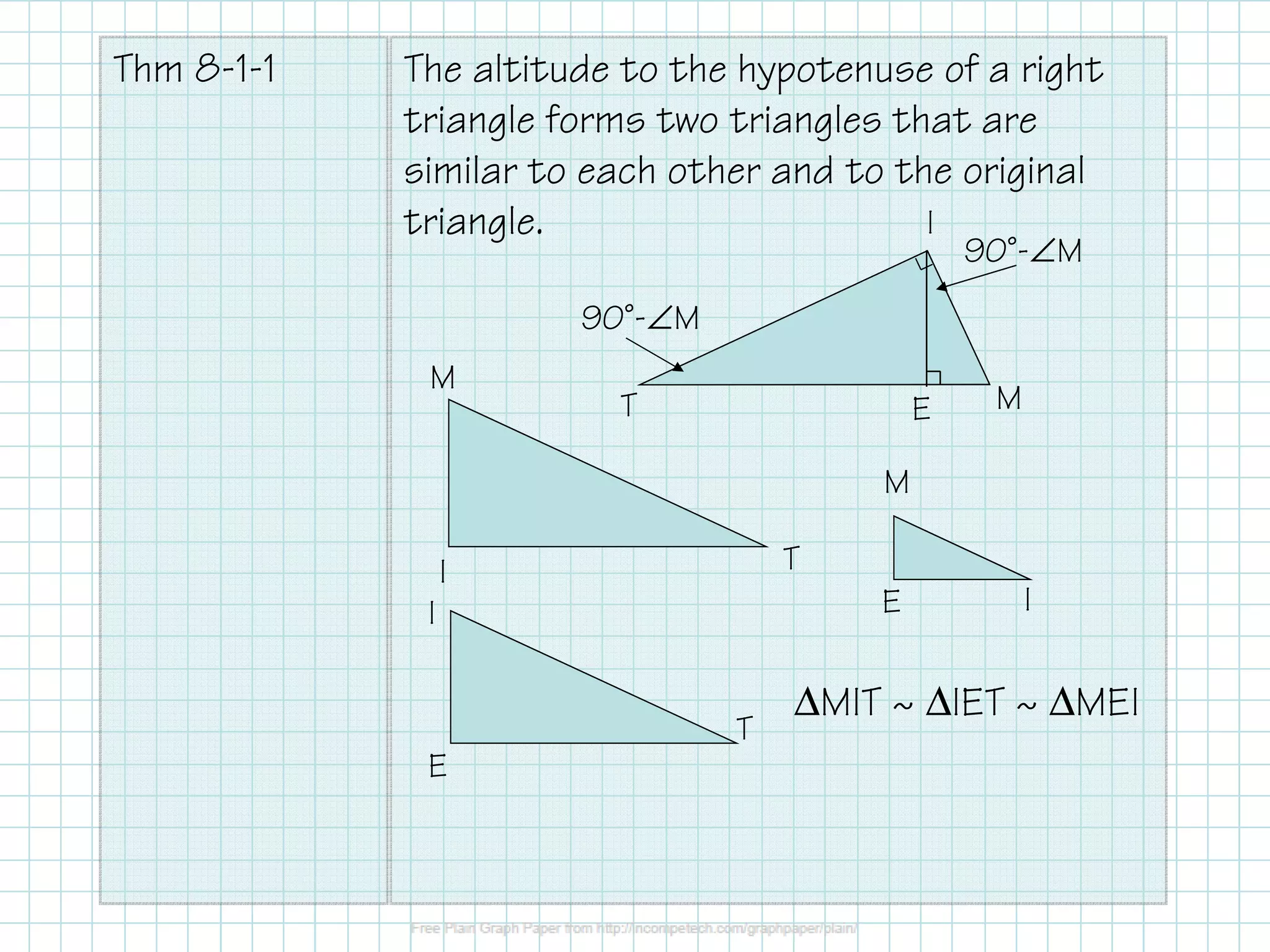
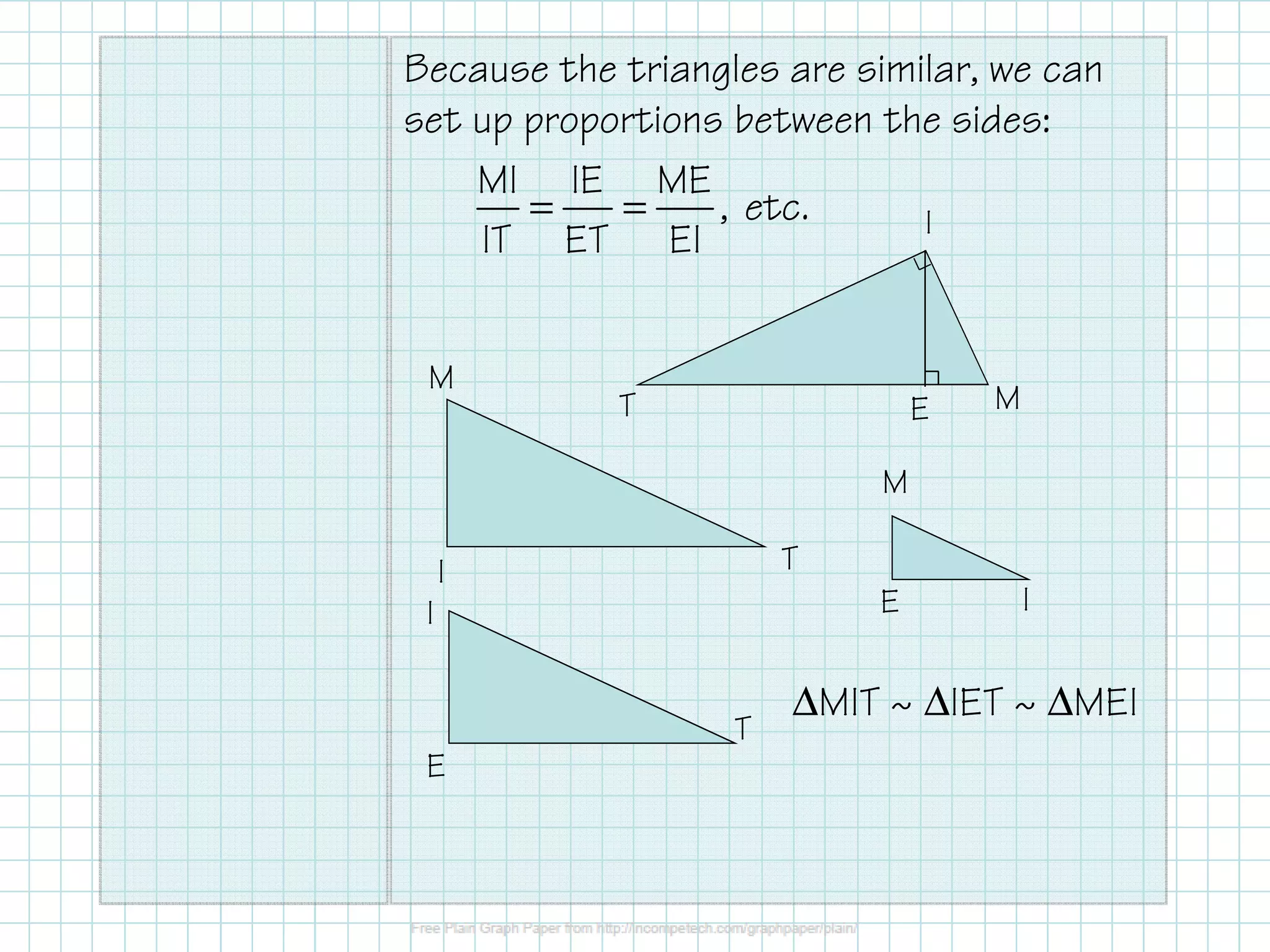
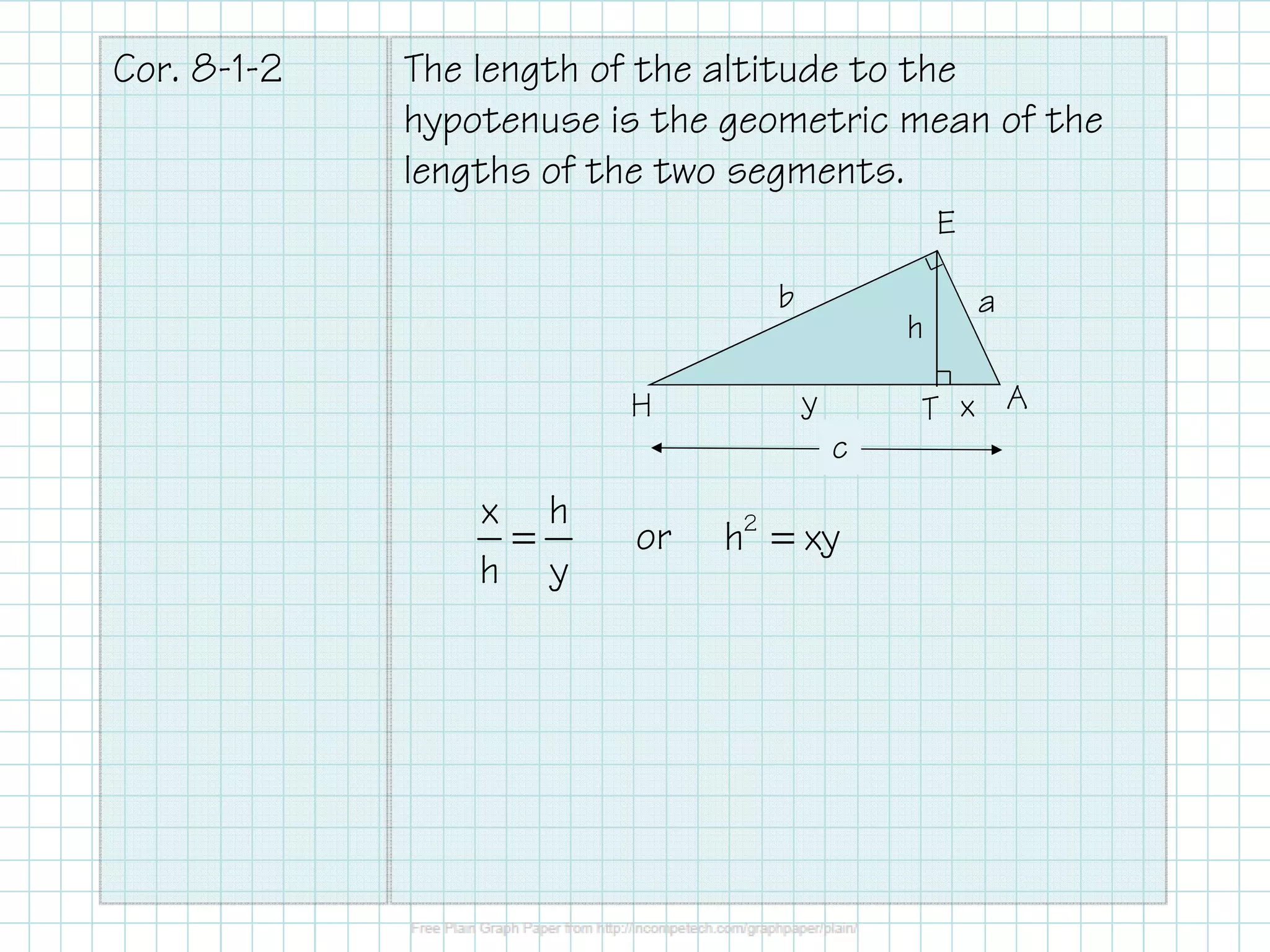

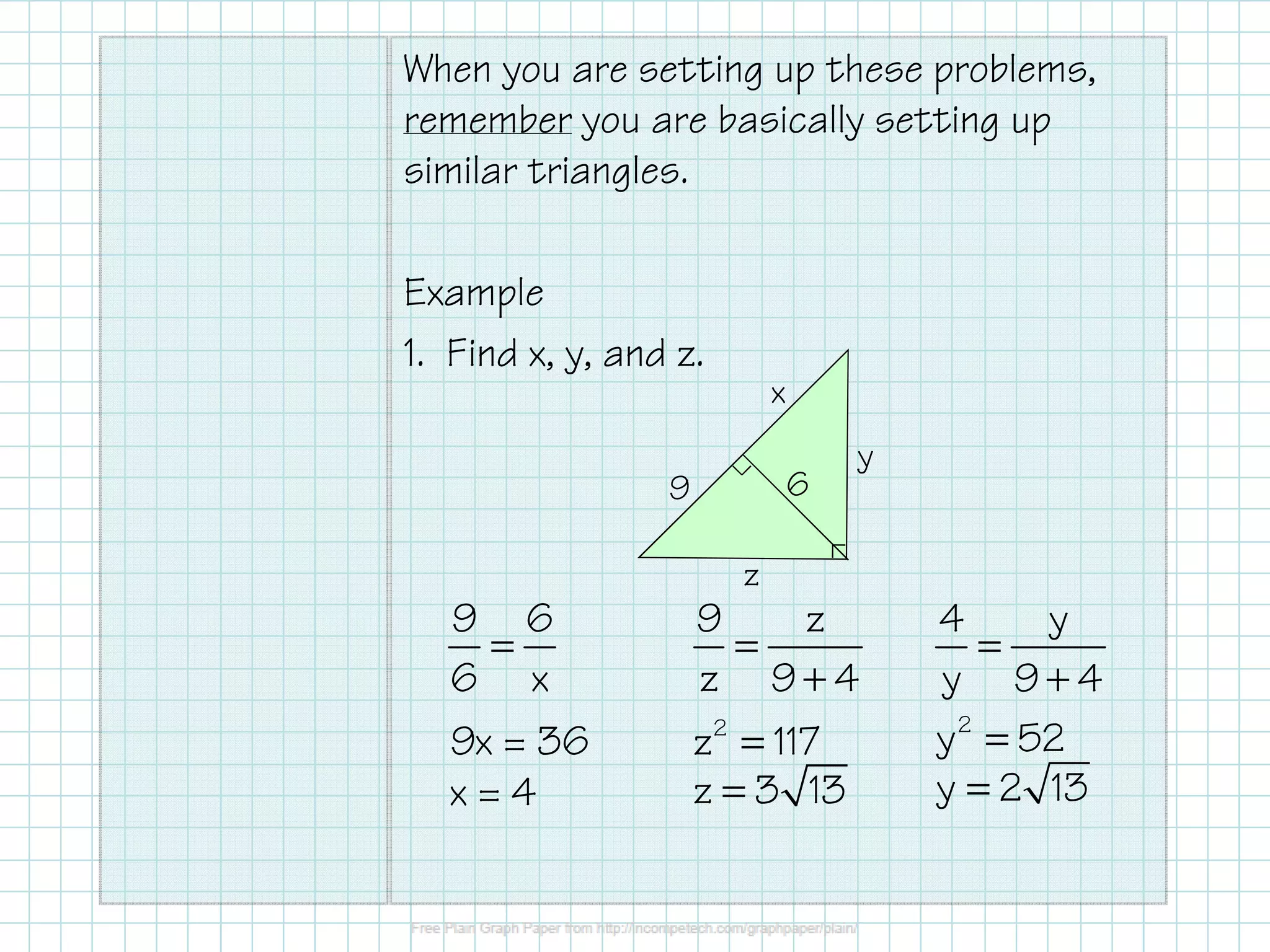
The document discusses the application of geometric means in right triangles, including how to find segment lengths and solve problems using similarity relationships. It explains important theorems related to the altitude to the hypotenuse and the legs of the triangles, highlighting how these are adeptly similar to each other. Examples provided illustrate the calculation of unknown lengths in these triangles.






