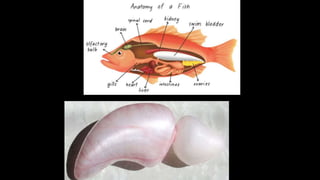
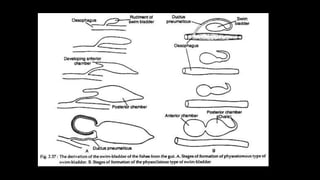
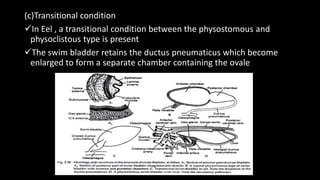
The document discusses the functions and structures of the air bladder and Weberian ossicles in bony fishes, explaining their roles in buoyancy regulation, hydrostatics, and sound production. It outlines the basic structure, types of swim bladders (physostomous, physoclistous, and transitional), and their functionality in respiration and equilibrium within water. The Weberian ossicles enhance sound transmission to the inner ear and are sensitive to changes in swim-bladder volume, acting as pressure registers and auditory organs.