Human geography is the study of cultural aspects found throughout the world, including language, religion, economic and governmental systems, and how they relate to the places where they originate and spread. Some key topics covered are:
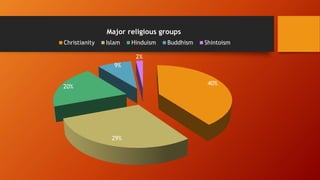
- The major world religions and their percentages of followers.
- Different types of economic systems including traditional, command, market, and mixed systems.
- Social classes and examples of class structures.
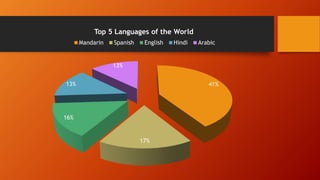
- The most commonly spoken languages worldwide and their percentages of speakers.
- A brief definition of music as an art form using sound and silence.














![What is Social Classes
• Social class (or simply "class"), as in a class society, is a set
of concepts in the social sciences and political
theory centered on models of social stratification in which
people are grouped into a set of hierarchical social
categories,[1] the most common being the upper, middle, and
lower classes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/humangeography-140619081928-phpapp01/85/Human-Geography-16-320.jpg)