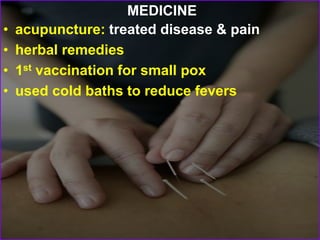
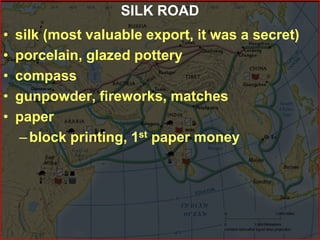
The civilization that began along China's river systems 3,500 years ago continues today due to China's relative geographic isolation. China's geography, with natural barriers like mountain ranges and long rivers, isolated it from other civilizations, causing early settlers to develop self-sufficient goods rather than trade. Throughout China's history, dynasties like the Shang, Zhou, Qin, and Han expanded its political boundaries and advanced Chinese culture, establishing a Confucian social philosophy emphasizing family duties that still influences Chinese society. China saw itself as the center of civilization amid surrounding "barbarians."