Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times

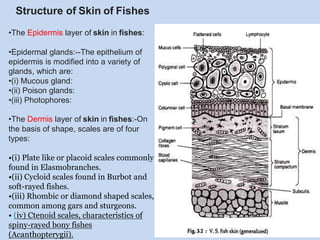
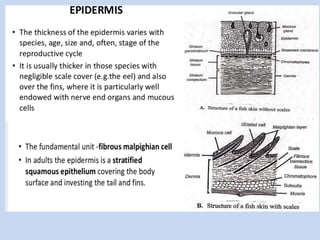
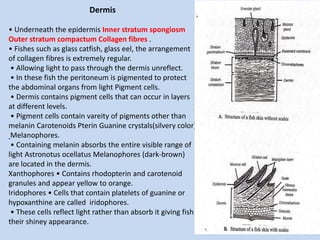

The document discusses the structure of fish skin, noting that it consists of an epidermis layer containing glands like mucous and poison glands, and a dermis layer where scales come in four types - placoid, cycloid, rhombic, and ctenoid. The dermis contains pigment cells like melanophores, xanthophores, and iridophores that contain pigments like melanin, carotenoids, and guanine crystals which give fishes their color and ability to reflect light. References on fish skin structure include modern textbooks by Kotpal and books on zoology by S.M. Sexsena and




