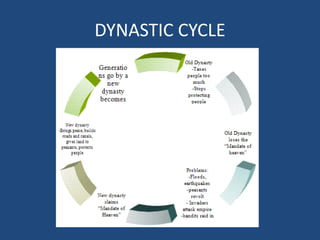
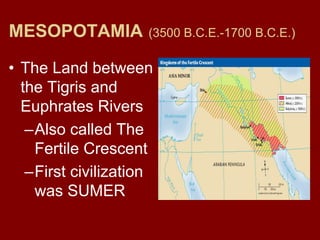
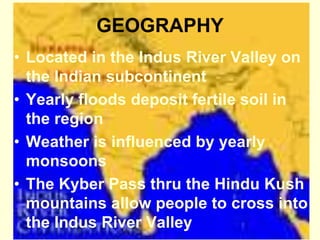
This document provides an overview of early river valley civilizations including Mesopotamia, Ancient Egypt, the Indus River Valley civilization, and China. It discusses the key factors that led to the rise of civilization in fertile river valleys between 3500-1700 BCE, including abundant crops, food surpluses, and waterways for transportation. For each civilization, it summarizes the impact of geography, political structures, economies, religions, social hierarchies, innovations, and arts that developed. It also briefly outlines the Phoenicians and Hebrews as other influential ancient peoples.






















![INNOVATIONS
• Well-planned cities (streets at 90o
angles)
• Sewer systems and garbage bins
• Private and public baths
• Kilns for baking bricks
• Public wells provided water
• Written language (mostly
pictographic)
[The Arayans brought the Sanskrit
language when they took over]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rivervalleycivilizations-230131044720-2fb07ae0/85/RIVER-VALLEY-CIVILIZATIONS-ppt-25-320.jpg)