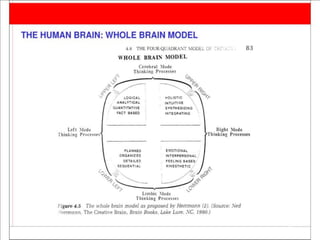
The document discusses resources, curriculum, and learning processes for engineering students. It notes that engineering curriculum includes basic sciences, engineering sciences, and applied sciences. The successful student is motivated, takes advantage of university resources, and is interested in the engineering curriculum. Determinants of efficient learning include meaningful material, psychological state, and learning strategies like practice and summaries. Creativity is also discussed as important for engineers, with the creative process involving recognizing problems, intense focus, relaxation, illumination of solutions, and evaluation.