This document provides an overview of industrial robot technology, including:
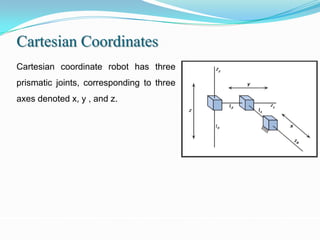
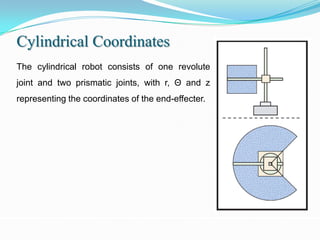
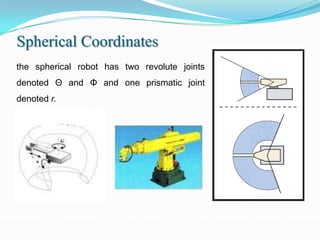
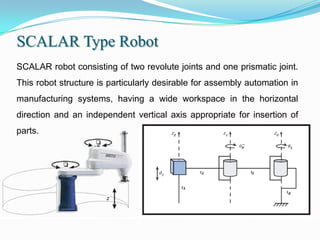
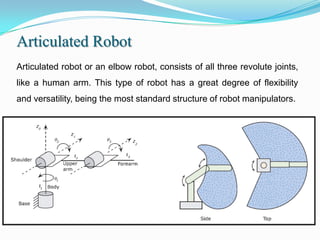
1) It outlines different robot coordinate systems (Cartesian, cylindrical, spherical) and robot types (SCARA, articulated).
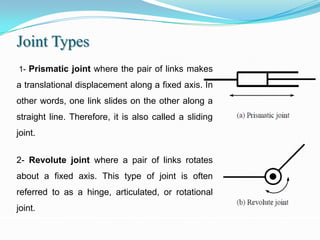
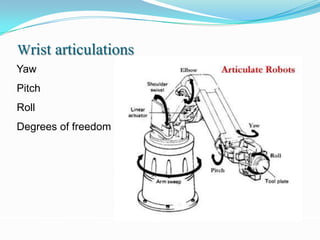
2) It describes the different types of robot joints (prismatic and revolute) and wrist articulations (yaw, pitch, roll).
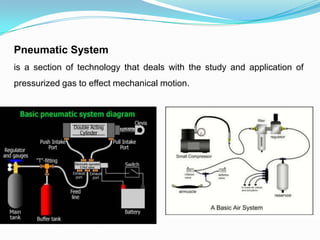
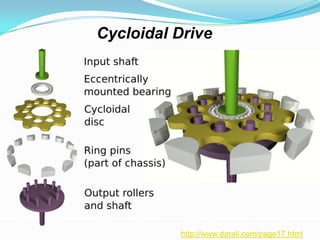
3) It discusses various drive mechanisms for robot motion including mechanical drives using ball screws or gears, and pneumatic, hydraulic, and electrical systems. It provides examples of speed reducers like harmonic drives and planetary gearheads.