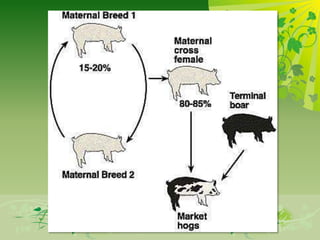
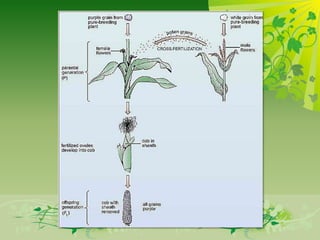
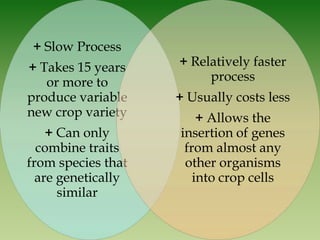
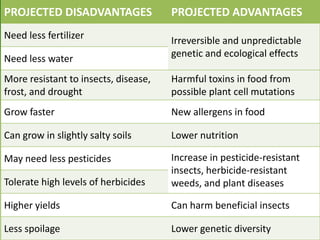
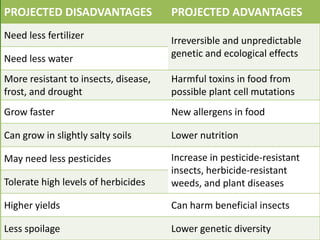
This document discusses genetically modified foods (GMFs) and outlines some of their potential risks and benefits. It begins by differentiating genetic engineering, which alters an organism's DNA, from traditional crossbreeding. The document then provides examples of GMFs like crops modified to be pesticide-resistant. Both the projected disadvantages of GMFs, like unpredictable genetic effects and increased resistant pests, and advantages, like higher yields and need for less water, are listed. It concludes by asking readers to evaluate the most important risks and benefits of GMFs.