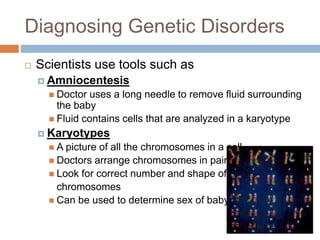
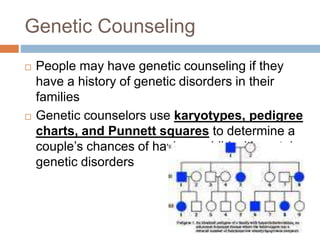
This document discusses several human genetic disorders including cystic fibrosis, sickle-cell disease, hemophilia, Huntington's disease, and Down syndrome. Genetic disorders are abnormal conditions caused by mutations in genes or chromosomes that are inherited or can be passed down from parent to offspring. The document describes the causes and symptoms of each disorder and current treatments. It also discusses tools used to diagnose genetic disorders like amniocentesis, karyotypes, and the role of genetic counseling in assessing family histories and risks.