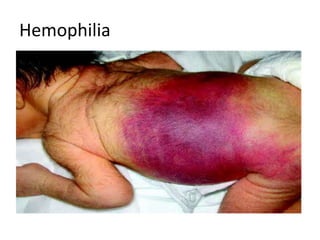
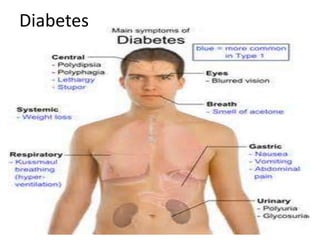
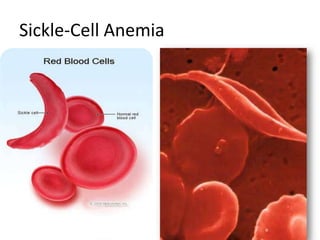
Hemophilia is a genetic disease where males have excessive bleeding due to failures in blood clotting. Symptoms include prolonged bleeding after procedures like circumcision or vaccinations. Treatment involves regular injections of clotting factor replacements. Diabetes is caused by the body's inability to properly metabolize or respond to insulin, leading to excessive urination and thirst. It has both genetic and environmental causes. Sickle-cell anemia causes red blood cells to take on a sickle shape, which can block blood flow and lead to infection before age 20 if untreated. It predominantly affects those of African descent.