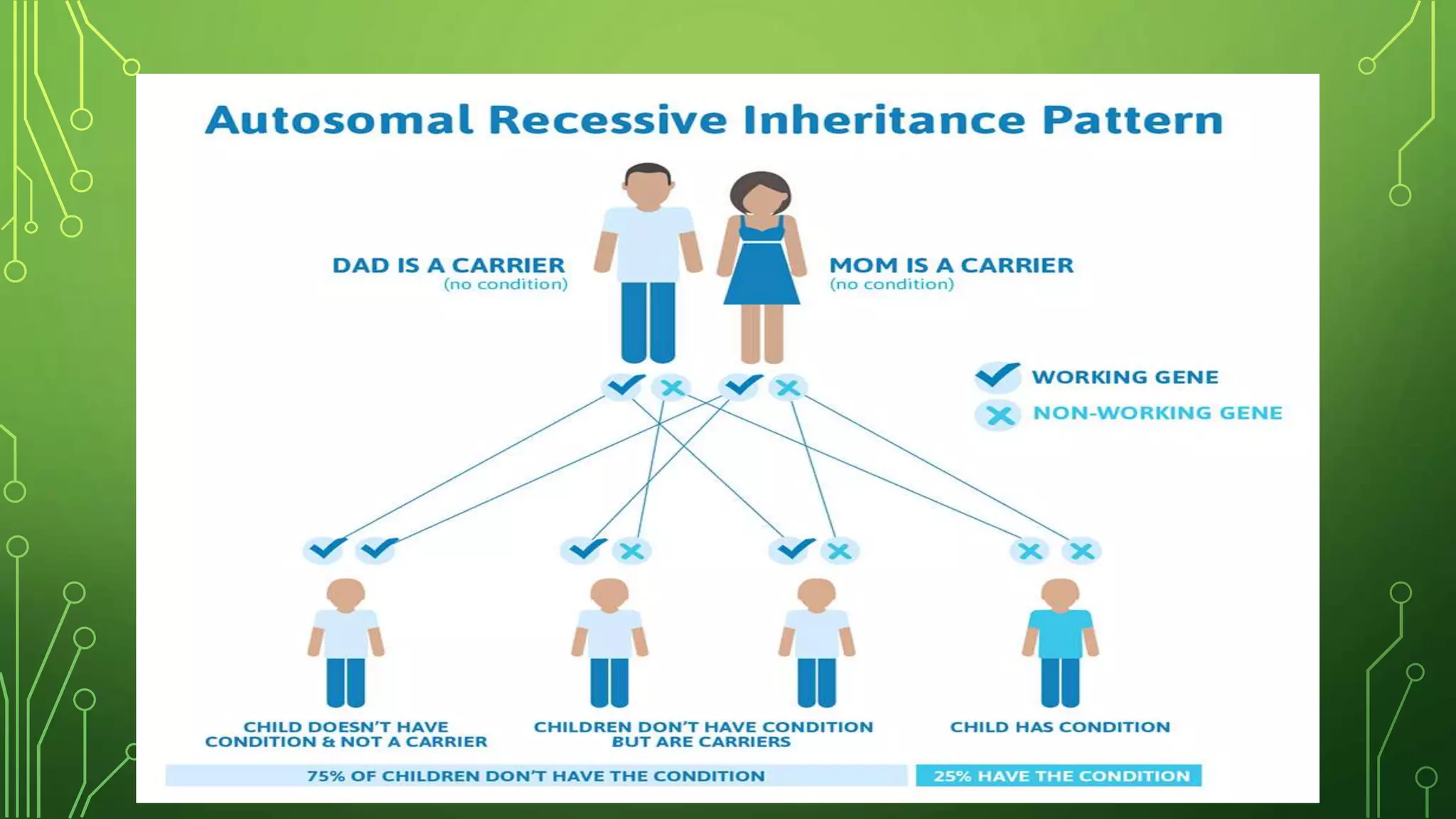
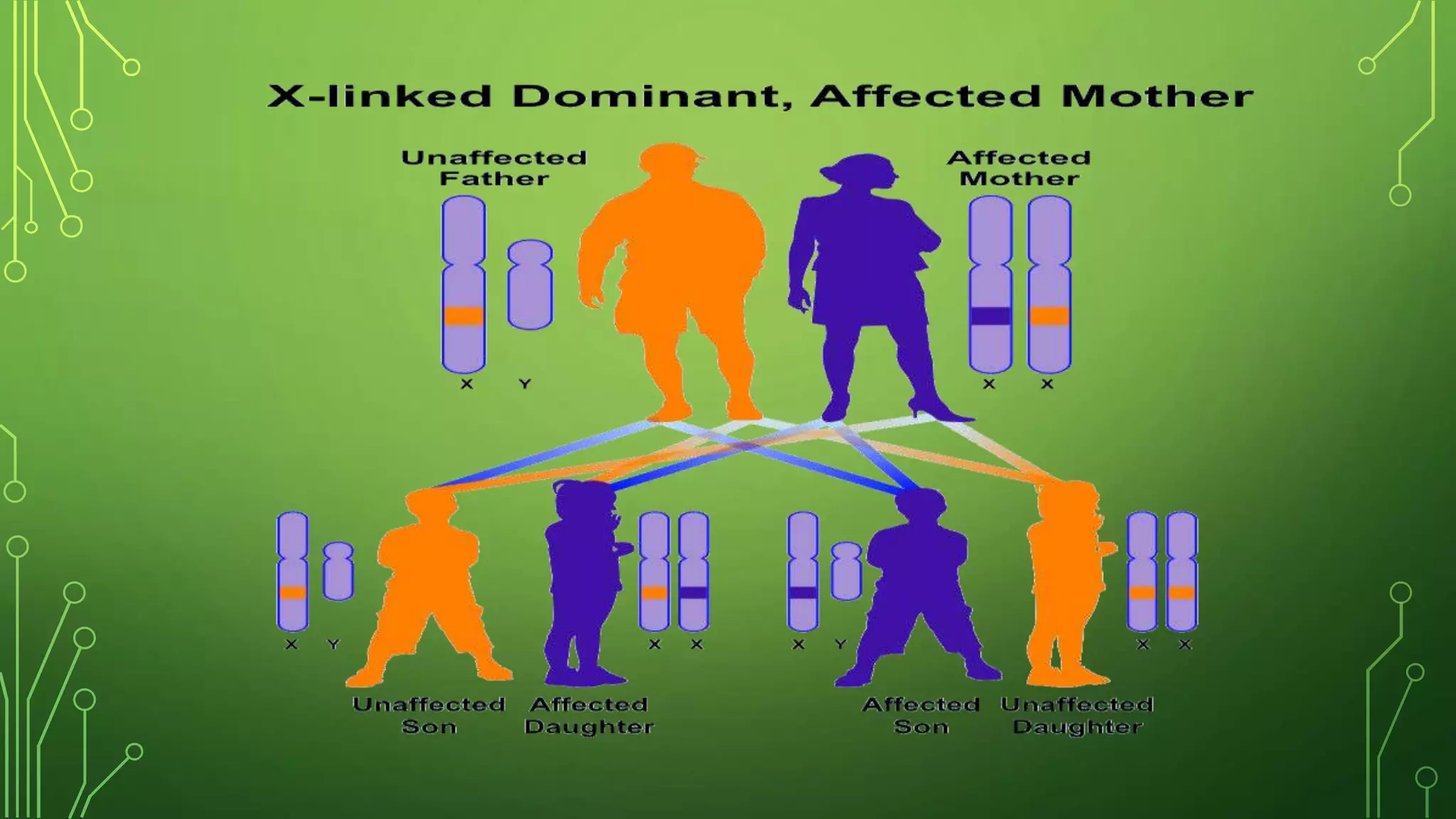
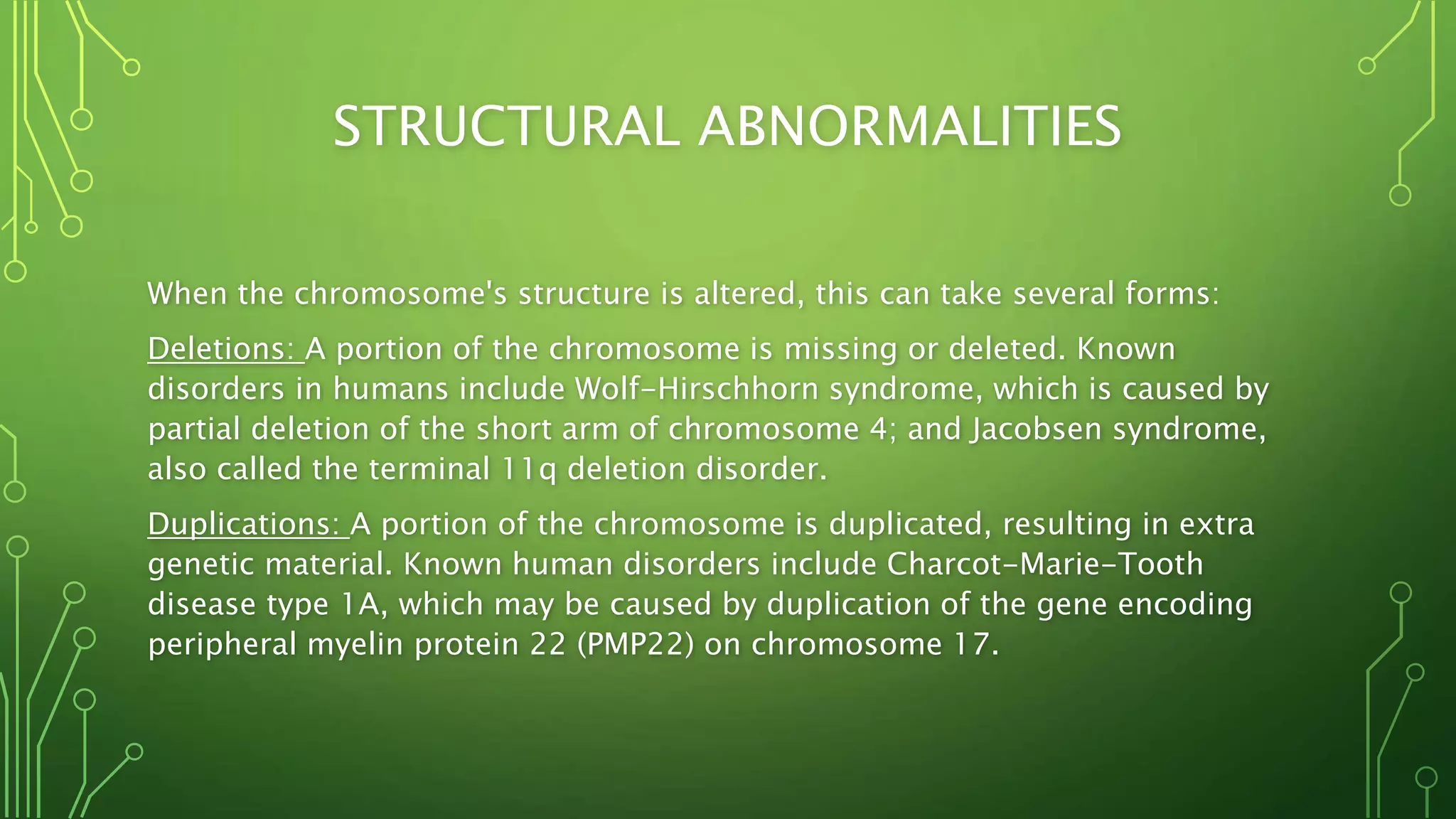
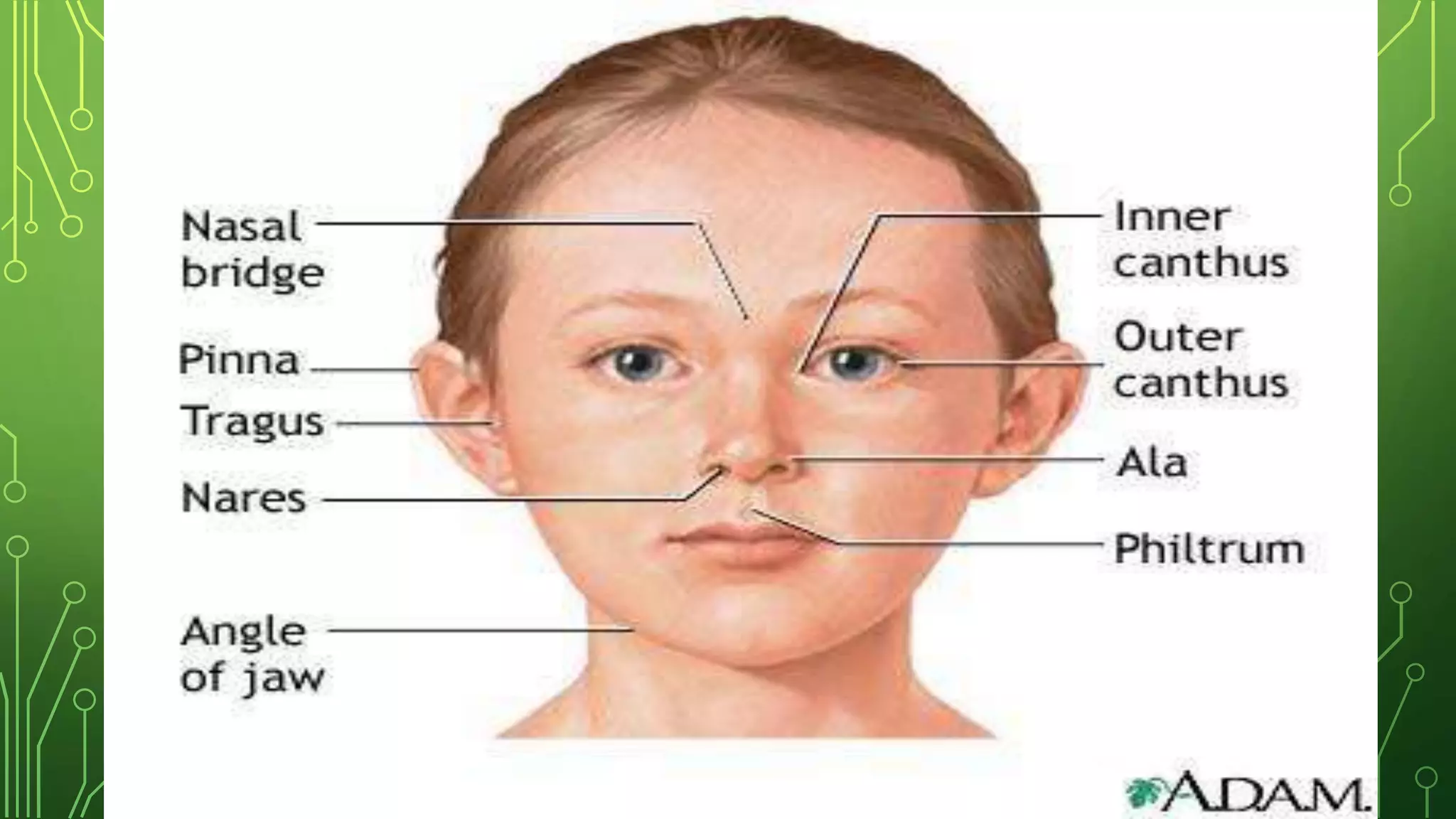
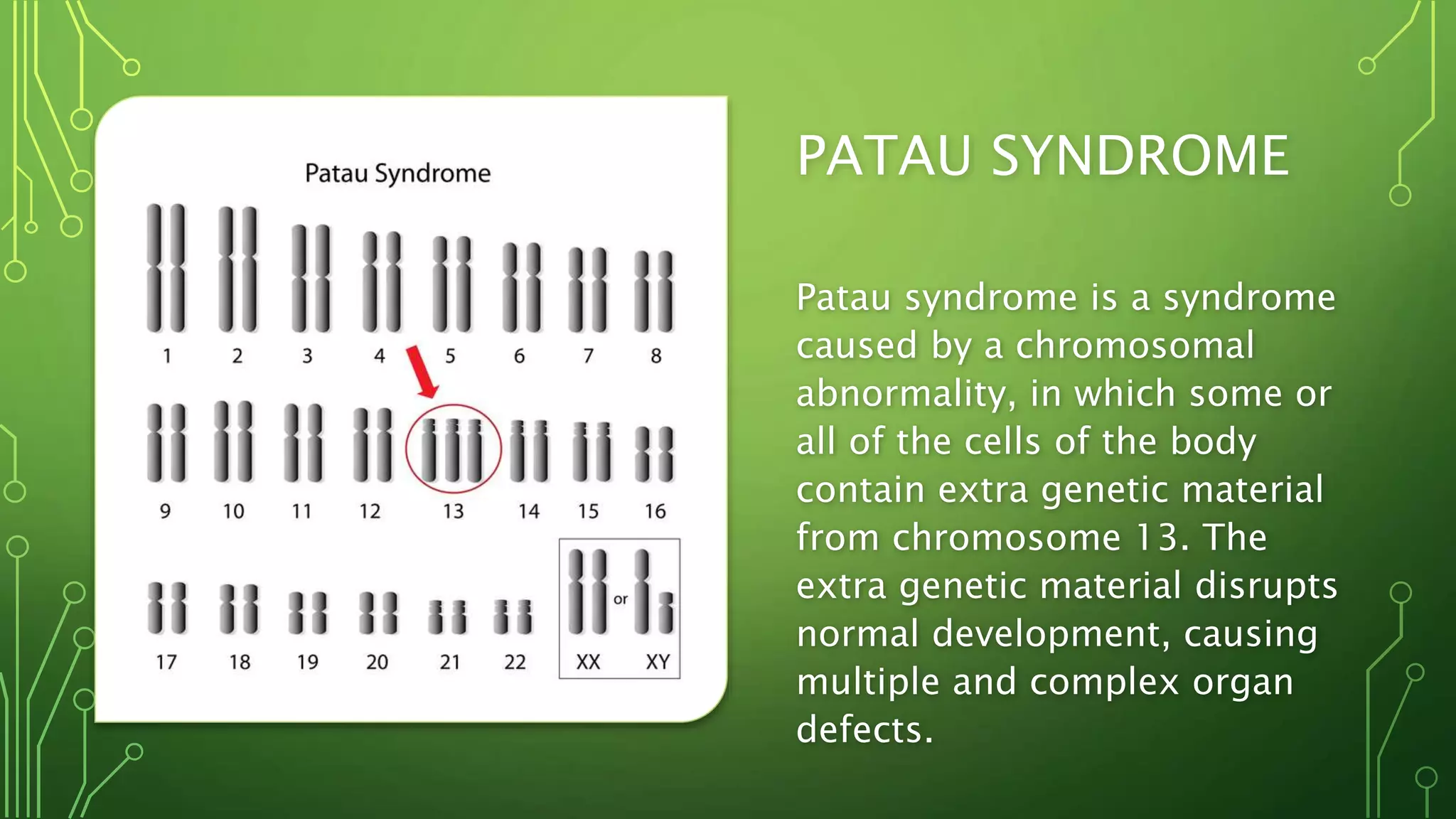
This document discusses genetic disorders, their causes, classification, and examples. It begins by defining genetics and genetic disorders. Genetic disorders can be caused by mutations in one gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (multifactorial). They are classified based on inheritance patterns (autosomal dominant, recessive, X-linked) or chromosome abnormalities (numerical, structural). Examples of common single-gene disorders discussed include cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Huntington's disease. Examples of chromosomal disorders include Down syndrome, Edward syndrome, and Turner syndrome. Cancer is also discussed as having both genetic and environmental causes.