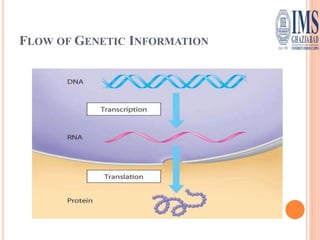
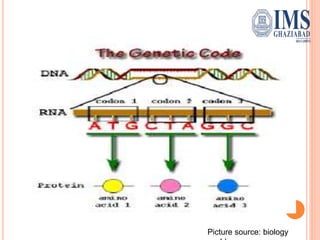
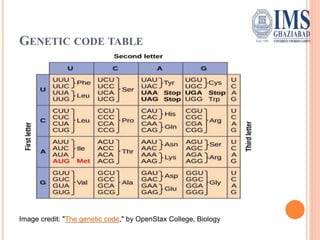
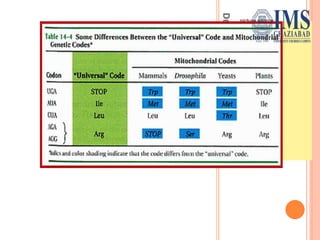
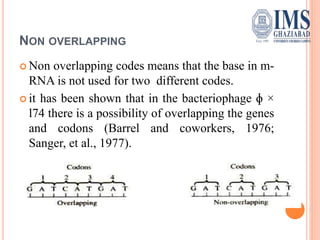
The document explains the genetic code, defined as the sequence of DNA nucleotides read as codons that determine amino acid sequences in protein synthesis. It details the characteristics of the genetic code, including its triplet nature, universality, and properties such as being comma-less and non-overlapping. Historical contributions from key scientists in deciphering the genetic code are also highlighted.