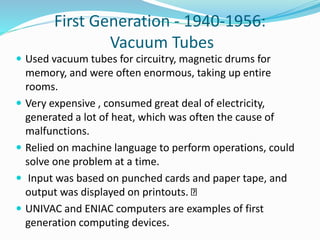
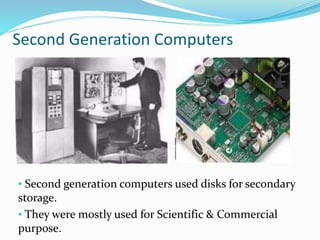
The document summarizes the five generations of computers from the 1940s to present. The first generation used vacuum tubes, were large in size, and could only solve one problem at a time. The second generation used transistors, were smaller and more efficient. The third generation used integrated circuits and operating systems. The fourth generation used microprocessors and were smaller, more powerful personal computers. The fifth generation, present and beyond, involves artificial intelligence and parallel processing to develop self-learning computers that can understand natural language.