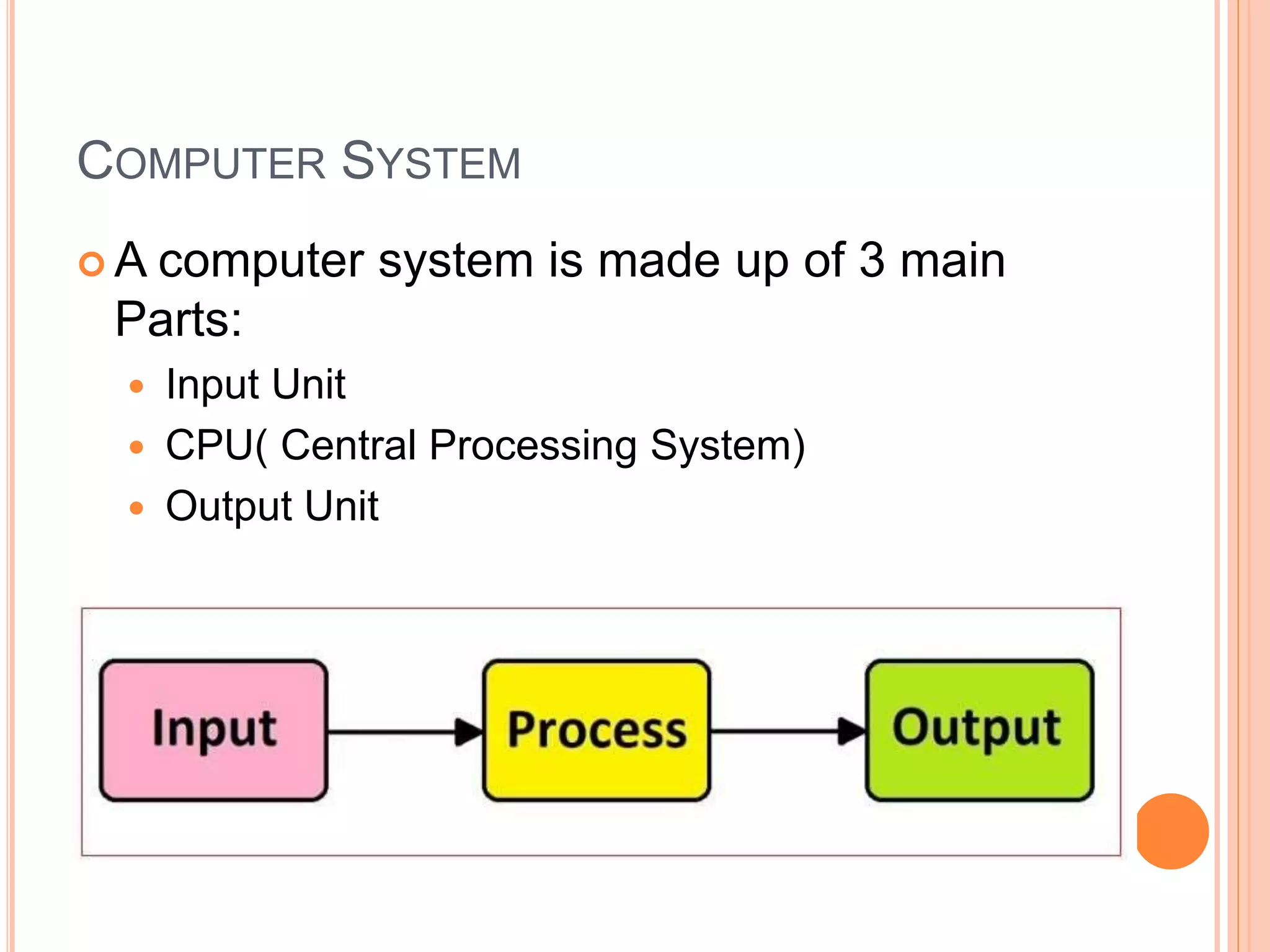
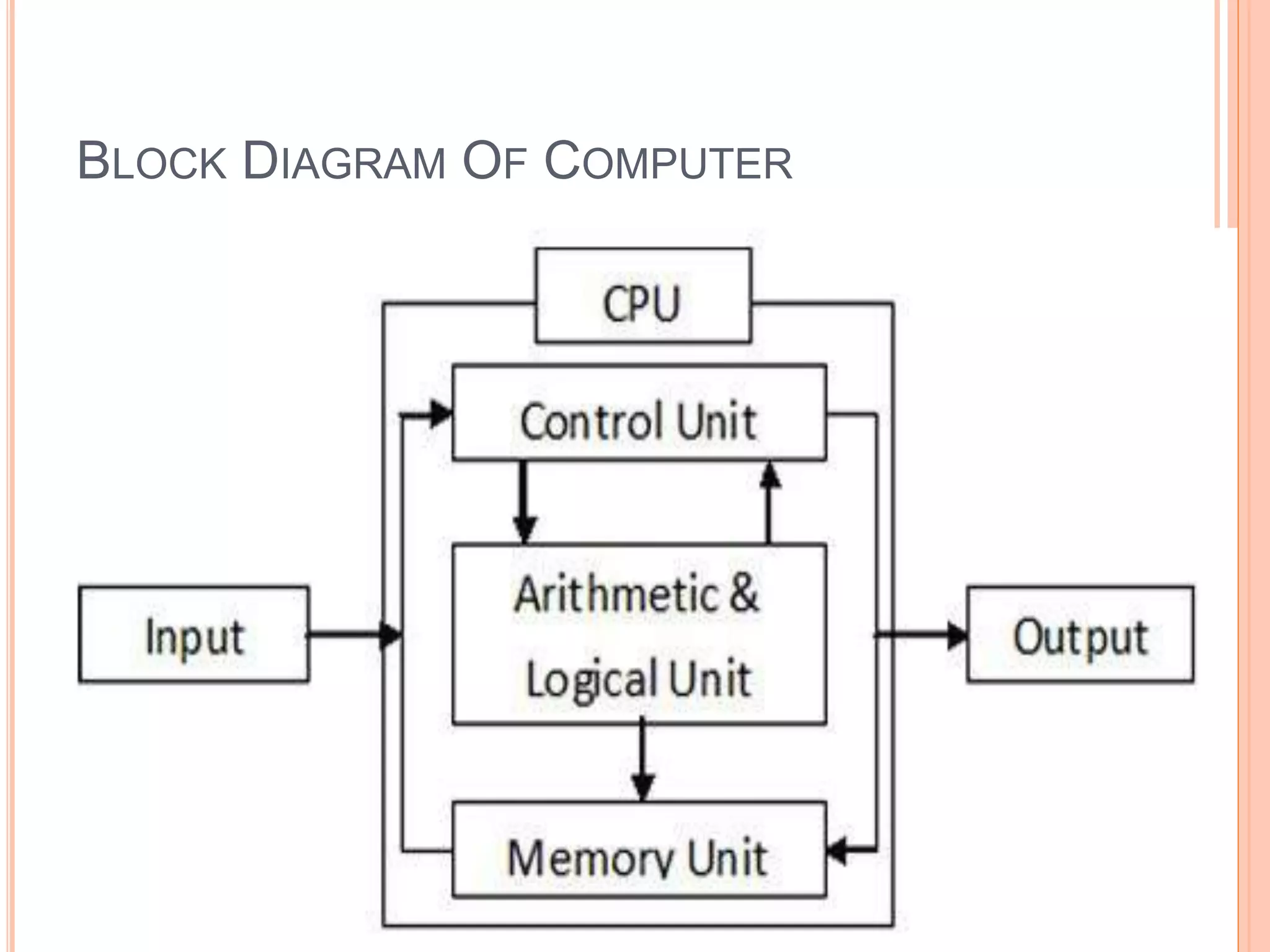
This document discusses computer memory units and storage capacity. It defines the basic units of storage like a bit, byte, kilobyte, megabyte, etc. and explains how they relate to each other. It then provides a block diagram of the main components of a computer system including the input, CPU and output units. The CPU contains the control unit, ALU and memory unit. It describes the functions of each of these components and how they work together to process data in the computer.