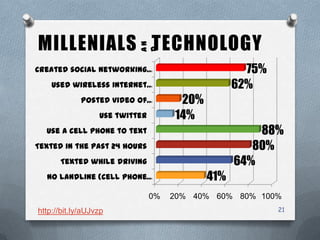
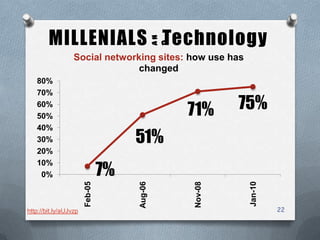
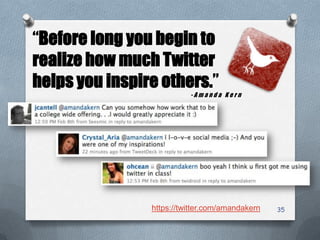
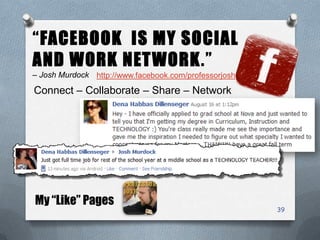
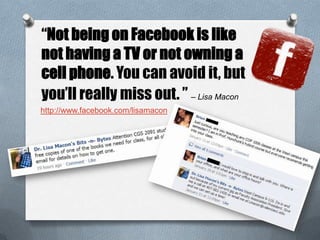
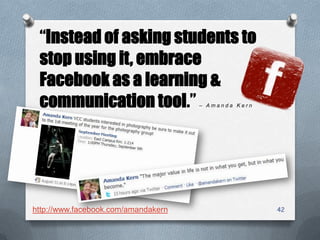
The presentation outlines characteristics and engagement strategies for various generational cohorts in the workforce, particularly focusing on Baby Boomers, Generation X, and Millennials. It highlights the differing work ethics, communication styles, and motivational messages for each generation, stressing the importance of tailored approaches in training and organizational involvement. Additionally, it discusses the impact of technology on Millennials, their learning preferences, and the need for interactivity in educational and workplace settings.