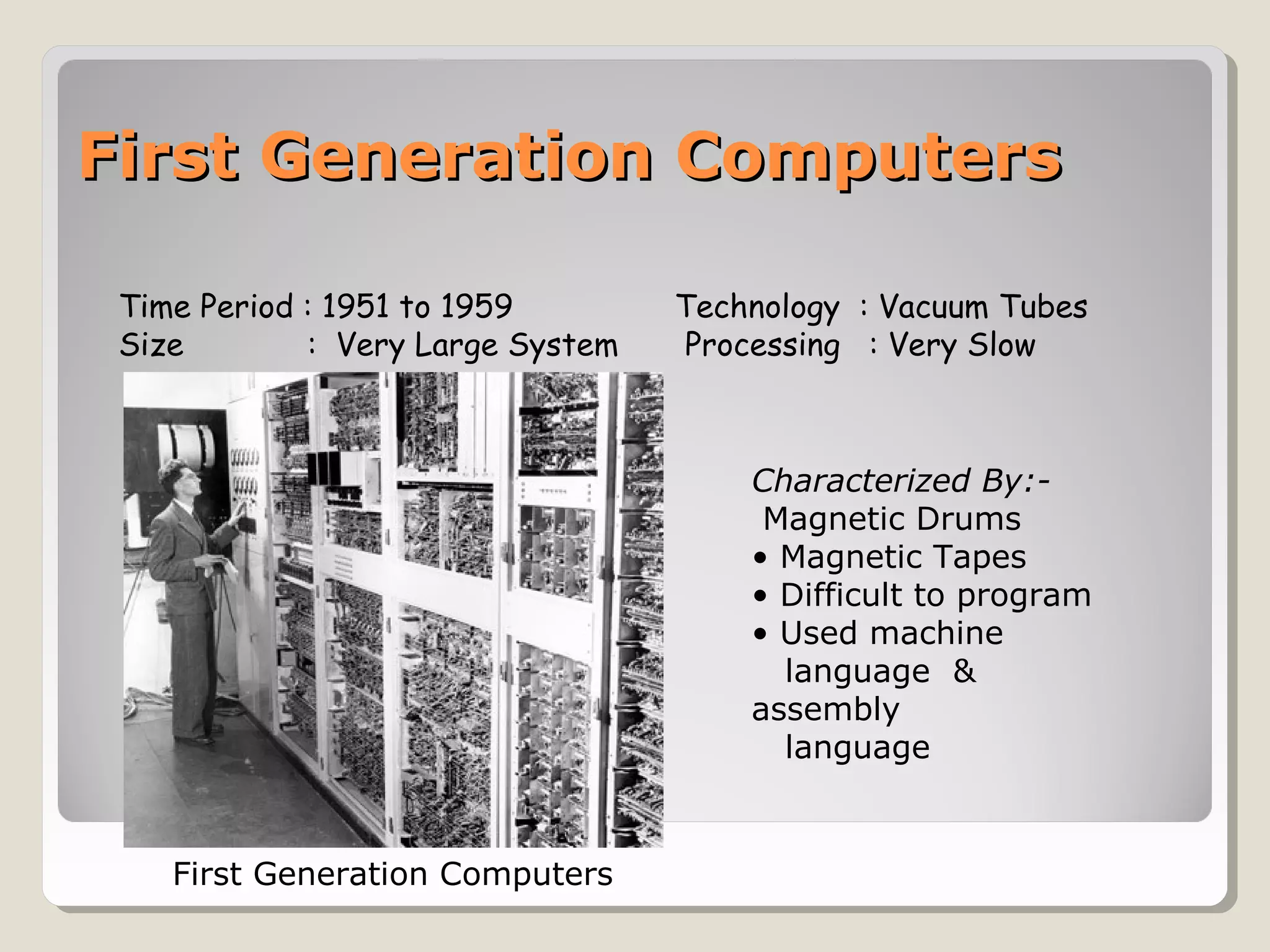
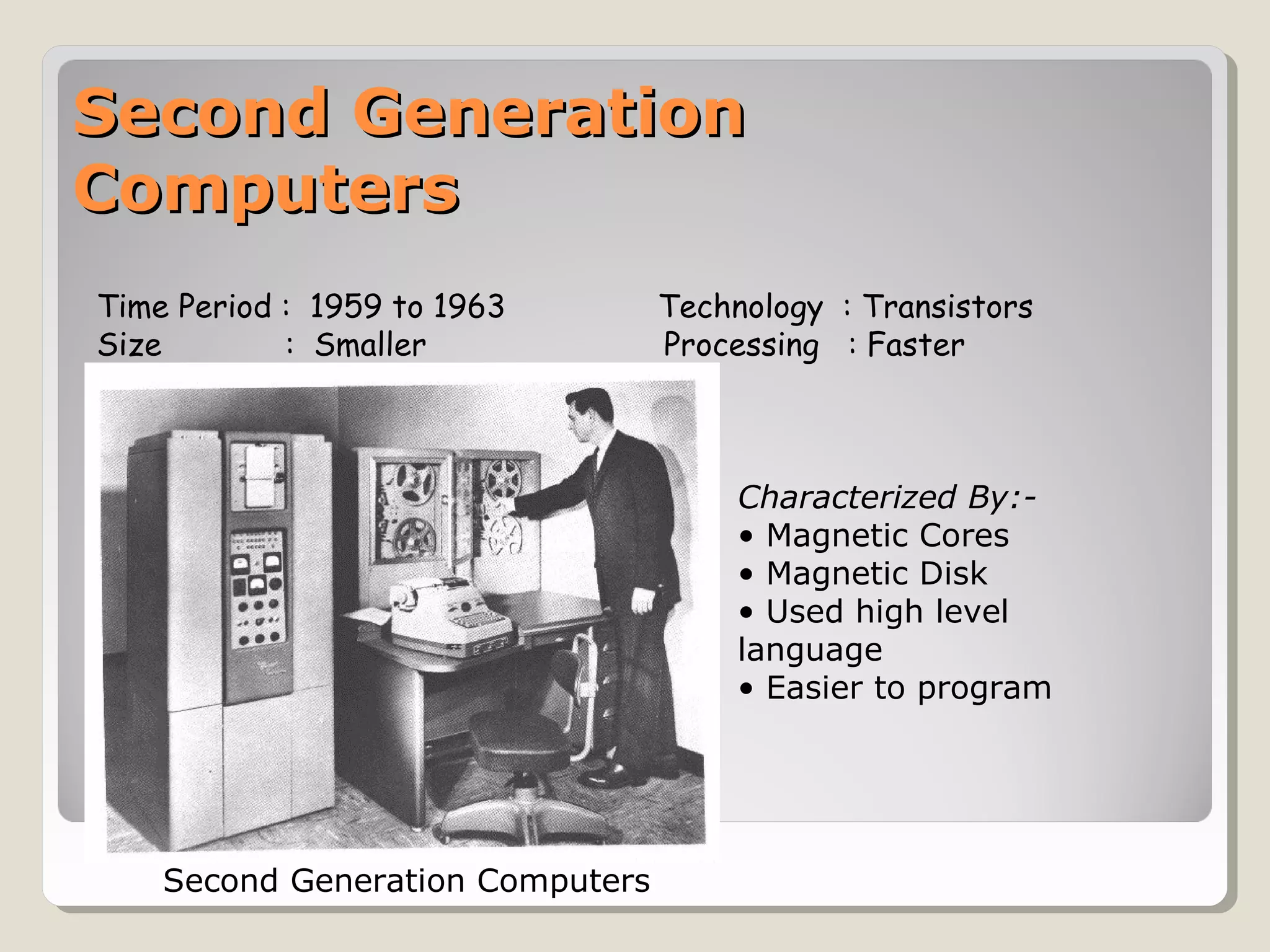
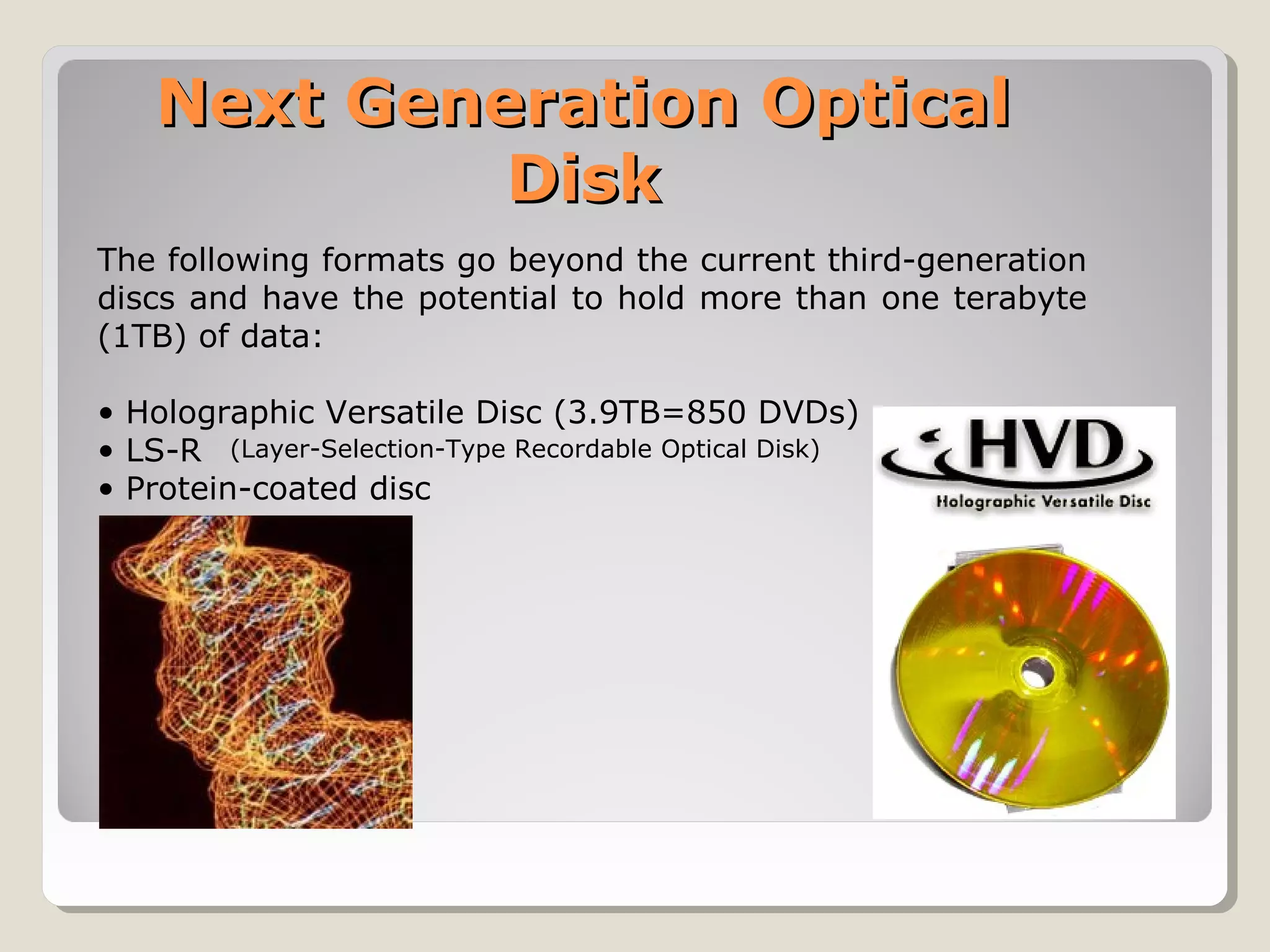
The document outlines the evolution of computers across five generations, detailing their time periods, technologies, sizes, processing speeds, and key characteristics. It highlights advancements from vacuum tubes in the first generation to the integration of artificial intelligence in the fifth generation, along with advancements in data storage technologies like holographic discs. Additionally, it discusses the promising future of touch screen technology with innovations like Synaptic's 'clear pad.'