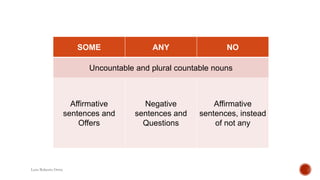
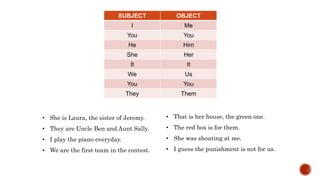
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various English grammar topics including countable and uncountable nouns, the use of pronouns, simple past tense constructions, and advice using the verb 'should'. It explains the distinctions between 'some' and 'any' in different sentence structures and outlines rules for regular and irregular verb forms in the past tense. Additionally, it discusses how to ask quantity questions using 'how much' and 'how many'.