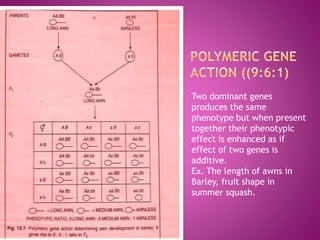
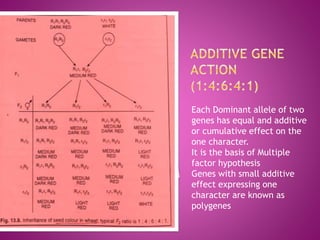
The document discusses different types of gene interactions:
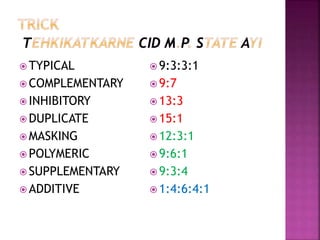
- Epistasis refers to one gene affecting the expression of another gene. It modifies typical dihybrid ratios.
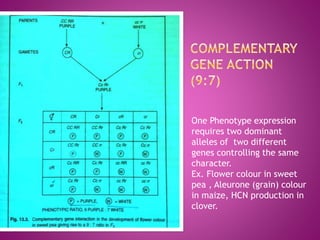
- Complementary gene action produces a 9:7 ratio where two dominant alleles are required to produce the phenotype.
- Inhibitory gene action produces a 13:3 ratio where a dominant gene prevents expression of another dominant gene.
- Masking gene action produces a 12:3:1 ratio where one gene masks the expression of another.
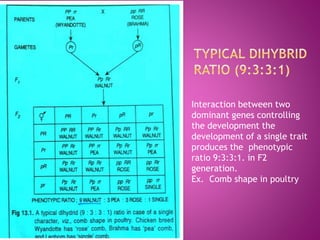
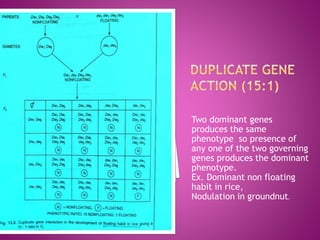
Examples of different gene interactions in traits such as seed color, flower color, and plant morphology are provided.