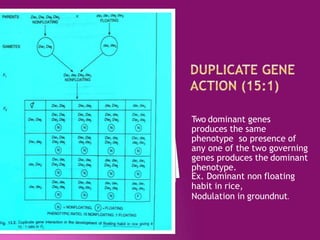
Gene interaction refers to the way that two or more genes influence each other's expression when controlling the same phenotypic character. There are several types of gene interaction that modify the typical dihybrid ratio seen in a genetic cross between organisms with two differing gene pairs (9:3:3:1). These include complementary gene action (9:7), inhibitory gene action (13:3), duplicate gene action (15:1), masking gene action (12:3:1), polymeric gene action (9:6:1), and supplementary gene action (9:3:4). Epistasis occurs when one gene affects the expression of another gene, and all types of gene interaction are examples of epistatic effects.