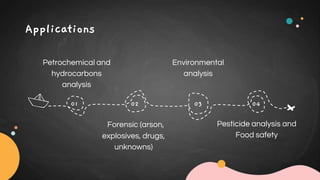
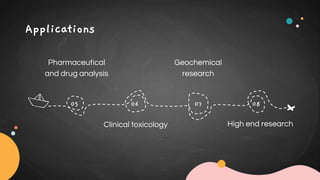
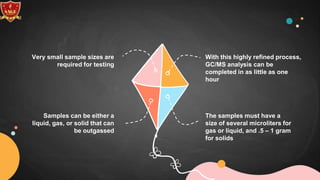
GC-MS combines gas chromatography and mass spectrometry to separate and identify components in a mixture. In GC-MS, the sample is vaporized and carried by a gas through a column where components separate based on interaction with the stationary phase. The separated components then enter the mass spectrometer where they are ionized by electrons and broken into fragments. The mass analyzer separates the fragments by mass and charge, and the detector produces a mass spectrum that can identify molecules based on their fragmentation pattern. GC-MS is used in applications like petrochemical analysis, environmental analysis, forensics, pharmaceutical analysis, and clinical toxicology due to its ability to analyze small sample sizes and identify unknown chemical structures.