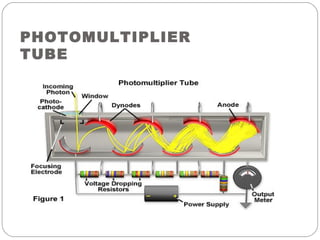
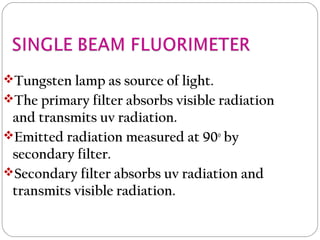
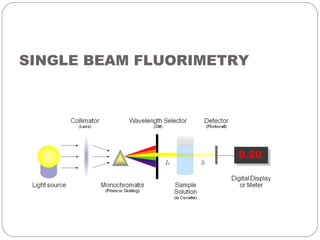
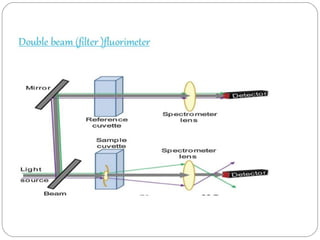
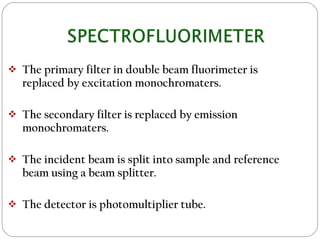
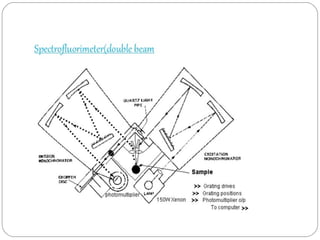
This document discusses instrumentation used in fluorimetry. It describes various light sources like mercury arc lamps, xenon arc lamps, and tungsten lamps. It also discusses filters, monochromators, sample cells, and detectors like photomultiplier tubes that are used. Different types of fluorimeters are described, including single beam, double beam, and spectrofluorimeters. Finally, some applications of fluorimetry are mentioned such as determination of inorganic substances, use in nuclear research, as fluorescent indicators, and in organic analysis.










![1] Determination of inorganic substances
Determination of ruthenium ions in presence of
other platinum metals.
Determination of aluminum (III) in alloys.
Determination of boron in steel by complex formed
with benzoin.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flourimetrycha-170827122527/85/Flourimetry-22-320.jpg)
![2]Nuclear research
Field determination of uranium salts.
3]Fluorescent indicators
Mainly used in acid-base titration.
e.g.:
eosin- colorless-green.
Fluorescein:colourless-green.
Quinine sulphate: blue-violet.
Acridine: green-violet](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flourimetrycha-170827122527/85/Flourimetry-23-320.jpg)
![5] organic analysis
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of organic
aromatic compounds present in cigarette smoke, air
pollutants, automobile exhaust
6]Liquid chromatography
Fluorescence is an imp method of determining
compounds as they appear at the end of
chromatogram or capillary electrophoresis column.
7]determination of vitamin B1 &B2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flourimetrycha-170827122527/85/Flourimetry-24-320.jpg)
