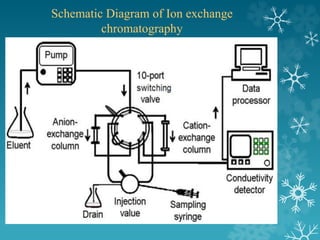
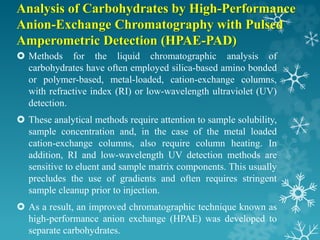
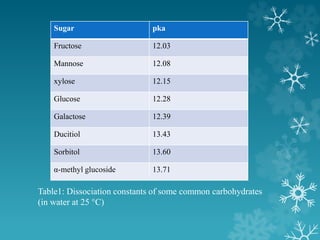
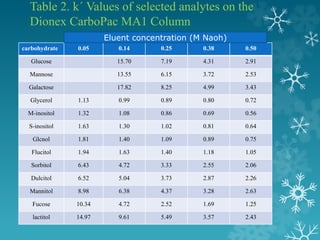
This document summarizes a seminar on ion exchange chromatography. It introduces the topic, covering the basic principles of how ion exchange chromatography separates ions and polar molecules using stationary phases with positively or negatively charged groups. It then discusses the types of ion exchange resins, including classifications based on chemical nature and source. Examples of applications are given, such as separating similar ions, water softening, demineralization, separating sugars and amino acids. The document concludes by discussing some advantages and disadvantages of ion exchange chromatography.
![Seminar on ion exchange chromatography
PRESENTED BY
MANOJ KUMAR . M
H.T.NO.636217885003
M.Pharmacy 1st year
UNDER GUIDANCE OF
DR.S.Y. MANJUNATH
DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICAL ANALYSIS
SRIKRUPA INSTITUTE OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES
[AFFILIATED TO OSMANIA UNIVERSITY]
[Approved by PCI;AICTE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ionexcghngefinal-180420090105/85/Ion-excghnge-chromatography-1-320.jpg)