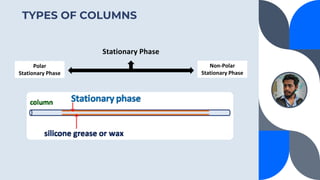
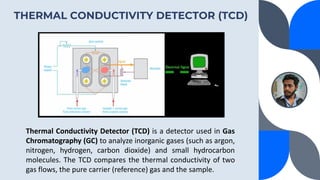
The document provides a detailed overview of gas chromatography (GC), a laboratory technique used to separate mixtures into their components using a mobile phase and a stationary phase. It explains the principles, working procedures, types of GC, and the use of detectors such as flame ionization and thermal conductivity detectors to analyze compounds. Additionally, it covers concepts like retention time, the interpretation of chromatograms, and practical examples of analyzing compounds like paracetamol and banana oil.