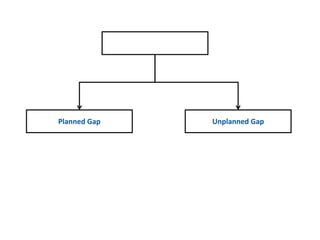
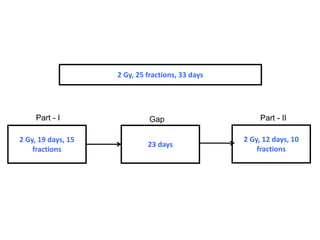
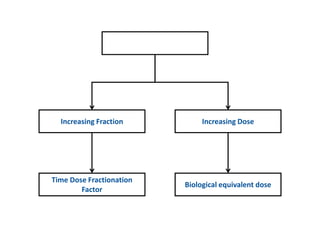
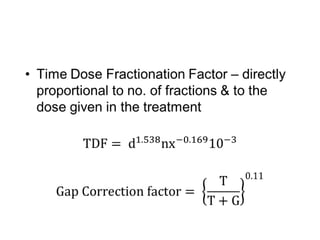
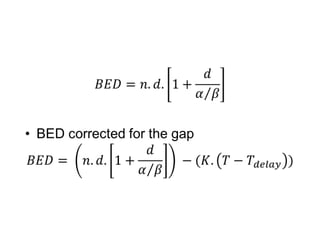
This document discusses planned and unplanned gaps in radiation therapy treatment schedules. Planned gaps are built into the schedule to account for tumor repopulation during weekends and holidays. Unplanned gaps negatively impact treatment outcomes by prolonging the overall time and allowing tumors to regrow. The effects of gaps depend on the prolongation length, tumor proliferation rate, and timing of the interruption. Corrections like increasing the dose or number of fractions are sometimes made to account for biological effects of treatment gaps.