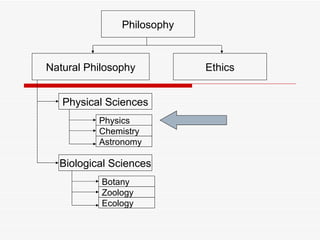
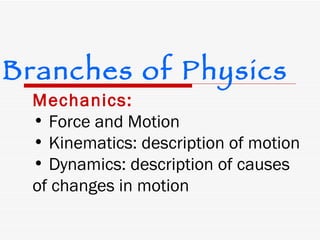
Physics is the basic science that studies matter and energy. It is a systematically organized body of knowledge based on observable facts about nature. Physics includes several main branches that study different aspects of matter and energy, such as mechanics, thermodynamics, waves, electricity and magnetism, and modern physics. The scientific method is used in physics to make hypotheses, conduct experiments, and develop theories to build understanding of natural phenomena.