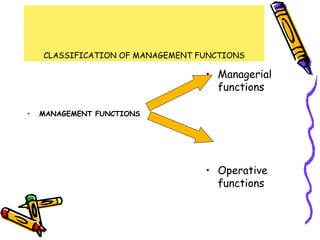
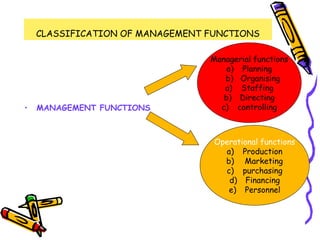
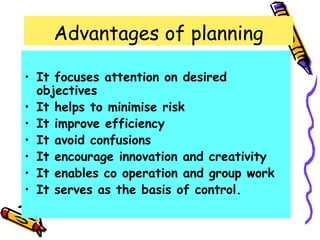
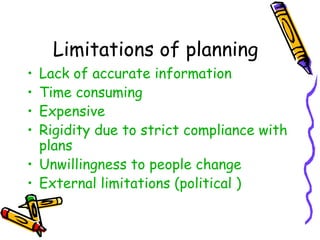
This document discusses the key functions of management. It outlines managerial functions like planning, organizing, staffing, directing and controlling. It also discusses operational functions like production, marketing, purchasing and financing. For each function, it provides definitions from management experts and discusses steps, importance, advantages, limitations and features. The functions of management are classified into managerial and operational categories to effectively coordinate organizational activities.