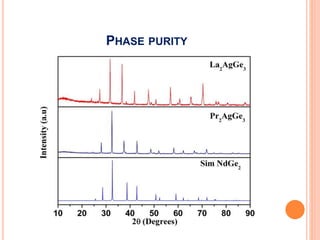
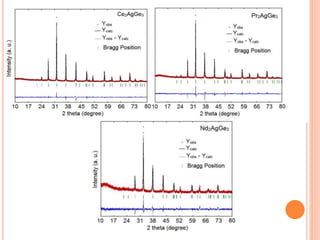
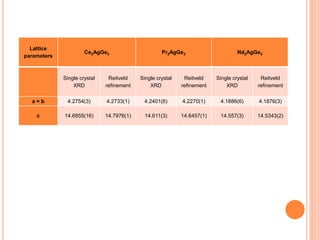
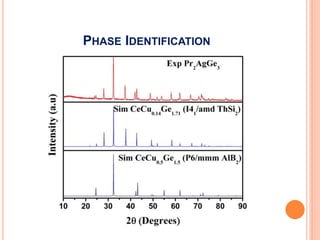
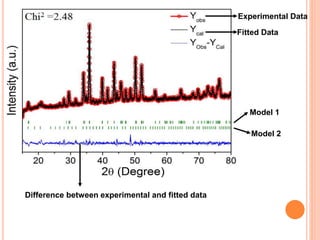
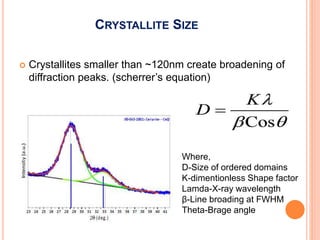
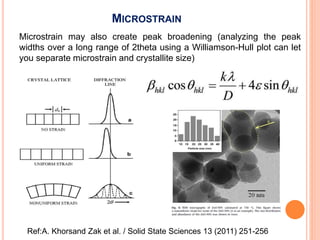
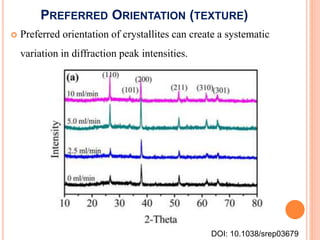
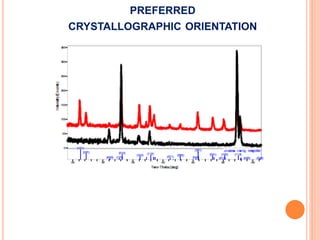
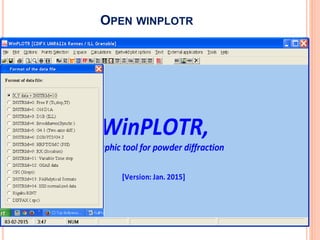
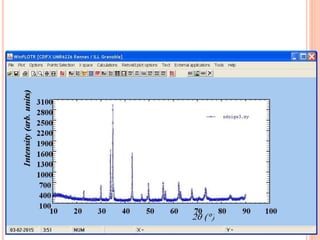
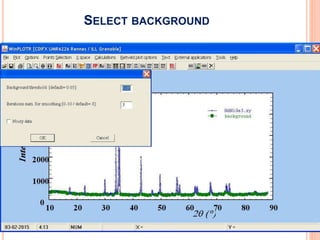
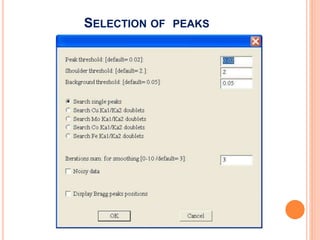
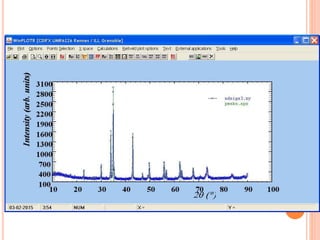
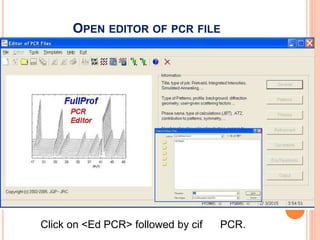
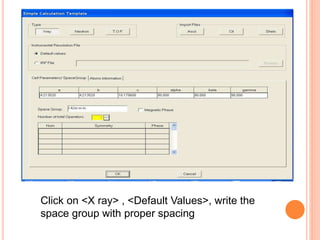
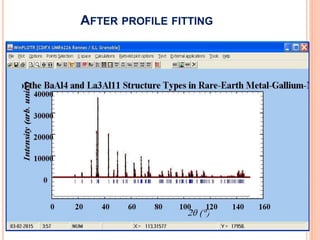
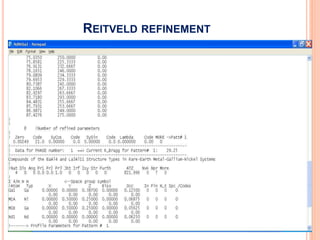
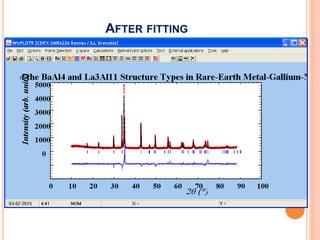
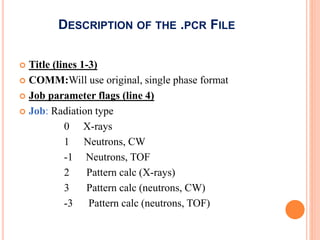
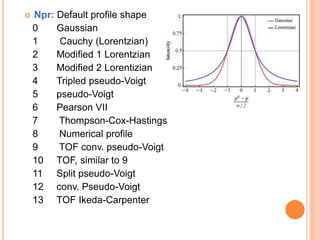
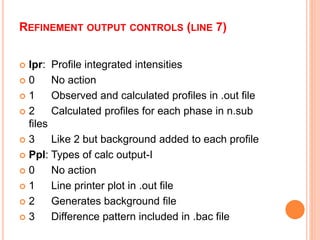
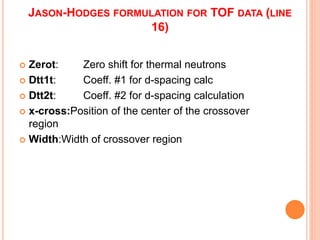
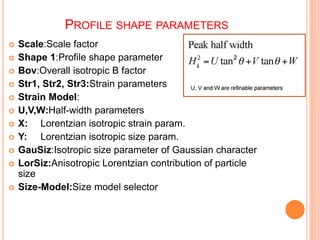
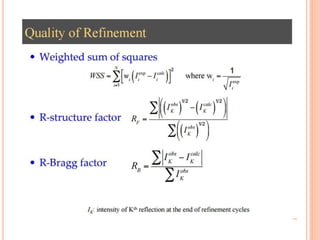
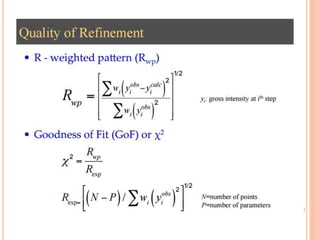
The document discusses the use of Rietveld refinement for analyzing powder X-ray diffraction data. Rietveld refinement allows for the determination of phase purity, identification of crystal structures, refinement of structural parameters, quantitative phase analysis, and calculation of properties like lattice parameters, atomic positions, thermal vibrations, grain size, and magnetic moments. The document provides examples of Rietveld refinement output and parameters that can be refined.