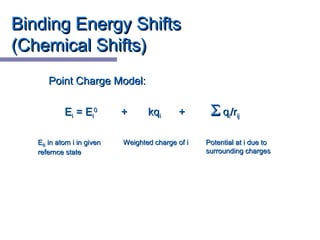
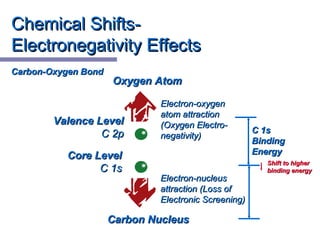
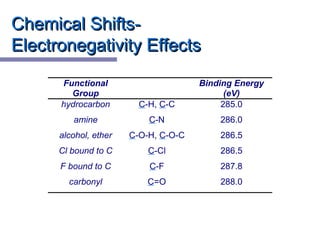
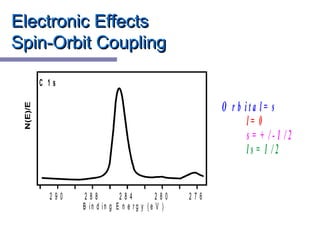
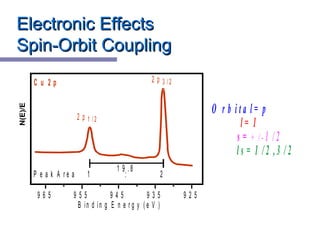
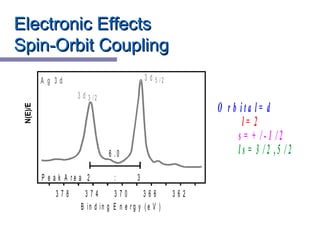
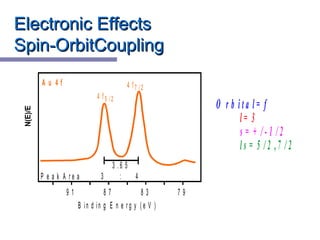
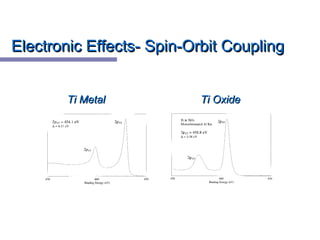
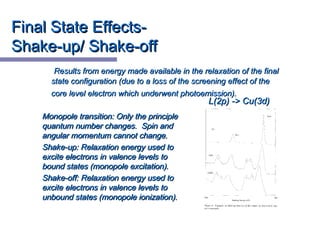
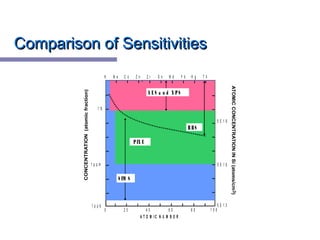
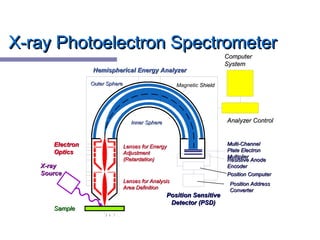
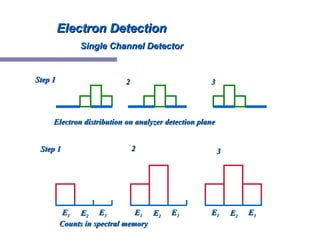
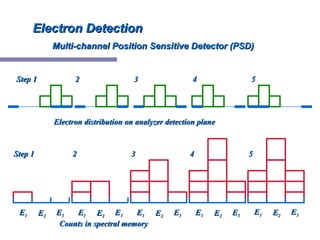
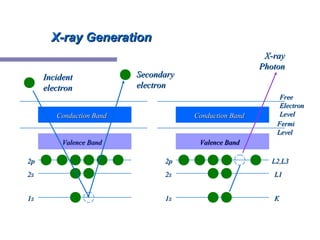
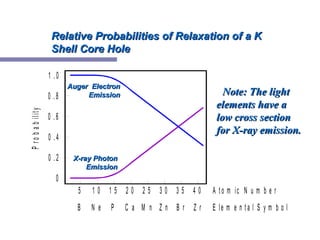
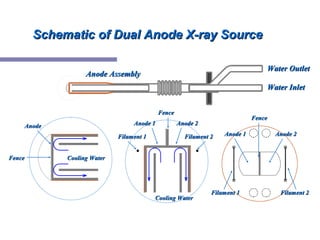
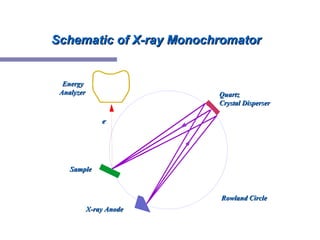
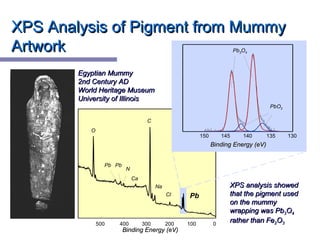
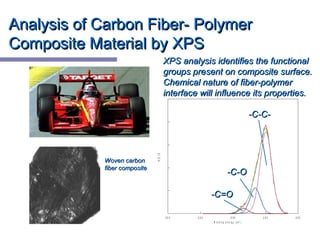
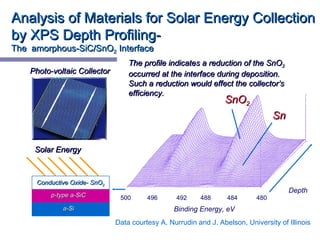
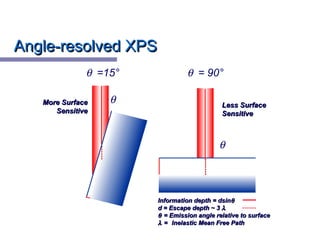
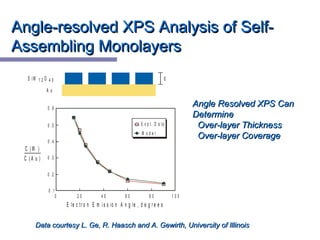
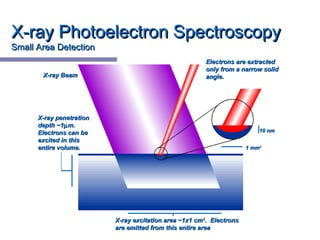
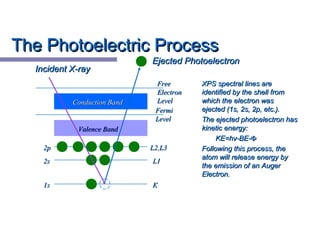
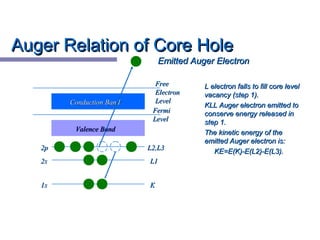
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a technique for analyzing the chemical composition of surfaces by measuring the kinetic energy of emitted electrons resulting from X-ray excitation. Developed in the 1960s, XPS is widely utilized in surface analysis and relies on the photoelectric effect, with various factors influencing the binding energy of electrons. The document discusses the principles, instrumentation, and applications of XPS, emphasizing its significance in examining surface characteristics and chemical states.







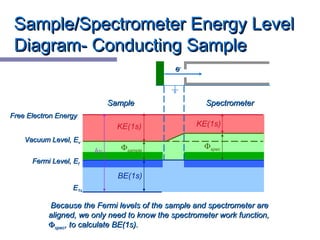
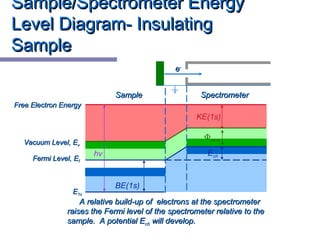
![Free electrons (those giving rise to conductivity) findFree electrons (those giving rise to conductivity) find
an equal potential which is constant throughout the material.an equal potential which is constant throughout the material.
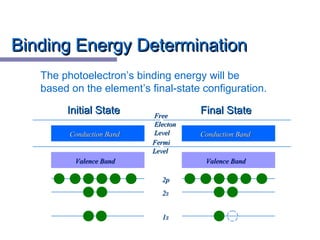
Fermi-Dirac Statistics:Fermi-Dirac Statistics:
f(E) = 1f(E) = 1
exp[(E-Eexp[(E-Eff)/kT] + 1)/kT] + 1
1.01.0
f(E)f(E)
00
0.50.5
EEff1. At T=0 K:1. At T=0 K: f(E)=1 for E<Ef(E)=1 for E<Eff
f(E)=0 for E>Ef(E)=0 for E>Eff
2. At kT<<E2. At kT<<Eff (at room temperature kT=0.025 eV)(at room temperature kT=0.025 eV)
f(E)=0.5 for E=Ef(E)=0.5 for E=Eff
T=0 KT=0 K
kT<<EkT<<Eff
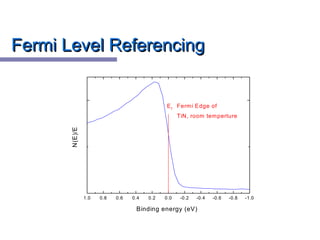
Fermi Level ReferencingFermi Level Referencing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pesradha-181004154003/85/Photo-Electron-Spectroscopy-12-320.jpg)