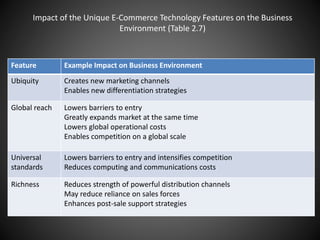
There are several business models emerging in e-commerce, including consumer-to-consumer (C2C) models like eBay that allow consumers to connect and conduct business, peer-to-peer (P2P) models like The Pirate Bay that enable file sharing, and mobile commerce (m-commerce) models like eBay Mobile that extend e-commerce to wireless devices. E-commerce enablers provide infrastructure for e-commerce through hardware, software, networking, security, payment systems, and other services. The unique features of the internet like ubiquity, standards, and interactivity impact industry structure by lowering barriers to entry and intensifying competition.