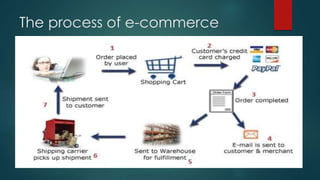
This document discusses e-commerce, including its definition, history, types, advantages, and future. E-commerce involves the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet. It has grown significantly since the 1990s with companies like Amazon and eBay. There are different types of e-commerce models including business-to-business, business-to-consumer, and consumer-to-consumer. E-commerce provides advantages such as lower costs, 24/7 access, and a large customer reach. However, it also poses disadvantages like lack of personal interaction and product experience before purchase. The future of e-commerce is predicted to include technologies like biometric payments, social media marketing, faster delivery, and 3D printing of