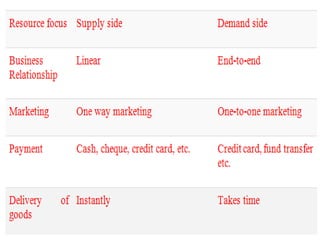
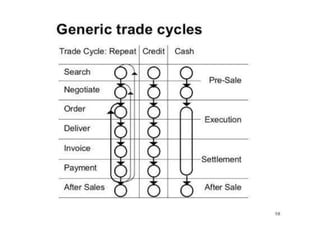
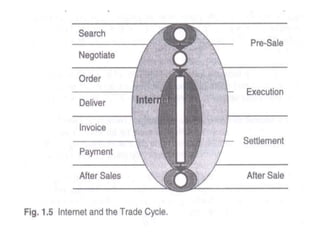
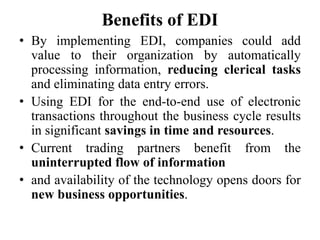
The document provides an overview of e-commerce, including definitions and explanations of key terms. It discusses traditional commerce and how e-commerce differs, focusing on how electronic networks like the internet enable firms and individuals to conduct business. The document also outlines several e-commerce models (B2B, B2C, etc.), advantages and disadvantages, and how e-commerce has impacted organizational structures and human resource management practices through digital transformation.