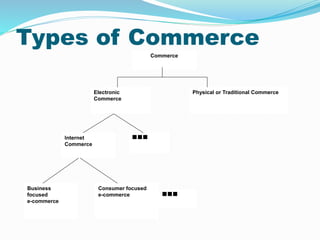
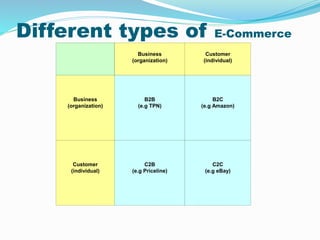
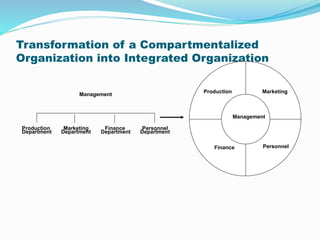
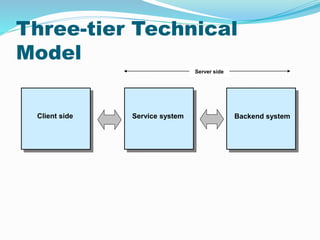
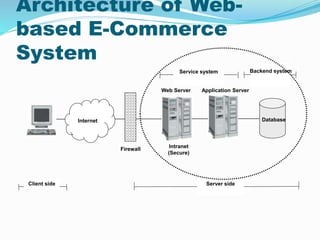
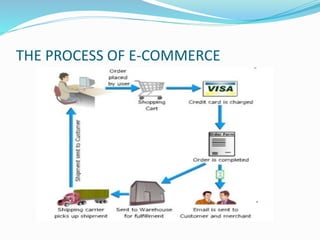
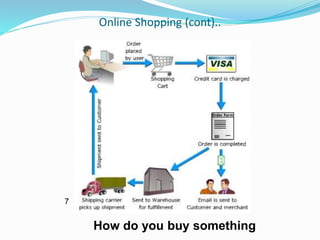
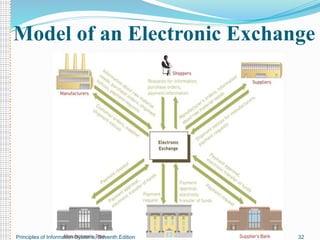
This document provides an overview of e-commerce. It defines e-commerce as the process of buying, selling, transferring or exchanging products, services and information via electronic networks and computers. The brief history outlines the evolution of e-commerce from the 1970s with EDI and EFT to the growth of online commerce in the 1990s-2000s with the commercialization of the internet. The document categorizes the different types of e-commerce including B2C, B2B, C2C and m-commerce. It discusses the benefits of e-commerce to organizations like global reach and cost reduction, and to consumers like more products and cheaper prices. The document also outlines some common business applications of e-commerce