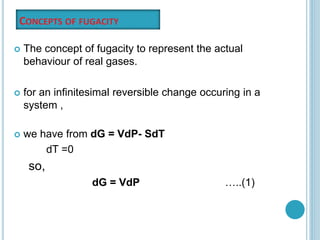
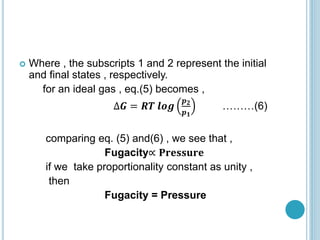
Fugacity is a concept introduced by Gilbert Lewis to represent the escaping tendency of real gases and their behavior in solutions. Fugacity (f) is defined such that the change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG) for any process involving real gases can be written as ΔG = RTln(f2/f1), similar to the ideal gas equation but using fugacity rather than pressure. For ideal gases, fugacity is equal to pressure, but for real gases f/p is not constant and decreases with decreasing pressure. The gas is considered ideal at very low pressures where f/p approaches 1, allowing fugacities to be determined at other pressures. Fugacities have the same units as pressure.