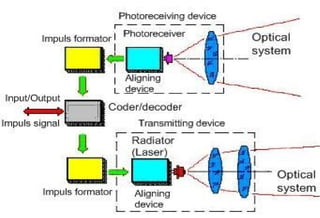
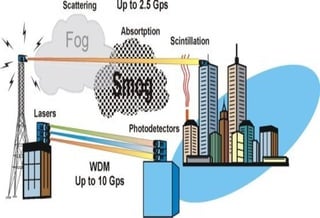
This document discusses free space optics, also known as free space photonics, which transmits information using invisible light beams between telescopes over distances of several kilometers. It works by using two telescopes that transmit and receive the light beams, offering transmission capacities ranging from 100Mbps to 2.5Gbps. The key advantages are that it provides a flexible networking solution at low cost with unlimited bandwidth, as long as there is a line of sight between the telescopes. However, it faces challenges from atmospheric factors, physical obstructions, changes in pointing stability, and solar interference.