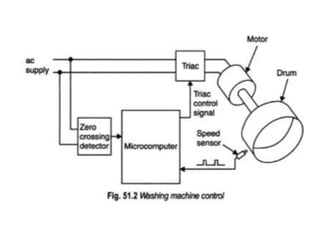
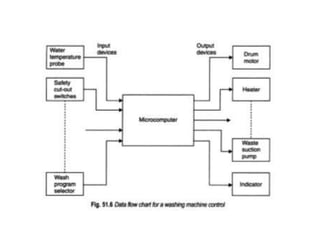
The document discusses washing machines and their components. It begins by showing a block diagram of the input and output devices connected to the controller in an electronic washing machine. It then discusses various aspects of washing machines such as the types of sensors and actuators used, fuzzy logic control, different washing programs, and miscellaneous features. The key components discussed are the controller, motor, sensors to measure speed and detect water level, and actuators like the water valve and heater.






















![Waching machine[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wachingmachine1-190420045344/85/Waching-machine-1-28-320.jpg)