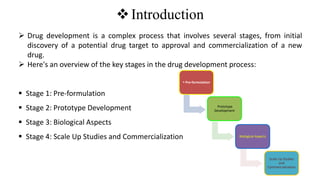
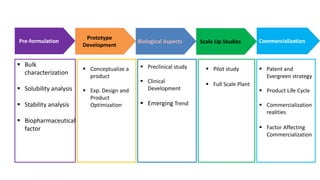
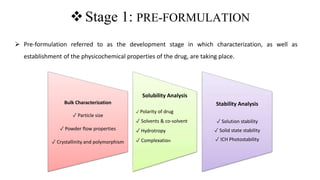
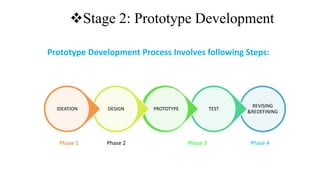
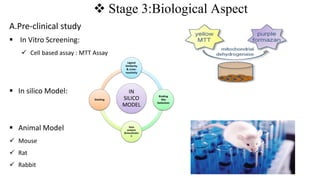
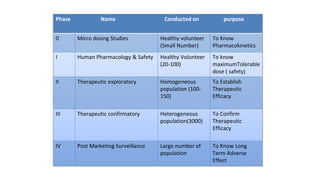
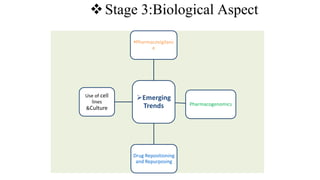
The document outlines the four stages of drug development: pre-formulation, prototype development, biological aspects, and scale-up studies leading to commercialization. Each stage involves critical processes such as characterization, safety and efficacy testing, and the transition to large-scale production, ensuring that drugs meet regulatory standards. Key emerging trends in this field include pharmacovigilance and drug repurposing, emphasizing the importance of developing cost-effective and safe pharmaceutical products.