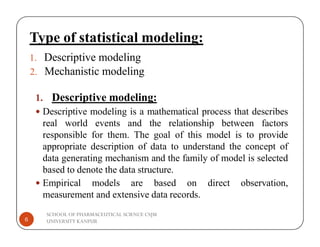
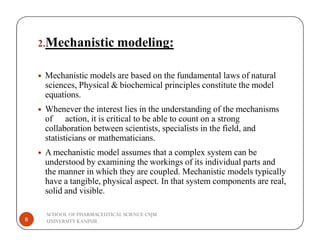
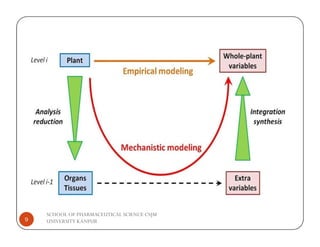
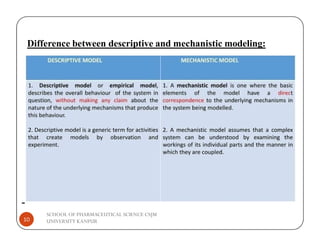
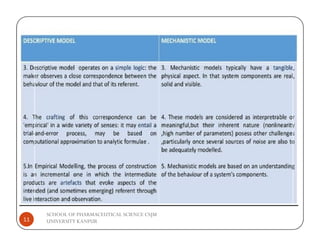
The document discusses the role of statistical modeling in pharmaceutical research and development, highlighting its importance in improving quality while reducing costs and time in drug discovery. It distinguishes between descriptive and mechanistic modeling, each serving different purposes in understanding data and system behaviors. The challenges faced by the pharmaceutical industry necessitate the development of new modeling approaches to enhance the overall drug development process.