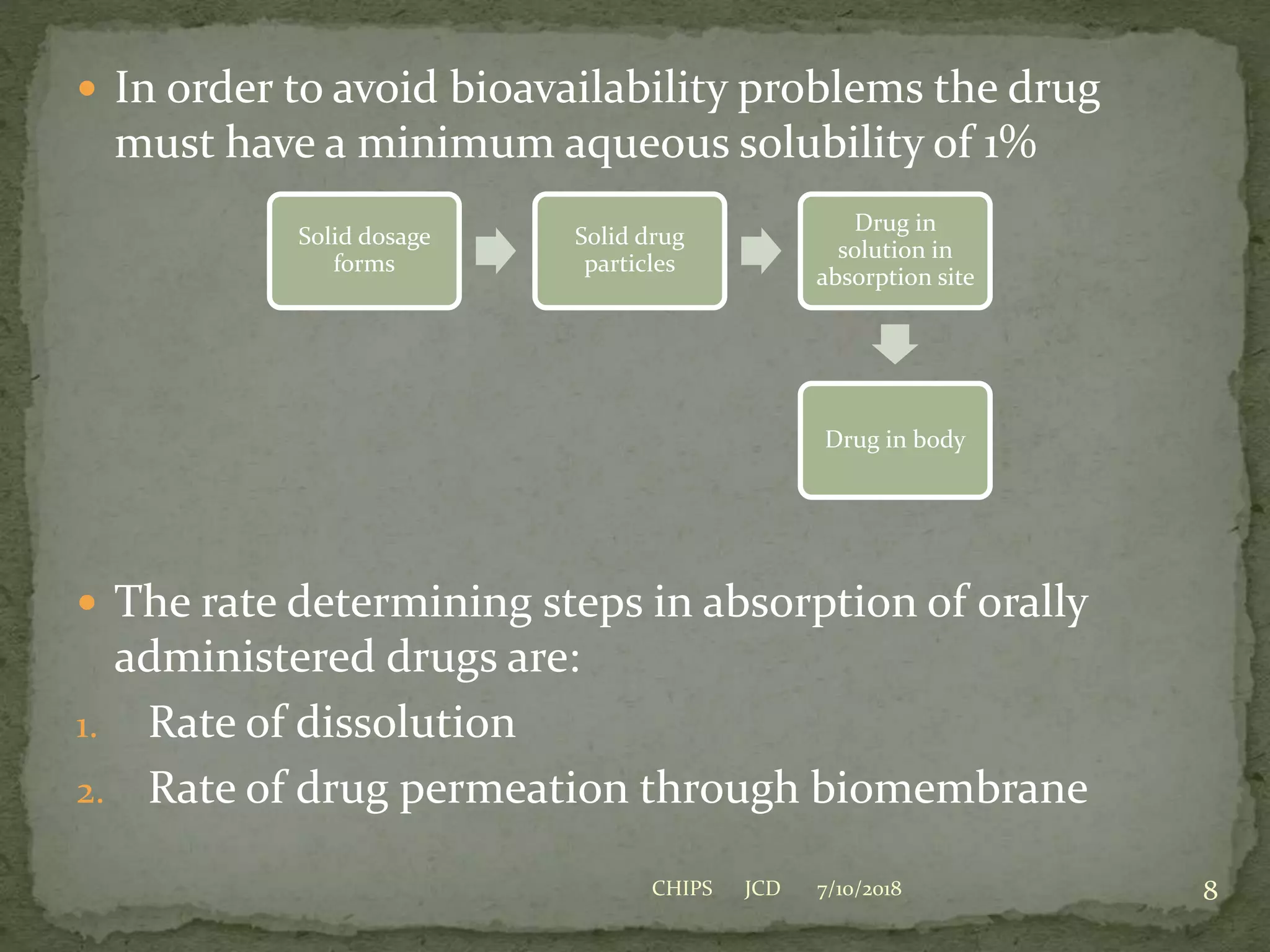
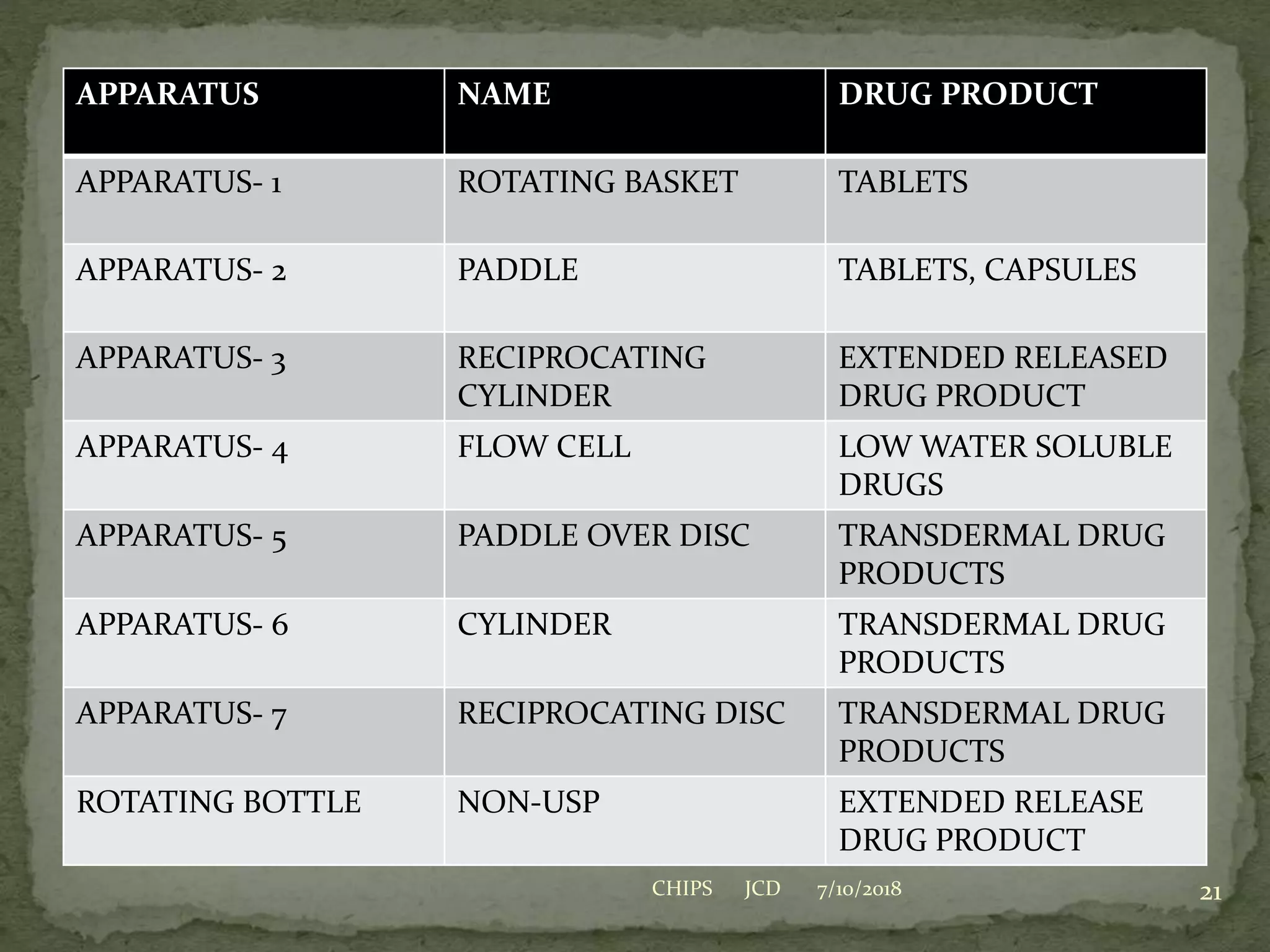
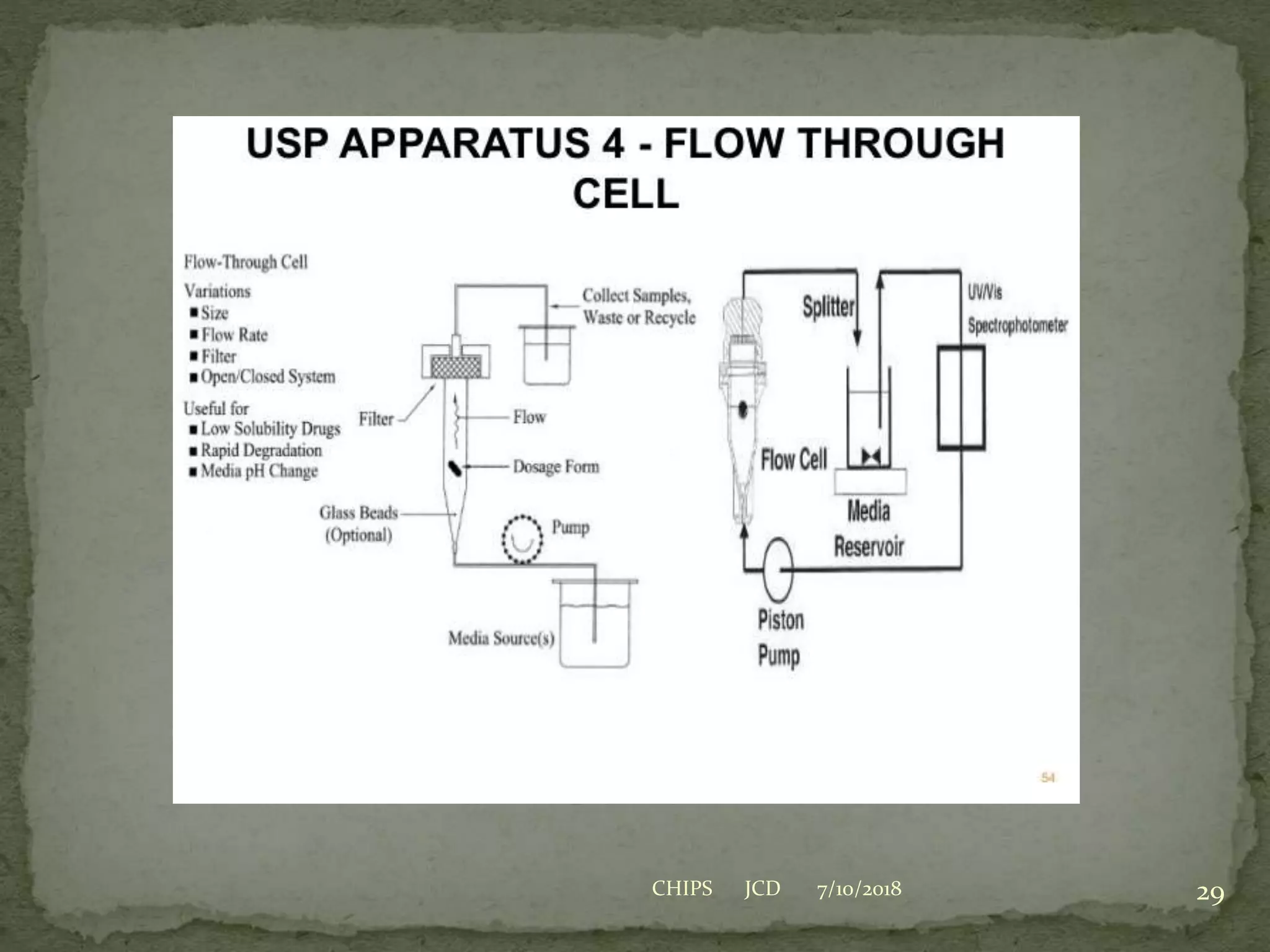
Biopharmaceutics is the study of physicochemical properties of drugs and how they influence the drug's bioavailability. Key factors that can impact bioavailability include the drug's solubility, dissolution rate, and permeability. For an orally administered drug, the drug must first dissolve in the gastrointestinal fluids before it can be absorbed through the gastrointestinal membranes and enter systemic circulation. The rate of dissolution is often the slowest step and thus rate-limiting for poorly water soluble drugs. Techniques such as reducing particle size, use of salt forms, and amorphous forms can increase dissolution rate and bioavailability.